|
Little Thuringian Forest
The Little Thuringian Forest (german: Kleiner Thüringer Wald) is a region of mountains and hills that lies southwest of Suhl and northwest of Schleusingen, and extends as far as an imaginary line from Schmeheim via Bischofrod and Gethles to Rappelsdorf. Its length is about , its width varies between and . Its name is not to be understood in an orographic or geographic sense, but is due to the marked similarity of its bedrock to that of the Thuringian Forest to the north of it. Geography The region extends northwest from Schleusingen, beginning near Rappelsdorf, via Gethles, Ahlstädt, Bischofrod, Keulrod, Eichenberg to north of the ''Sandberg'' near Grub, in the northwest of Hildburghausen district, parallel to the Thuringian Forest range. The Little Thuringian Forest is surrounded on all sides by forested mountains formed of Buntsandstein and Muschelkalk, some of which rise over 200 metres above it. Geology Geologically, the Little Thuringian Forest is a horst tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suhl
Suhl () is a city in Thuringia, Germany, located SW of Erfurt, NE of Würzburg and N of Nuremberg. With its 37,000 inhabitants, it is the smallest of the six urban districts within Thuringia. Together with its northern neighbour-town Zella-Mehlis, Suhl forms the largest urban area in the Thuringian Forest with a population of 46,000. The region around Suhl is marked by up to 1,000-meter-high mountains, including Thuringia's highest peak, the Großer Beerberg (983 m), approximately NE of the city centre. Suhl was first mentioned in 1318 and stayed a small mining and metalworking town, until industrialization broke through in late 19th century and Suhl became a centre of Germany's arms production, specialized on rifles and guns with companies such as Sauer & Sohn. Furthermore, the engineering industry was based in Suhl with Simson, a famous car and moped producer. In 1952, Suhl became one of East Germany's 14 district capitals, which led to a government-directed period of ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variscan Orogeny
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea. Nomenclature The name ''Variscan'', comes from the Medieval Latin name for the district '' Variscia'', the home of a Germanic tribe, the Varisci; Eduard Suess, professor of geology at the University of Vienna, coined the term in 1880. ( Variscite, a rare green mineral first discovered in the Vogtland district of Saxony in Germany, which is in the Variscan belt, has the same etymology.) ''Hercynian'', on the other hand, derives from the Hercynian Forest. Both words were descriptive terms of strike directions observed by geologists in the field, ''variscan'' for southwest to northeast, ''hercynian'' for northwest to southeast. The ''variscan'' direction reflected the direction of ancient fold belts cropping out throughout Germany and adjacent countries and the meaning shifted f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of Thuringia
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Uplands
The Central UplandsDickinson (1964), p.18 ff. (german: die MittelgebirgeN.B. In German die ''Mittelgebirge'' (plural) refers to the Central Uplands; das ''Mittelgebirge'' refers to a low mountain range or upland region (''Mittel'' = "medium" and ''-gebirge'' = "range").) is one of the three major natural regions of Germany. It stretches east to west across the country. To the north lies the North German Plain or Northern Lowland; to the south, the Alps and the Alpine Foreland. Formation The German Central Uplands, like the Scandinavian and British mountain ranges and the Urals, belong to the oldest mountains of Europe, even if their present-day appearance has only developed relatively recently. In the Carboniferous, i.e. about 350 million years ago, Variscan mountain ranges were formed in central Europe by the uplifting caused by tectonic plate collision. Immediately after their formation the erosion of the mountains began under the influence of exogenous processes durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schneeberg (Suhl)
The Schneeberg is a mountain, 692.4 metres high, that marks the southernmost boundary point of the borough of Suhl in the German state of Thuringia. The mountain is forested down to the valley in the south. Its southern mountainside belongs to the parish of Grub and Eichenberg, both small forest villages near Themar in the county of Hildburghausen. The Schneeberg is the highest point of the Little Thuringian Forest. A hiking trail runs over the wooded Schneeberg linking Dolmar to the Rennsteig The () is a ridge walk as well as an historical boundary path in the Thuringian Forest, Thuringian Highland and Franconian Forest in Central Germany. The long-distance trail runs for about from and the valley in the northwest to and the r ... trail. References {{reflist Mountains under 1000 metres Mountains of Thuringia Thuringian Forest Suhl Hildburghausen (district) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the enabling laws of each country or the regulations of the international organizations involved. Generally speaking though, protected areas are understood to be those in which human presence or at least the exploitation of natural resources (e.g. firewood, non-timber forest products, water, ...) is limited. The term "protected area" also includes marine protected areas, the boundaries of which will include some area of ocean, and transboundary protected areas that overlap multiple countries which remove the borders inside the area for conservation and economic purposes. There are over 161,000 protected areas in the world (as of October 2010) with more added daily, representing between 10 and 15 percent of the world's land surface area. As of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
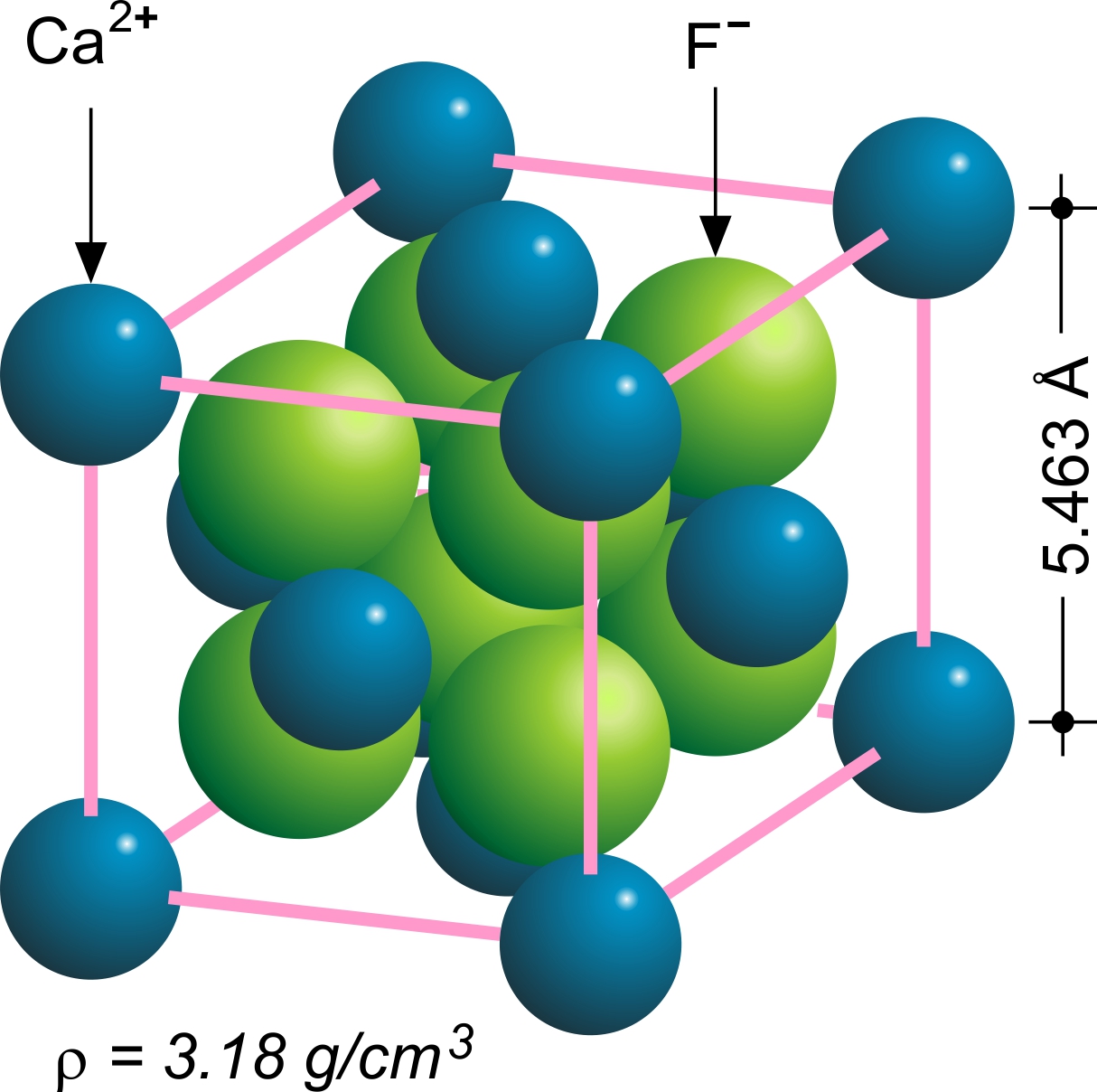
Fluorite
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon. The Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratch hardness comparison, defines value 4 as fluorite. Pure fluorite is colourless and transparent, both in visible and ultraviolet light, but impurities usually make it a colorful mineral and the stone has ornamental and lapidary uses. Industrially, fluorite is used as a flux for smelting, and in the production of certain glasses and enamels. The purest grades of fluorite are a source of fluoride for hydrofluoric acid manufacture, which is the intermediate source of most fluorine-containing fine chemicals. Optically clear transparent fluorite lenses have low dispersion, so lenses made from it exhibit less chromatic aberration, making them valuable in microscopes and telescopes. Fluorite optics ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baryte
Baryte, barite or barytes ( or ) is a mineral consisting of barium sulfate ( Ba S O4). Baryte is generally white or colorless, and is the main source of the element barium. The ''baryte group'' consists of baryte, celestine (strontium sulfate), anglesite (lead sulfate), and anhydrite (calcium sulfate). Baryte and celestine form a solid solution (Ba,Sr)SO4. Names and history The radiating form, sometimes referred to as ''Bologna Stone'', attained some notoriety among alchemists for specimens found in the 17th century near Bologna by Vincenzo Casciarolo. These became phosphorescent upon being calcined. Carl Scheele determined that baryte contained a new element in 1774, but could not isolate barium, only barium oxide. Johan Gottlieb Gahn also isolated barium oxide two years later in similar studies. Barium was first isolated by electrolysis of molten barium salts in 1808 by Sir Humphry Davy in England. The American Petroleum Institute specification API 13/ ISO 135 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron Ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the form of magnetite (, 72.4% Fe), hematite (, 69.9% Fe), goethite (, 62.9% Fe), limonite (, 55% Fe) or siderite (, 48.2% Fe). Ores containing very high quantities of hematite or magnetite (greater than about 60% iron) are known as "natural ore" or "direct shipping ore", meaning they can be fed directly into iron-making blast furnaces. Iron ore is the raw material used to make pig iron, which is one of the main raw materials to make steel—98% of the mined iron ore is used to make steel. In 2011 the ''Financial Times'' quoted Christopher LaFemina, mining analyst at Barclays Capital, saying that iron ore is "more integral to the global economy than any other commodity, except perhaps oil". Sources Metallic iron is virtually unk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gruber Berg
__NOTOC__ Gruber is a German surname from Austria and Bavaria, referring to a person from a geological depression, mine, or pit. It is the most common surname in Austria (see List of most common surnames). Places * Gruber Mountains, Antarctica * Gruber, Manitoba, former settlement in the Canadian province of Manitoba * Camp Gruber, Oklahoma Army National Guard facility, named for Edmund L. Gruber People People whose family name is or was Gruber * Andreas Gruber (born 1954), Austrian screenwriter and director * Barbara Gruber (born 1977), German ski mountaineer * Christoph Gruber (born 1976), Austrian alpine skier * David Gruber, American Marine Biologist * Edmund L. Gruber (1879–1941) US Army general, composer of military music, and brother of William R. Gruber * Ferry Gruber (1926–2004), Austrian-German tenor in opera and operetta * Florian Gruber (born 1983), German racing driver * Frank Gruber (writer) (1904–1969), writer of Westerns and detective fiction * Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zechstein
The Zechstein (German either from ''mine stone'' or ''tough stone'') is a unit of sedimentary rock layers of Middle to Late Permian ( Guadalupian to Lopingian) age located in the European Permian Basin which stretches from the east coast of England to northern Poland. The name Zechstein was formerly also used as a unit of time in the geologic timescale, but nowadays it is only used for the corresponding sedimentary deposits in Europe. The Zechstein lies on top of the Rotliegend; on top of the Zechstein is the Buntsandstein or Bunter. Formation The evaporite rocks of the Zechstein formation were laid down by the Zechstein Sea, an epicontinental or epeiric sea that existed in the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the Permian period. The Zechstein Sea occupied the region of what is now the North Sea, plus lowland areas of Britain and the north European plain through Germany and Poland. The Zechstein sea lay in the rain shadow of the Central Pangean Mountains to the south. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fold (geology)
In structural geology, a fold is a stack of originally planar surfaces, such as sedimentary strata, that are bent or curved during permanent deformation. Folds in rocks vary in size from microscopic crinkles to mountain-sized folds. They occur as single isolated folds or in periodic sets (known as ''fold trains''). Synsedimentary folds are those formed during sedimentary deposition. Folds form under varied conditions of stress, pore pressure, and temperature gradient, as evidenced by their presence in soft sediments, the full spectrum of metamorphic rocks, and even as primary flow structures in some igneous rocks. A set of folds distributed on a regional scale constitutes a fold belt, a common feature of orogenic zones. Folds are commonly formed by shortening of existing layers, but may also be formed as a result of displacement on a non-planar fault (''fault bend fold''), at the tip of a propagating fault (''fault propagation fold''), by differential compaction or due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |