|
List Of Model Organisms
This is a list of model organisms used in scientific research. Viruses Phages (infecting prokaryotes): * ''Escherichia virus Lambda'' (Phage lambda) * Phi X 174, the first DNA genome ever to be sequenced (circular, 5386 base pairs in length), shortly after the RNA genome of bacteriophage MS2 (in 1976). * T4 phage Animal viruses: * SV40 * '' Human alphaherpesvirus (''Herpes simplex virus) Plant viruses: * Tobacco mosaic virus Bacteria * ''Escherichia coli'' (''E. coli''), common Gram-negative gut bacterium widely used in molecular genetics. Main lab strain is 'K-12'. * ''Bacillus subtilis,'' endospore forming Gram-positive bacterium. Main lab strain is '168'. * ''Caulobacter crescentus,'' bacterium that divides into two distinct cells used to study cellular differentiation. * ''Mycoplasma genitalium,'' minimal organism and human STD pathogen. * ''Aliivibrio fischeri,'' quorum sensing, bioluminescence and animal-bacterial symbiosis with Hawaiian bobtail squid. * '' Bacteroides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Coli At 10000x, Original
E, or e, is the fifth Letter (alphabet), letter and the second vowel#Written vowels, vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Letter names, ''e'' (pronounced ); plural ''es'', ''Es'', or ''E's''. It is the most commonly used letter in many languages, including Czech language, Czech, Danish language, Danish, Dutch language, Dutch, English language, English, French language, French, German language, German, Hungarian language, Hungarian, Latin language, Latin, Latvian language, Latvian, Norwegian language, Norwegian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Swedish language, Swedish. Name In English, the name of the letter is the "long E" sound, pronounced . In most other languages, its name matches the letter's pronunciation in open syllables. History The Latin letter 'E' differs little from its source, the Greek alphabe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endospore
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in Gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of '' Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 25 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synechocystis Sp
''Synechocystis'' is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism. Like all cyanobacteria, ''Synechocystis'' branches on the evolutionary tree from its ancestral root, '' Gloeobacter violaceus''. ''Synechocystis'' is not diazotrophic, and is closely related to another model organism, ''Cyanothece ''Cyanothece'' is a genus of unicellular, diazotrophic, oxygenic photosynthesizing cyanobacteria. Modern organisms and cellular organization In 1976, Jiří Komárek defined the prokaryotic cyanobacteria genus ''Cyanothece'' as distinct from '' ...'' ATCC 51442. It has been suggested that originally ''Synechocystis'' possessed the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, but lost the genes required for the process. ''Synechocystis'' can detect light and move in the direction of light. See also * ''Synechocystis'' run-and-tumble References {{Taxonbar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synechocystis
''Synechocystis'' is a genus of unicellular, freshwater cyanobacteria in the family Merismopediaceae. It includes a strain, ''Synechocystis'' sp. PCC 6803, which is a well studied model organism A model organism is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Mo .... Like all cyanobacteria, ''Synechocystis'' branches on the evolutionary tree from its ancestral root, '' Gloeobacter violaceus''. ''Synechocystis'' is not diazotrophic, and is closely related to another model organism, '' Cyanothece'' ATCC 51442. It has been suggested that originally ''Synechocystis'' possessed the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen, but lost the genes required for the process. ''Synechocystis'' can detect light and move in the direction of light. See also * ''Synechocystis'' run-and-tumble References {{Taxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Microbiota
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density of any human-associated microbial community studied so far, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. About 55% of the dry mass of feces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteroides Thetaiotaomicron
''Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron'' is a Gram-negative, obligate anaerobic bacterium and a prominent member of the human gut microbiota, particularly within the large intestine. ''B. thetaiotaomicron'' belongs to the ''Bacteroides'' genus – a group that is known for its role in the complex microbial community of the gut microbiota. Its proteome, consisting of 4,779 members, includes a system for obtaining and breaking down dietary polysaccharides that would otherwise be difficult to digest for the human body. The bacterium encodes for enzymes such as glycoside hydrolases and polysaccharide lyases, allowing it to break down dietary fibers, such as cellulose and hemicellulose, into fermentable substrates. This metabolic activity generates short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate and propionate, which are absorbed by the host and provide critical energy sources for colonic cells. ''B. thetaiotaomicron'' is an opportunistic pathogen and may become virulent in immunocompromised in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawaiian Bobtail Squid
__NOTOC__ ''Euprymna scolopes'', also known as the Hawaiian bobtail squid, is a species of bobtail squid in the family Sepiolidae native to the central Pacific Ocean, where it occurs in shallow coastal waters off the Hawaiian Islands and Midway Island.Reid, A. & P. Jereb 2005. Family Sepiolidae. ''In:'' P. Jereb & C.F.E. Roper, eds. ''Cephalopods of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of species known to date. Volume 1. Chambered nautiluses and sepioids (Nautilidae, Sepiidae, Sepiolidae, Sepiadariidae, Idiosepiidae and Spirulidae)''. FAO Species Catalogue for Fishery Purposes. No. 4, Vol. 1. Rome, FAO. pp. 153–203. The type specimen was collected off the Hawaiian Islands and is located at the National Museum of Natural History in Washington, D.C. ''Euprymna scolopes'' grows to in mantle length. Hatchlings weigh and mature in 80 days. Adults weigh up to . In the wild, ''E. scolopes'' feeds on species of shrimp, including '' Halocaridina rubra'', '' Palaemon debi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiosis
Symbiosis (Ancient Greek : living with, companionship < : together; and ''bíōsis'': living) is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction, between two organisms of different species. The two organisms, termed symbionts, can for example be in Mutualism (biology), mutualistic, commensalism, commensalistic, or parasitism, parasitic relationships. In 1879, Heinrich Anton de Bary defined symbiosis as "the living together of unlike organisms". The term is sometimes more exclusively used in a restricted, mutualistic sense, where both symbionts contribute to each other's subsistence. This means that they benefit each other in some way. Symbiosis can be ''obligate'' (or ''obligative''), which means that one, or both of the organisms depend on each other for survival, or ''facultative'' (optional), when they can also subsist independently. Symbiosis is also classified by physical attachment. Symbionts forming a single body live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence is the emission of light during a chemiluminescence reaction by living organisms. Bioluminescence occurs in multifarious organisms ranging from marine vertebrates and invertebrates, as well as in some Fungus, fungi, microorganisms including some bioluminescent bacteria, Dinoflagellate, dinoflagellates and terrestrial arthropods such as Firefly, fireflies. In some animals, the light is bacteriogenic, produced by symbiosis, symbiotic bacteria such as those from the genus ''Vibrio''; in others, it is autogenic, produced by the animals themselves. In most cases, the principal chemical reaction in bioluminescence involves the reaction of a substrate called luciferin and an enzyme, called luciferase. Because these are generic names, luciferins and luciferases are often distinguished by the species or group, e.g. firefly luciferin or Vargulin, cypridina luciferin. In all characterized cases, the enzyme Catalysis, catalyzes the Redox, oxidation of the luciferin resultin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
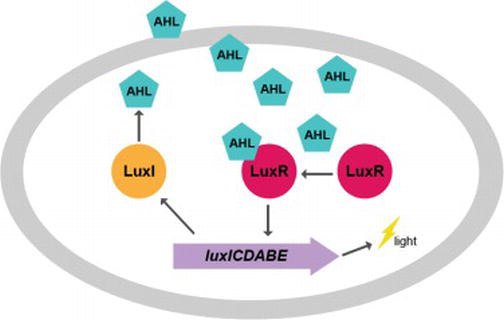
Quorum Sensing
In biology, quorum sensing or quorum signaling (QS) is the process of cell-to-cell communication that allows bacteria to detect and respond to cell population density by gene regulation, typically as a means of acclimating to environmental disadvantages. Quorum sensing is a type of cellular signaling, and can be more specifically considered a type of paracrine signaling. However, it also contains traits of autocrine signaling: a cell produces both an autoinducer molecule and the receptor for the autoinducer. As one example, quorum sensing enables bacteria to restrict the expression of specific genes to the high cell densities at which the resulting phenotypes will be most beneficial, especially for phenotypes that would be ineffective at low cell densities and therefore too energetically costly to express. Many species of bacteria use quorum sensing to coordinate gene expression according to the density of their local population. In a similar fashion, some social insects use q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliivibrio Fischeri
''Aliivibrio fischeri'' (formerly ''Vibrio fischeri'') is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped bacterium found globally in marine environments. This bacterium grows most effectively in water with a salt concentration at around 20g/L, and at temperatures between 24 and 28°C. This species is non-pathogenic and has bioluminescent properties. It is found predominantly in symbiosis with various marine animals, such as the Hawaiian bobtail squid. It is heterotrophic, oxidase-positive, and motile by means of a tuft of polar flagella. Free-living ''A. fischeri'' cells survive on decaying organic matter. The bacterium is a key research organism for examination of microbial bioluminescence, quorum sensing, and bacterial-animal symbiosis. It is named after Bernhard Fischer, a German microbiologist. ''Aliivibrio fischeri'' is the family '' Vibrionaceae.'' This family of bacteria tend to have adaptable metabolisms that can adjust to diverse circumstances. This flexibility may contribute to ''A. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (also known as ''MG','' Mgen, or since 2018, ''Mycoplasmoides genitalium'') is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics, including the macrolide azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment, is becoming prevalent. The bacterium was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of '' Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Symptoms of infection Mgen is a bacterium recognized for causing urethritis in both men and women along with cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |