|
Mycoplasma Genitalium
''Mycoplasma genitalium'' (also known as ''MG','' Mgen, or since 2018, ''Mycoplasmoides genitalium'') is a sexually transmitted, small and pathogenic bacterium that lives on the mucous epithelial cells of the urinary and genital tracts in humans. Medical reports published in 2007 and 2015 state that Mgen is becoming increasingly common. Resistance to multiple antibiotics, including the macrolide azithromycin, which until recently was the most reliable treatment, is becoming prevalent. The bacterium was first isolated from the urogenital tract of humans in 1981, and was eventually identified as a new species of '' Mycoplasma'' in 1983. It can cause negative health effects in men and women. It also increases the risk for HIV spread with higher occurrences in those previously treated with the azithromycin antibiotics. Symptoms of infection Mgen is a bacterium recognized for causing urethritis in both men and women along with cervicitis and pelvic inflammation in women ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexually Transmitted Infection
A sexually transmitted infection (STI), also referred to as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and the older term venereal disease (VD), is an infection that is Transmission (medicine), spread by Human sexual activity, sexual activity, especially Sexual intercourse, vaginal intercourse, anal sex, oral sex, or sometimes Non-penetrative sex#Manual sex, manual sex. STIs often do not initially cause symptoms, which results in a risk of transmitting them to others. The term ''sexually transmitted infection'' is generally preferred over ''sexually transmitted disease'' or ''venereal disease'', as it includes cases with no Signs and symptoms#Symptomatic, symptomatic disease. Symptoms and signs of STIs may include vaginal discharge, penile discharge, genital ulcers, ulcers on or around the genitals, and pelvic pain. Some STIs can cause infertility. Bacterial STIs include Chlamydia infection, chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. Viral STIs include genital warts, genital herpes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). Pre-symptomatic is the adjective categorising the time periods during which the medical conditions are asymptomatic. Subclinical and paucisymptomatic are other adjectives categorising either the asymptomatic infections (i.e., subclinical infections), or the psychosomatic illnesses and mental disorders expressing a subset of symptoms but not the entire set an explicit medical diagnosis requires. Examples An example of an asymptomatic disease is cytomegalovirus (CMV) which is a member of the herpes virus family. "It is estimated that 1% of all newborns are infected with CMV, but the majority of infections are asymptomatic." (Knox, 1983; Kumar et al. 1984) In some diseases, the proportion of asymptomatic cases can be important. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symptomatic Treatment
Symptomatic treatment, supportive care, supportive therapy, or palliative treatment is any medical therapy of a disease that only affects its symptoms, not the underlying cause. It is usually aimed at reducing the signs and symptoms for the comfort and well-being of the patient, but it also may be useful in reducing organic consequences and sequelae of these signs and symptoms of the disease. In many diseases, even in those whose etiologies are known (e.g., most viral diseases, such as influenza and Rift Valley fever), symptomatic treatment is the only treatment available so far. For more detail, see supportive therapy. For conditions like cancer, arthritis, neuropathy, tendinopathy, and injury, it can be useful to distinguish treatments that are supportive/palliative and cannot alter the natural history of the disease ( disease modifying treatments). Examples Examples of symptomatic treatments: * Analgesics, to reduce pain * Anti-inflammatory agents, for inflammation ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-gonococcal Urethritis
Nongonococcal urethritis (NGU) is inflammation of the urethra that is not caused by gonorrheal infection. For treatment purposes, doctors usually classify infectious urethritis in two categories: gonococcal urethritis, caused by gonorrhea, and nongonococcal urethritis (NGU). Symptoms and signs The symptoms of urethritis can include pain or a burning sensation upon urination (dysuria), a white/cloudy discharge and a feeling that one needs to pass urine frequently. For men, the signs and symptoms are discharge from the penis, burning or pain when urinating, itching, irritation, or tenderness. In women, the signs and symptoms are discharge from vagina, burning or pain when urinating, anal or oral infections, abdominal pain, or abnormal vaginal bleeding, which may be an indication that the infection has progressed to Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. NGU is transmitted by touching the mouth, penis, vagina or anus by penis, vagina or anus of a person who has NGU. NGU is more common in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to make millions to billions of copies of a specific DNA sample rapidly, allowing scientists to amplify a very small sample of DNA (or a part of it) sufficiently to enable detailed study. PCR was invented in 1983 by American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation. Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications including biomedical research and forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chorionic Villi
Chorionic villi are Wiktionary:villus, villi that sprout from the chorion to provide maximal contact area with maternal blood. They are an essential element in pregnancy from a histology, histomorphologic perspective, and are, by definition, a products of conception, product of conception. Branches of the umbilical arteries carry embryonic blood to the villi. After circulating through the capillaries of the villi, blood returns to the embryo through the umbilical vein. Thus, villi are part of the border between maternal and fetal blood during pregnancy. Structure Villi can also be classified by their relations: * Floating villi float freely in the intervillous space. They exhibit a bi-layered epithelium consisting of cytotrophoblasts with overlaying syncytium (syncytiotrophoblast). * Anchoring (stem) villi stabilize the mechanical integrity of the placental-maternal interface. Development The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic vil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infertility
In biology, infertility is the inability of a male and female organism to Sexual reproduction, reproduce. It is usually not the natural state of a healthy organism that has reached sexual maturity, so children who have not undergone puberty, which is the body's start of fertility, reproductive capacity, are excluded. It is also a normal state in women after menopause. In humans, ''infertility'' is defined as the inability to become pregnant after at least one year of unprotected and regular sexual intercourse involving a male and female partner. There are many causes of infertility, including some that Assisted reproductive technology, medical intervention can treat. Estimates from 1997 suggest that worldwide about five percent of all heterosexual couples have an unresolved problem with infertility. Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year, with estimates ranging from 12% to 28%. Male infertility is responsible for 20–30% of infert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
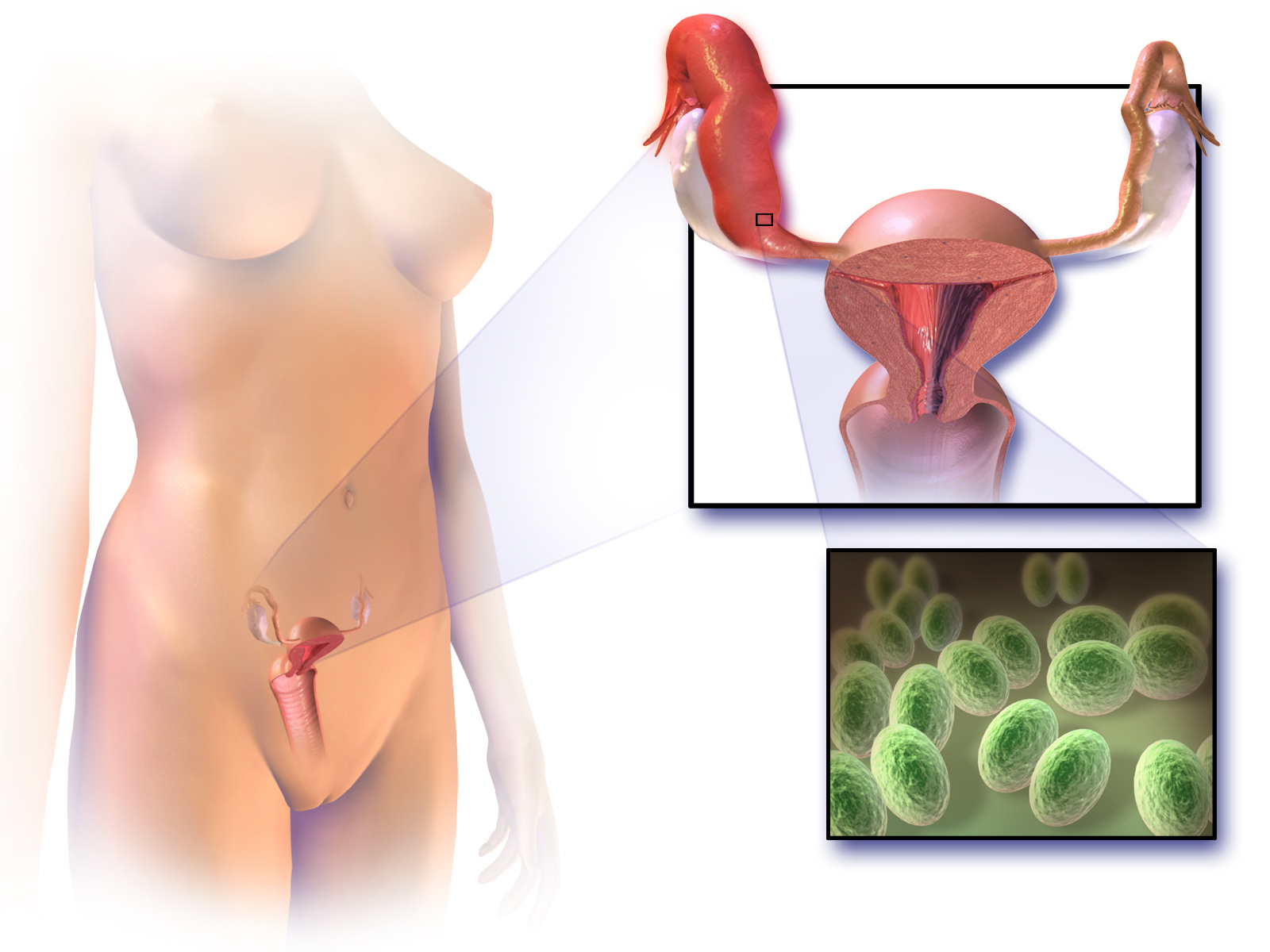
Salpingitis
Salpingitis is an infection causing inflammation in the fallopian tubes (also called ''salpinges''). It is often included in the umbrella term of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), along with endometritis, oophoritis, myometritis, parametritis, and peritonitis. Signs and symptoms The symptoms usually appear after a menstrual period. The most common are: an abnormal smell and colour of vaginal discharge, fever, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and frequent urination. Pain may be felt during ovulation, during periods, during sexual intercourse, on both sides of the abdomen, and lower back. Causes The infection usually has its origin in the vagina and ascends to the fallopian tube from there. Because the infection can spread via the lymph vessels, infection in one fallopian tube usually leads to infection of the other. Risk factors It's been theorized that retrograde menstrual flow and the cervix opening during menstruation allow the infection to reach the fallopian tubes. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endometritis
Endometritis is inflammation of the inner lining of the uterus (endometrium). Symptoms may include fever, lower abdominal pain, and abnormal vaginal bleeding or discharge. It is the most common cause of infection after childbirth. It is also part of spectrum of diseases that make up pelvic inflammatory disease. Endometritis is divided into acute and chronic forms. The acute form is usually from an infection that passes through the cervix as a result of an abortion, during menstruation, following childbirth, or as a result of douching or placement of an IUD. Risk factors for endometritis following delivery include Caesarean section and prolonged rupture of membranes. Chronic endometritis is more common after menopause. The diagnosis may be confirmed by endometrial biopsy. Ultrasound may be useful to verify that there is no retained tissue within the uterus. Treatment is usually with antibiotics. Recommendations for treatment of endometritis following delivery includes cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), also known as pelvic inflammatory disorder, is an infection of the upper part of the female reproductive system, mainly the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries, and inside of the pelvis. Often, there may be no symptoms. Signs and symptoms, when present, may include lower abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, fever, dysuria, burning with urination, dyspareunia, pain with sex, postcoital bleeding, bleeding after sex, or irregular menstruation. Untreated PID can result in long-term complications including infertility, ectopic pregnancy, chronic pelvic pain, and Infectious causes of cancer, cancer. The disease is caused by bacteria that spread from the vagina and cervix. It has been reported that infections by ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' or ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are present in 75 to 90 percent of cases. However, in the UK it is reported by the NHS that infections by ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'' and ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are responsible for only a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysuria
Dysuria refers to painful or uncomfortable urination. It is one of a constellation of ''irritative'' bladder symptoms (also sometimes referred to as lower urinary tract symptoms), which includes nocturia and urinary frequency. Diagnosis The clinician should also look for physical findings of fever, rash, direct tenderness over the bladder area, and joint pain. Physical findings of increased temperature, increased pulse, low blood pressure in the presence of dysuria can indicate systemic infection. Urological obstruction due to stone or tumor can result in findings of hematuria, decreased urination, and bladder spasms. All these physical findings should be looked for carefully while obtaining history. History regarding recent sexual activity is crucial. Urinalysis is the most useful test to start the work up in a patient of dysuria. Urinalysis positive for nitrite carries a high predictive value of a positive urine culture. Also, urine dipstick showing leukocytes as equal predic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary System
The human urinary system, also known as the urinary tract or renal system, consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, bladder, and the urethra. The purpose of the urinary system is to eliminate waste from the body, regulate blood volume and blood pressure, control levels of Electrolyte, electrolytes and Metabolite, metabolites, and regulate Acid–base homeostasis, blood pH. The urinary tract is the body's drainage system for the eventual removal of urine. The kidneys have an extensive blood supply via the Renal artery, renal arteries which leave the kidneys via the renal vein. Each kidney consists of functional units called nephrons. Following filtration of blood and further processing, waste (in the form of urine) exits the kidney via the ureters, tubes made of smooth muscle fibres that propel urine towards the urinary bladder, where it is stored and subsequently expelled through the urethra during urination. The female and male urinary system are very similar, differin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |