|
Longissimus
The longissimus () is the muscle lateral to the semispinalis muscles. It is the longest subdivision of the erector spinae muscles that extends forward into the transverse processes of the posterior cervical vertebrae. Structure Longissimus thoracis et lumborum The longissimus thoracis et lumborum is the intermediate and largest of the continuations of the erector spinae. In the lumbar region (longissimus lumborum), where it is as yet blended with the iliocostalis, some of its fibers are attached to the whole length of the posterior surfaces of the transverse processes and the accessory processes of the lumbar vertebrae, and to the anterior layer of the lumbodorsal fascia. In the thoracic region (longissimus thoracis), it is inserted, by rounded tendons, into the tips of the transverse processes of all the thoracic vertebrae, and by fleshy processes into the lower nine or ten ribs between their tubercles and angles. Longissimus cervicis The longissimus cervicis (transver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erector Spinae Muscles
The erector spinae ( ) or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes ( gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) to maintain stable posture standing or sitting. Structure The erector spinae is not just one muscle, but a group of muscles and tendons which run more or less the length of the spine on the left and the right, from the sacrum, or sacral region, and hips to the base of the skull. They are also known as the sacrospinalis group of muscles. These muscles lie on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae and extend throughout the lumbar, thoracic, and cervical regions. The erector spinae is covered in the lumbar and thoracic regions by the thoracolumbar fascia, and in the cervical region by the nuchal ligament. This large muscular and tendinous mass varies in size and structure at different parts of the vertebral column. In the sacral region, it is narrow and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
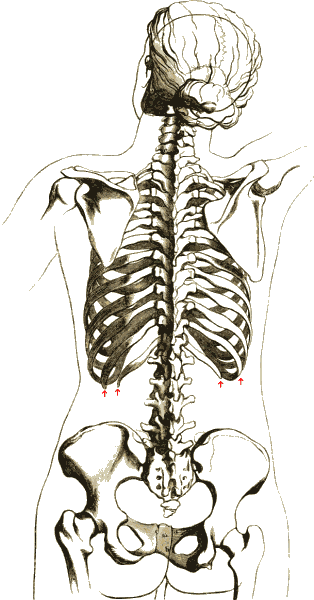
Ribs
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core (anatomy), core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human skeleton, human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration (thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semispinalis Muscles
The semispinalis muscles are a group of three muscles belonging to the transversospinales. These are the semispinalis capitis, the semispinalis cervicis and the semispinalis thoracis. Location The semispinalis capitis (''complexus'') is situated at the upper and back part of the neck, deep to the splenius muscles, and medial to the longissimus cervicis and longissimus capitis. It arises by a series of tendons from the tips of the transverse processes of the upper six or seven thoracic and the seventh cervical vertebrae, and from the articular processes of the three cervical vertebrae above this ( C4-C6). The tendons, uniting, form a broad muscle, which passes upward, and is inserted between the superior and inferior nuchal lines of the occipital bone. It lies deep to the trapezius muscle and can be palpated as a firm round muscle mass just lateral to the cervical spinous processes. The semispinalis cervicis (or ''semispinalis colli''), arises by a series of tendinous and fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib Cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and therefore has a major ventilatory fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinalis
The spinalis is a portion of the erector spinae, a bundle of muscles and tendons, located nearest to the spine. It is divided into three parts: Spinalis dorsi, spinalis cervicis, and spinalis capitis. Spinalis dorsi Spinalis dorsi, the medial continuation of the sacrospinalis, is scarcely separable as a distinct muscle. It is situated at the medial side of the longissimus dorsi, and is intimately blended with it; it arises by three or four tendons from the spinous processes of the first two lumbar and the last two thoracic vertebrae: these, uniting, form a small muscle which is inserted by separate tendons into the spinous processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae, the number varying from four to eight. It is intimately united with the semispinalis dorsi, situated beneath it. Spinalis cervicis Spinalis cervicis, or spinalis colli, is an inconstant muscle, which arises from the lower part of the nuchal ligament, the spinous process of the seventh cervical, and sometimes from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Branch Of Spinal Nerve
The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep (a.k.a. intrinsic or true) muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back. A spinal nerve splits within the intervertebral foramen to form a dorsal ramus and a ventral ramus. The dorsal ramus then turns to course posterior-ward before splitting into a medial branch and a lateral branch. Both these branches provide motor innervation to deep back muscles. In the neck and upper back, the medial branch is also responsible for providing sensory innervation of the skin; in the lower back, the lateral branch does so. All medial branches additionally also provide sensory innervation to the zygapophyseal joints and periosteum of the vertebral column. Structure Ventral root axons join with dorsal root ganglia to form mixed spinal nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Process
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones. Etymology The word "mastoid" is derived from the Greek word for "breast", a reference to the shape of this bone. Surfaces Outer surface Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles. It is perforated by numerous foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits a vein to the transverse sinus and a small branch of the occipital artery to the dura mater. The position and size of this foramen are very variable; it is not always present; sometimes it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal and the occipital. Mastoid process The mastoid process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliocostalis
Iliocostalis muscle is the muscle immediately lateral to the longissimus that is the nearest to the furrow that separates the epaxial muscles from the hypaxial. It lies very deep to the fleshy portion of the serratus posterior muscle. It laterally flexes the vertebral column to the same side. Structure Iliocostalis muscle has a common origin from the iliac crest, the sacrum, the thoracolumbar fascia, and the spinous processes of the vertebrae from T11 to L5. Iliocostalis cervicis (cervicalis ascendens) arises from the angles of the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth ribs, and is inserted into the posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of the fourth, fifth, and sixth cervical vertebrae. Iliocostalis thoracis (musculus accessorius; iliocostalis thoracis) arises by flattened tendons from the upper borders of the angles of the lower six ribs medial to the tendons of insertion of the iliocostalis lumborum; these become muscular, and are inserted into the upper bord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoid
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its center, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splenius Capitis
The splenius capitis () () is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae cervical vertebra, in the neck and upper Thoracic vertebrae, thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head. Structure It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the Vertebra prominens, seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae. The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. The splenius capitis muscle is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Processes
The articular process or zygapophysis ( + apophysis) of a vertebra is a projection of the vertebra that serves the purpose of fitting with an adjacent vertebra. The actual region of contact is called the ''articular facet''.Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 Articular processes spring from the junctions of the pedicles and laminæ, and there are two right and left, and two superior and inferior. These stick out of an end of a vertebra Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ... to lock with a zygapophysis on the next vertebra, to make the backbone more stable. * The superior processes or prezygapophysis project upward from a lower vertebra, and their articular surfaces are directed more or less backward (oblique coronal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |