|
Luapeleamoeba
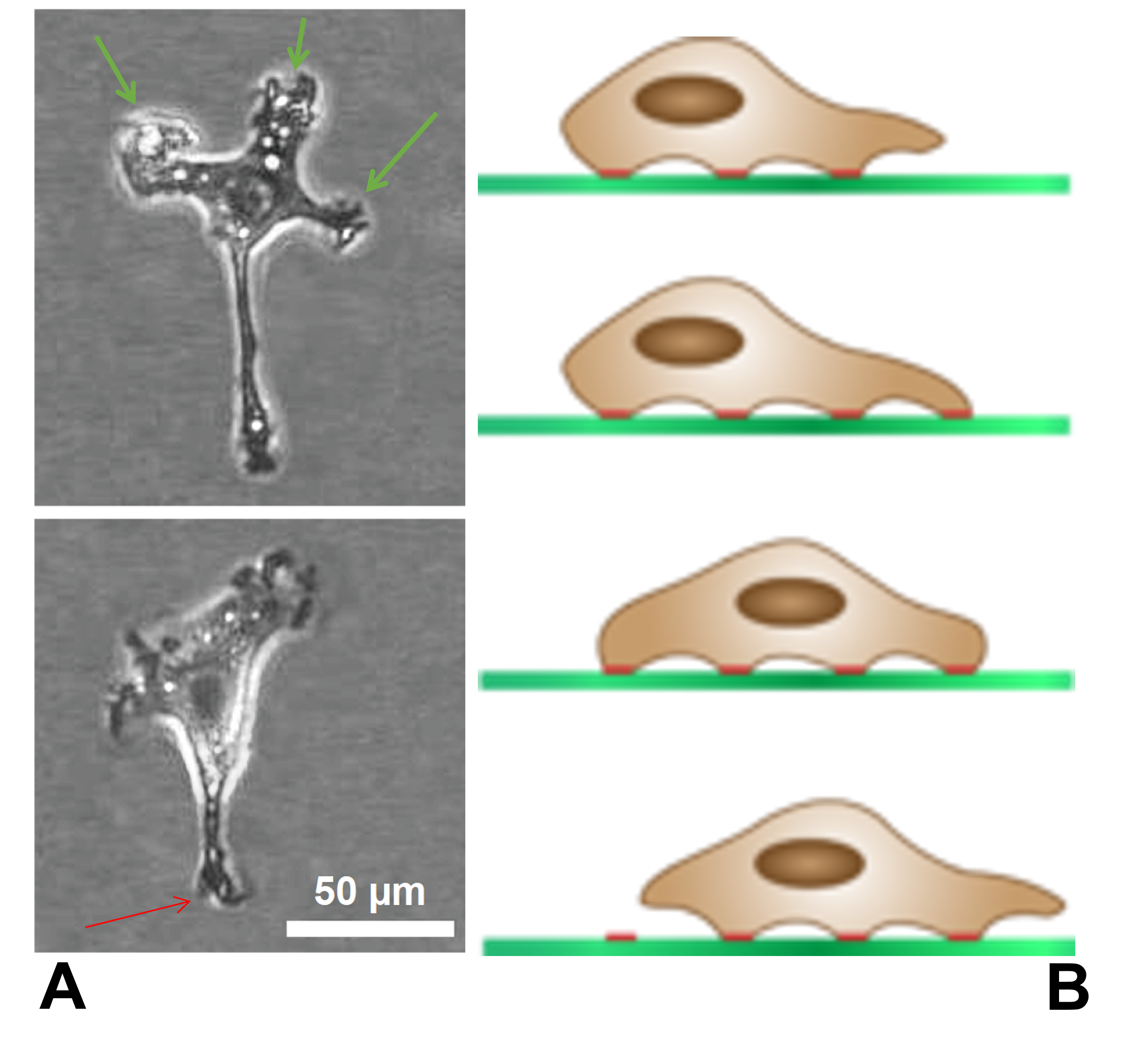
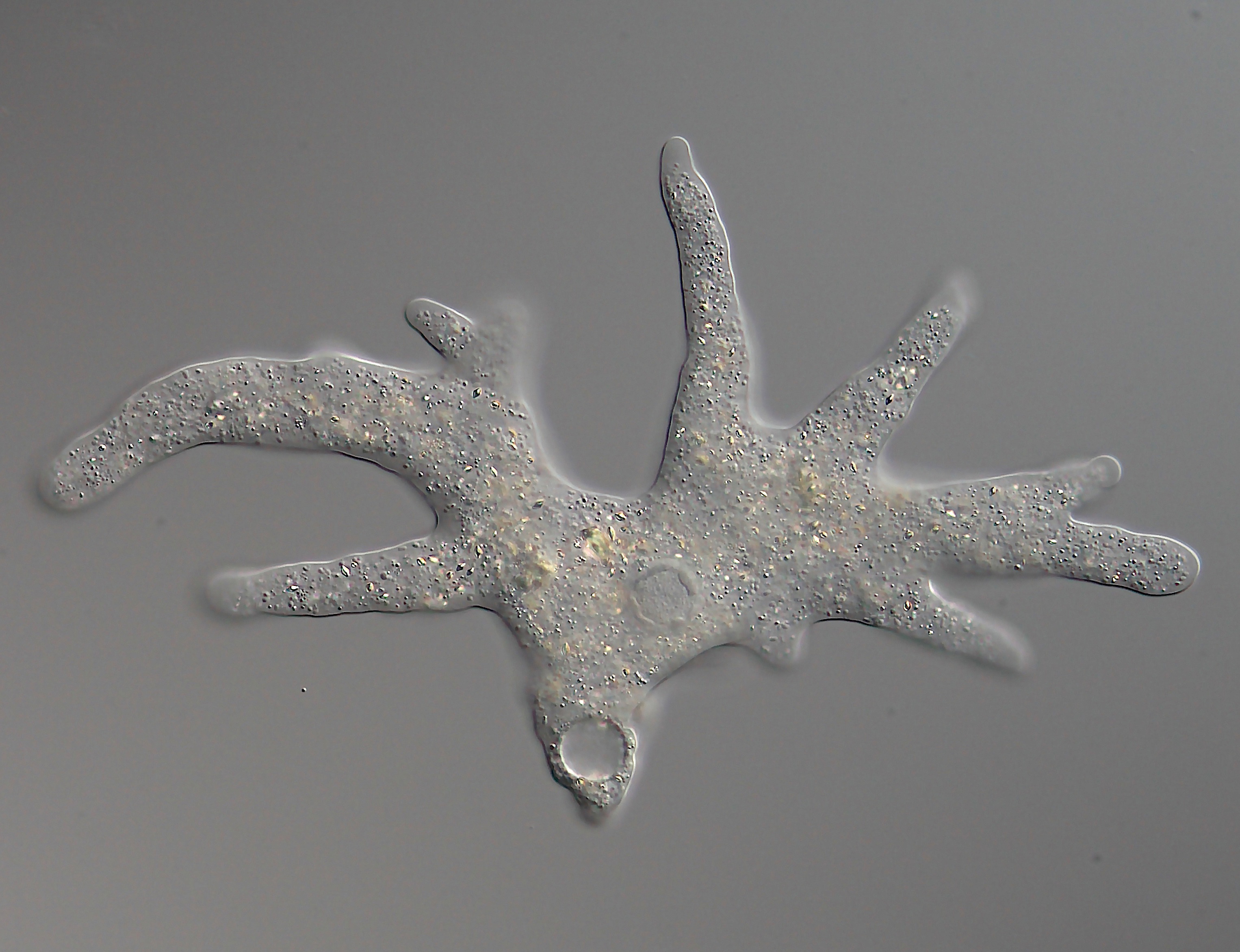
''Luapeleamoeba'' is a genus of naked amoebae of the family Acanthamoebidae. Morphology ''Luapeleamoeba'' are uninucleate amoebae that, during locomotion, generate a single broad, hyaline lamellipodium with inferior triangular pseudopodia at the edge directing the movement. Behind the lamellipodium there's a thick region of cytoplasm with granules containing a contractile vacuole usually posterior to the single nucleus. There is a big nucleolus with a diameter at least half of the nucleus' diameter. There is a centrosomal region near the nucleus with a Golgi apparatus, other vesicles, and an electron-dense lamellate microtubule-organizing center, which is visibly smaller and less lamellate than those seen in other acanthamoeboid genera. The amoeba is thickest near the contractile vacuole and the nucleus, and tapers gradually toward the edges, giving the overall appearance of a small shield volcano. The floating form is round, although not smooth. No flagella have been seen. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luapeleamoeba Hula
''Luapeleamoeba hula'' () is a species of acanthamoebid amoeba described in 2016, capable of producing protosteloid fruiting bodies that consist of a stalk with one spore. It was obtained from dead māmaki leaves from the Manuka Natural Area Reserve in Hawai'i, USA. It has also been found in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Etymology The specific epithet, '' hula'', references how the spore of this species changes shape continuously as if it were dancing. Morphology ''L. hula'' sorocarps have an average height of 23.7 μm and are made up of a single spore and an inflexible stalk that's 8.97 μm in length. There is an apophysis at the tip of the stalk, embedded within the spore. The spores are uninucleate and have a continuously variable shape, but typically have the shape of an upside-down pear when viewed from the side and round when viewed from the top. Spores germinate as uninucleate, non-flagellated amoebae, characteristic of the genus. The trophic amoebae are often fla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acanthamoebidae
Acanthamoebidae is a family of single-celled eukaryotes within the group Amoebozoa. It gets its name from ''Acanthamoeba'', its best-known member. However, it also includes other species, such as ''Comandonia operculata'' and '' Protacanthamoeba bohemica''. Many kinds of Acanthamoebidae are highly prevalent in the soil and water of a variety of environments. They are similar to Hartmannella, but have differently structured pseudopodia, in regard to the actin microfilaments that comprise them. Its most prominent member, ''Acanthamoeba'', can be potentially pathogenic to humans and animals. It has been described as having a common origin with the Entamoebidae and Dictyosteliida. Structure Members of Acanthamoebidae have a specific form of pseudopodia, dubbed acanthopodia. These acanthopodia are continuously formed and reabsorbed, protrude from every area of the cell’s surface, and are usually, short and fine. An exception would be ''A. astronyxis'' and ''A. comandoni'', in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporocarp (fungi)
The sporocarp (also known as fruiting body, fruit body or fruitbody) of fungi is a multicellular structure on which spore-producing structures, such as basidia or asci, are borne. The fruitbody is part of the sexual phase of a fungal life cycle, while the rest of the life cycle is characterized by vegetative mycelial growth and asexual spore production. The sporocarp of a basidiomycete is known as a ''basidiocarp'' or ''basidiome'', while the fruitbody of an ascomycete is known as an '' ascocarp''. Many shapes and morphologies are found in both basidiocarps and ascocarps; these features play an important role in the identification and taxonomy of fungi. Fruitbodies are termed ''epigeous'' if they grow on the ground, while those that grow underground are '' hypogeous''. Epigeous sporocarps that are visible to the naked eye, especially fruitbodies of a more or less agaricoid morphology, are often called mushrooms. Epigeous sporocarps have mycelia that extend undergroun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus (cell)
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellipodium
The lamellipodium (plural lamellipodia) (from Latin ''lamella'', related to ', "thin sheet", and the Greek radical ''pod-'', "foot") is a cytoskeletal protein actin projection on the leading edge of the cell. It contains a quasi-two-dimensional actin mesh; the whole structure propels the cell across a substrate. Within the lamellipodia are ribs of actin called microspikes, which, when they spread beyond the lamellipodium frontier, are called filopodia. The lamellipodium is born of actin nucleation in the plasma membrane of the cell and is the primary area of actin incorporation or microfilament formation of the cell. Description Lamellipodia are found primarily in all mobile cells, such as the keratinocytes of fish and frogs, which are involved in the quick repair of wounds. The lamellipodia of these keratinocytes allow them to move at speeds of 10–20 μm / min over epithelial surfaces. When separated from the main part of a cell, a lamellipodium can still cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopodia
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filaments and may also contain microtubules and intermediate filaments. Pseudopods are used for motility and ingestion. They are often found in amoebas. Different types of pseudopodia can be classified by their distinct appearances. Lamellipodia are broad and thin. Filopodia are slender, thread-like, and are supported largely by microfilaments. Lobopodia are bulbous and amoebic. Reticulopodia are complex structures bearing individual pseudopodia which form irregular nets. Axopodia are the phagocytosis type with long, thin pseudopods supported by complex microtubule arrays enveloped with cytoplasm; they respond rapidly to physical contact. Some pseudopodial cells are able to use multiple types of pseudopodia depending on the situation: Most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuole
A vacuole () is a membrane-bound organelle which is present in plant and fungal cells and some protist, animal, and bacterial cells. Vacuoles are essentially enclosed compartments which are filled with water containing inorganic and organic molecules including enzymes in solution, though in certain cases they may contain solids which have been engulfed. Vacuoles are formed by the fusion of multiple membrane vesicles and are effectively just larger forms of these. The organelle has no basic shape or size; its structure varies according to the requirements of the cell. Discovery Contractile vacuoles ("stars") were first observed by Spallanzani (1776) in protozoa, although mistaken for respiratory organs. Dujardin (1841) named these "stars" as ''vacuoles''. In 1842, Schleiden applied the term for plant cells, to distinguish the structure with cell sap from the rest of the protoplasm. In 1885, de Vries named the vacuole membrane as tonoplast. Function The function and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleolus
The nucleolus (, plural: nucleoli ) is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis, which is the synthesis of ribosomes. The nucleolus also participates in the formation of signal recognition particles and plays a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA, and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy. History The nucleolus was identified by bright-field microscopy during the 1830s. Little was known about the function of the nucleolus until 1964, when a study of nucleoli by John Gurdon and Donald Brown in the African clawed frog '' Xenopus laevis'' generated increasing interest in the function and detailed structure of the nucleolus. They found that 25% of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus (), also known as the Golgi complex, Golgi body, or simply the Golgi, is an organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. Part of the endomembrane system in the cytoplasm, it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the vesicles are sent to their destination. It resides at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. It is of particular importance in processing proteins for secretion, containing a set of glycosylation enzymes that attach various sugar monomers to proteins as the proteins move through the apparatus. It was identified in 1897 by the Italian scientist Camillo Golgi and was named after him in 1898. Discovery Owing to its large size and distinctive structure, the Golgi apparatus was one of the first organelles to be discovered and observed in detail. It was discovered in 1898 by Italian physician Camillo Golgi during an investigation of the nervous system. After first observing it under h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtubule-organizing Center
The microtubule-organizing center (MTOC) is a structure found in eukaryotic cells from which microtubules emerge. MTOCs have two main functions: the organization of eukaryotic flagella and cilia and the organization of the mitotic and meiotic spindle apparatus, which separate the chromosomes during cell division. The MTOC is a major site of microtubule nucleation and can be visualized in cells by immunohistochemical detection of γ-tubulin. The morphological characteristics of MTOCs vary between the different phyla and kingdoms. In animals, the two most important types of MTOCs are 1) the basal bodies associated with cilia and flagella and 2) the centrosome associated with spindle formation. Organization Microtubule-organizing centers function as the site where microtubule formation begins, as well as a location where free-ends of microtubules attract to. Within the cells, microtubule-organizing centers can take on many different forms. An array of microtubules can arrange themselve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava erupted from a stratovolcano. Repeated eruptions result in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are found wherever fluid low-silica lava reaches the surface of a rocky planet. However, they are most characteristic of ocean island volcanism associated with hot spots or with continental rift volcanism. They include the largest volcanoes on earth, such as Tamu Massif and Mauna Loa. Giant shield volcanoes are found on other planets of the Solar System, including Olympus Mons on Mars and Sapas Mons on Venus. Etymology The term 'shield volcano' is taken from the German term ''Schildvulkan'', coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess in 1888 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |