|
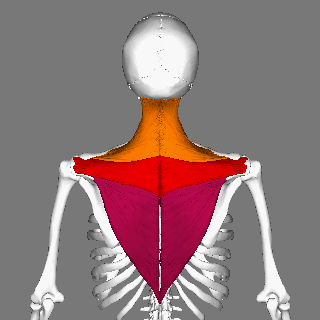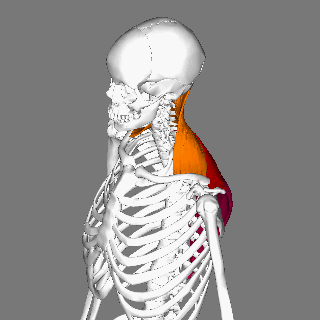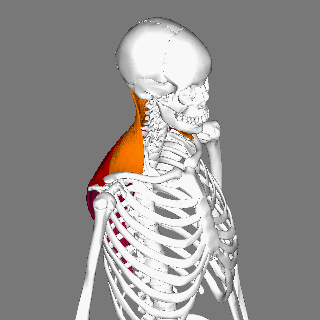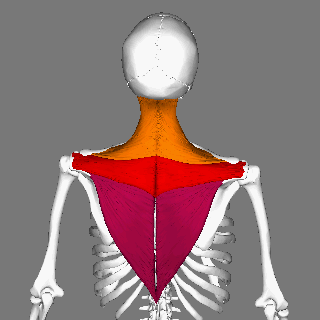
Splenius Capitis
The splenius capitis () () is a broad, straplike muscle in the back of the neck. It pulls on the base of the skull from the vertebrae cervical vertebra, in the neck and upper Thoracic vertebrae, thorax. It is involved in movements such as shaking the head. Structure It arises from the lower half of the nuchal ligament, from the spinous process of the Vertebra prominens, seventh cervical vertebra, and from the spinous processes of the upper three or four thoracic vertebrae. The fibers of the muscle are directed upward and laterally and are inserted, under cover of the sternocleidomastoideus, into the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and into the rough surface on the occipital bone just below the lateral third of the superior nuchal line. The splenius capitis is deep to sternocleidomastoideus at the mastoid process, and to the trapezius for its lower portion. It is one of the muscles that forms the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. The splenius capitis muscle is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Extremity
The upper Limb (anatomy), limbs or upper extremities are the forelimbs of an upright posture, upright-postured tetrapod vertebrate, extending from the scapulae and clavicles down to and including the digit (anatomy), digits, including all the musculatures and ligaments involved with the shoulder, elbow, wrist and knuckle joints. In humans, each upper limb is divided into the shoulder, arm, elbow, forearm, wrist and hand, and is primarily used for climbing, manual handling of loads, lifting and dexterity, manipulating objects. In anatomy, just as arm refers to the upper arm, leg refers to the lower leg. Definition In formal usage, the term "arm" only refers to the structures from the shoulder to the elbow, explicitly excluding the forearm, and thus "upper limb" and "arm" are not synonymous. However, in casual usage, the terms are often used interchangeably. The term "upper arm" is redundant in anatomy, but in informal usage is used to distinguish between the two terms. Structure I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
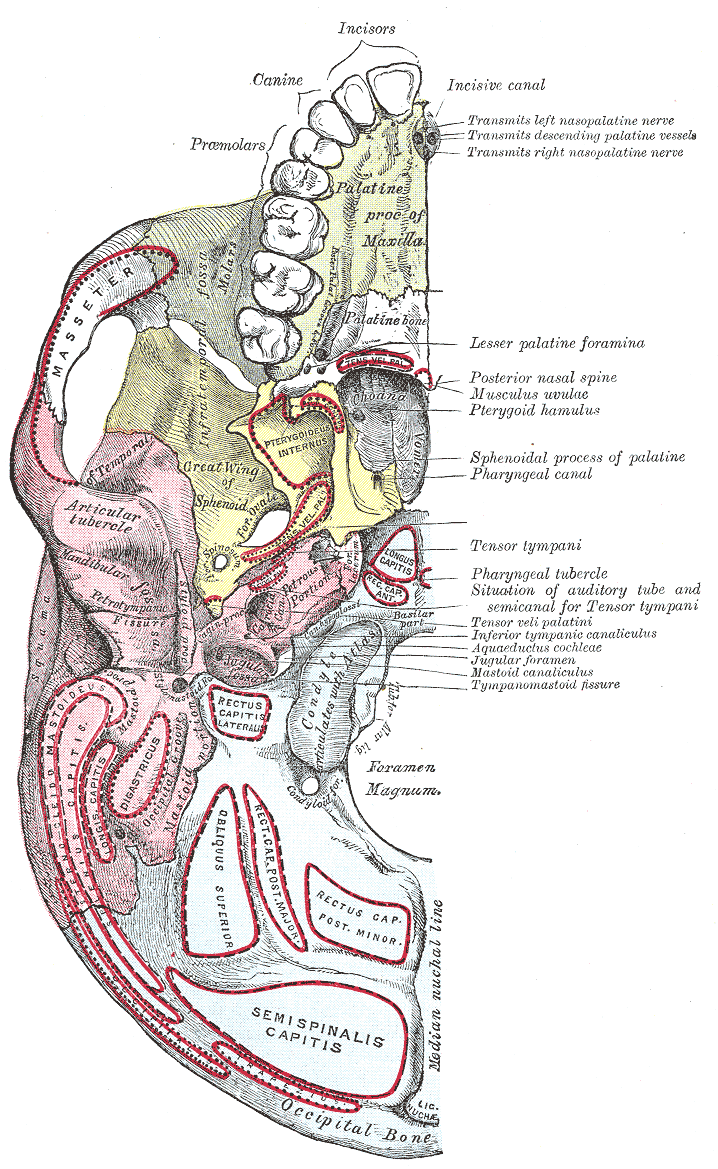
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone *Sphenoid bone *Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses * Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus * Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen * Foramen lacerum * Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen * Internal auditory meatus * Mastoid foramen * Sphenoidal emissary foramen * Foramen spinosum Sutures * Frontoethmoidal suture * Sphenofrontal suture * Sphenopetrosal suture * Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture * Sphenosquamosal suture Other * Sphenoidal lingula * Subarcuate fossa * Dorsum sellae * Jugular process * Petro-occipital fissure * Condylar canal * J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Head And Neck
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are great apes characterized by their hairlessness, bipedalism, and high intelligence. Humans have large brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, languages, and traditions (collectively termed institutions), each of which bolsters human society. Humans are also highly curious: the desire to understand and influence phenomena has motivated humanity's deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of The Torso
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to contract. Muscle tissue contains special contractile proteins called actin and myosin which interact to cause movement. Among many other muscle proteins, present are two regulatory proteins, troponin and tropomyosin. Muscle is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. Skeletal muscle tissue is striated consisting of elongated, multinucleate muscle cells called muscle fibers, and is responsible for movements of the body. Other tissues in skeletal muscle include tendons and perimysium. Smooth and cardiac muscle contract involuntarily, without conscious intervention. These muscle types may be activated both through the interaction of the central nervous system as well as by innervation from peripheral plexus or endocrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterolateral Triangle
The posterior triangle (or lateral cervical region) is a region of the neck. Boundaries The posterior triangle has the following boundaries: Apex: Union of the sternocleidomastoid and the trapezius muscles at the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone Anteriorly: Posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus Posteriorly: Anterior border of the trapezius Inferiorly: Middle one third of the clavicle Roof: Investing layer of the deep cervical fascia Floor: (From superior to inferior) 1) M. semispinalis capitis 2) M. splenius capitis 3) M. levator scapulae 4) M. scalenus posterior 5) M. scalenus medius Divisions The posterior triangle is crossed, about 2.5 cm above the clavicle, by the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle, which divides the space into two triangles: * an upper or occipital triangle * a lower or subclavian triangle (or supraclavicular triangle) Contents A) Nerves and plexuses: * Spinal accessory nerve (Cranial Nerve XI) * Branches of cerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spine
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sauropsid species, the cervical vertebrae bear cervical ribs. In lizards and saurischian dinosaurs, the cervical ribs are large; in birds, they are small and completely fused to the vertebrae. The vertebral transverse processes of mammals are homologous to the cervical ribs of other amniotes. Most mammals have seven cervical vertebrae, with the only three known exceptions being the manatee with six, the two-toed sloth with five or six, and the three-toed sloth with nine. In humans, cervical vertebrae are the smallest of the true vertebrae and can be readily distinguished from those of the thoracic or lumbar regions by the presence of a transverse foramen, an opening in each transverse process, through which the vertebral artery, verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Ramus Of Spinal Nerve
The dorsal ramus of spinal nerve, posterior ramus of spinal nerve, or posterior primary division is the posterior division of a spinal nerve. The dorsal rami provide motor innervation to the deep (a.k.a. intrinsic or true) muscles of the back, and sensory innervation to the skin of the posterior portion of the head, neck and back. A spinal nerve splits within the intervertebral foramen to form a dorsal ramus and a ventral ramus. The dorsal ramus then turns to course posterior-ward before splitting into a medial branch and a lateral branch. Both these branches provide motor innervation to deep back muscles. In the neck and upper back, the medial branch is also responsible for providing sensory innervation of the skin; in the lower back, the lateral branch does so. All medial branches additionally also provide sensory innervation to the zygapophyseal joints and periosteum of the vertebral column. Structure Ventral root axons join with dorsal root ganglia to form mixed spinal nerves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: * an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; * a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and * a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezoid, trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the spinous process of C7, the external occipital protuberance, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Nuchal Line
The nuchal lines are four curved lines on the external surface of the occipital bone: * The upper, often faintly marked, is named the highest nuchal line, but is sometimes referred to as the Mempin line or linea suprema, and it attaches to the epicranial aponeurosis. * Below the highest nuchal line is the superior nuchal line. To it is attached, the splenius capitis muscle, the trapezius muscle, and the occipitalis. * From the external occipital protuberance a ridge or crest, the external occipital crest also called the median nuchal line, often faintly marked, descends to the foramen magnum, and affords attachment to the nuchal ligament The nuchal ligament is a ligament at the back of the neck that is continuous with the supraspinous ligament. Structure The nuchal ligament extends from the external occipital protuberance on the skull and median nuchal line to the spinous p .... * Running from the middle of this line is the inferior nuchal line. Attached are the obliq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastoid Process
The mastoid part of the temporal bone is the posterior (back) part of the temporal bone, one of the bones of the skull. Its rough surface gives attachment to various muscles (via tendons) and it has openings for blood vessels. From its borders, the mastoid part articulates with two other bones. Etymology The word "mastoid" is derived from the Greek word for "breast", a reference to the shape of this bone. Surfaces Outer surface Its outer surface is rough and gives attachment to the occipitalis and posterior auricular muscles. It is perforated by numerous foramina (holes); for example, the mastoid foramen is situated near the posterior border and transmits a vein to the transverse sinus and a small branch of the occipital artery to the dura mater. The position and size of this foramen are very variable; it is not always present; sometimes it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal and the occipital. Mastoid process The mastoid process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoideus
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the sternum and the clavicle, hence it is said to have two heads: sternal head and clavicular head. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its center, and broader and thinner at either end. The sternal head is a round fasciculus, tendinous in front, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Vertebrae
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebra (anatomy), vertebrae of intermediate size between the cervical and lumbar vertebrae; they increase in size going towards the lumbar vertebrae. They are distinguished by the presence of Zygapophysial joint, facets on the sides of the bodies for Articulation (anatomy), articulation with the head of rib, heads of the ribs, as well as facets on the transverse processes of all, except the eleventh and twelfth, for articulation with the tubercle (rib), tubercles of the ribs. By convention, the human thoracic vertebrae are numbered T1–T12, with the first one (T1) located closest to the skull and the others going down the spine toward the lumbar region. General characteristics These are the general characteristics of the second through eighth thoracic vertebrae. The first and ninth through twelfth v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |