|
Lisan Al-Gharbi
Lisan al-Gharbi (, "Western dialect") is the name given to an extinct dialect of Berber that was spoken over much of the Atlantic plains of Morocco.B. FrankelHistory in Dispute: The Middle East since 1945. First series(St. James Press, 2003), p.206Awal, Numéros 19 à 21 (Maison des sciences de l'homme, 1999), p.157 It was closely related to Tashelhit. The Lisan al-Gharbi was the official language of the Barghawata Confederacy, and the idiom used in Salih ibn Tarif's "indigenous Qur'an". The |
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocco border, the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to Morocco–Western Sahara border, the south. Morocco also claims the Spain, Spanish Enclave and exclave, exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Plazas de soberanía, Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab culture, Arab, Berbers, Berber, Culture of Africa, African and Culture of Europe, European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bedouin
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu ( ; , singular ) are pastorally nomadic Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia (Iraq). The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert and Arabian Desert but spread across the rest of the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa after the spread of Islam. The English word ''bedouin'' comes from the Arabic ''badawī'', which means "desert-dweller", and is traditionally contrasted with ''ḥāḍir'', the term for sedentary people. Bedouin territory stretches from the vast deserts of North Africa to the rocky ones of the Middle East. They are sometimes traditionally divided into tribes, or clans (known in Arabic as ''ʿašāʾir''; or ''qabāʾil'' ), and historically share a common culture of herding camels, sheep and goats. The vast majority of Bedouins adhere to Islam, although there are some fewer numbers of Christian Bedouins present in the Fertile Cres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berbers In Morocco
Berbers, or the Berber peoples, also known as Amazigh or Imazighen, are a diverse grouping of distinct ethnic groups indigenous to North Africa who predate the arrival of Arabs in the Maghreb. Their main connections are identified by their usage of Berber languages, most of them mutually unintelligible, which are part of the Afroasiatic language family. They are indigenous to the Maghreb region of North Africa, where they live in scattered communities across parts of Morocco, Algeria, Libya, and to a lesser extent Tunisia, Mauritania, northern Mali and northern Niger. Smaller Berber communities are also found in Burkina Faso and Egypt's Siwa Oasis. Descended from Stone Age tribes of North Africa, accounts of the Imazighen were first mentioned in Ancient Egyptian writings. From about 2000 BC, Berber languages spread westward from the Nile Valley across the northern Sahara into the Maghreb. A series of Berber peoples such as the Mauri, Masaesyli, Massyli, Musulamii, Gaetu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igiliz
Igiliz (; ) is a Middle Ages, medieval village located in the Rural communes of Morocco, rural commune of Toughmart on the edge of the Sous valley in the Anti-Atlas mountains of Morocco. It is most known for being the birthplace of Ibn Tumart, founder of the Almohad Caliphate, Almohad caliphate. The village was known as place of pilgrimage by Ibn Tumart's followers during Almohad rule. As the Almohad caliphate collapsed, the village's location had become lost over time and was believed to be fictional until its discovery in 2006 with archeological searches starting in 2008. In 2022, the Igiliz archeological site was listed as a Historic Monuments and Sites of Morocco, national historic monument. In 2023, the site was opened to visitors and tourists. Etymology Igiliz is a Toponymy, toponym in Berber that can be translated to "mountain peak" or "isolated mountain". The village's full name in Berber, Igiliz-n-Warghen (, ), refers to the native Arghen tribe within the Masmuda triba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibn Tumart
Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad Ibn Tūmart (, ca. 1080–1130) was a Muslim religion, religious scholar, teacher and political leader, from the Sous in southern present-day Morocco. He founded and served as the spiritual and first military leader of the Almohad dynasty, Almohad movement, a puritanical reform movement launched among the Masmuda Berber people, Berbers of the Atlas Mountains. Ibn Tumart launched an open revolt against the ruling Almoravid dynasty, Almoravids during the 1120s. After his death his followers, the Almohads, went on to conquer much of North Africa and part of Spain. Although the Almohad movement itself was founded by Ibn Tumart, his disciple Abd al-Mu'min was the founder of the ruling dynasty and creator of the Almohad empire. Biography Early life Many of the details of Ibn Tumart's life were recorded by hagiography, hagiographers, whose accounts probably mix legendary elements from the Almohad doctrine of their founding figure and spiritual leader. Ib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Béjaïa
Béjaïa ( ; , , ), formerly known as Bougie and Bugia, is a Mediterranean seaport, port city and communes of Algeria, commune on the Gulf of Béjaïa in Algeria; it is the capital of Béjaïa Province. Geography Location Béjaïa owes its existence to its port, which also makes it prosperous. It is located in a sickle-shaped bay protected from the swell of offshore winds (northwest facing) by the advance of Cape Carbon (to the west of the city). The city is backed by :fr:Yemma Gouraya, Mount Gouraya located in a northwest position. This port site, in one of the most beautiful bays of the Maghreb and Mediterranean coast, is dominated in the background by the Babor Mountains, Babors mountain range. Another advantage is that the city is the outlet of the Soummam River, Soummam valley, a geographical corridor facing southwest. However, since the time when the city was a capital, there has been a divorce between the city and the region (Kabylia) linked to the difficulty of secur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains are a mountain range in the Maghreb in North Africa. They separate the Sahara Desert from the Mediterranean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean; the name "Atlantic" is derived from the mountain range, which stretches around through Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia. The mountains are associated with the Greek god Atlas (mythology), Atlas. The range's highest peak is Toubkal, which is in central Morocco, with an elevation of . The Atlas Mountains are primarily inhabited by Berbers, Berber populations. The terms for 'mountain' are ''Adrar'' and ''adras'' in some Berber languages, and these terms are believed to be cognates of the Toponymy, toponym ''Atlas''. The mountains are home to a number of animals and plants which are mostly found within Africa but some of which can be found in Europe. Many of these species are endangered and a few are already extinct. The weather is generally cool but summers are sunny, and the average temperature there is 25 °C. The Atlas Moun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Migrations To The Maghreb
The Arab migrations to the Maghreb involved successive waves of Human migration, migration and Settler, settlement by Arabs, Arab people in the Maghreb region of Africa, encompassing modern-day Algeria, Libya, Morocco and Tunisia. The process took place over several centuries, lasting from the early 7th century to the 17th century. The Arab migrants hailed from the Middle East, particularly the Arabian Peninsula, with later groups arriving from the Levant and Iraq. The influx of Arabs to the Maghreb began in the 7th century with the Muslim conquest of the Maghreb, Arab conquest of the Maghreb, when Arab armies conquered the region as part of the early Muslim conquests. This initial wave of Arab migration was followed by subsequent periods of migration and settlement, notably during the Umayyad Caliphate, Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliphates and later Arab dynasties. However, the most significant wave of Arab migration occurred in the 11th century with the arrival of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
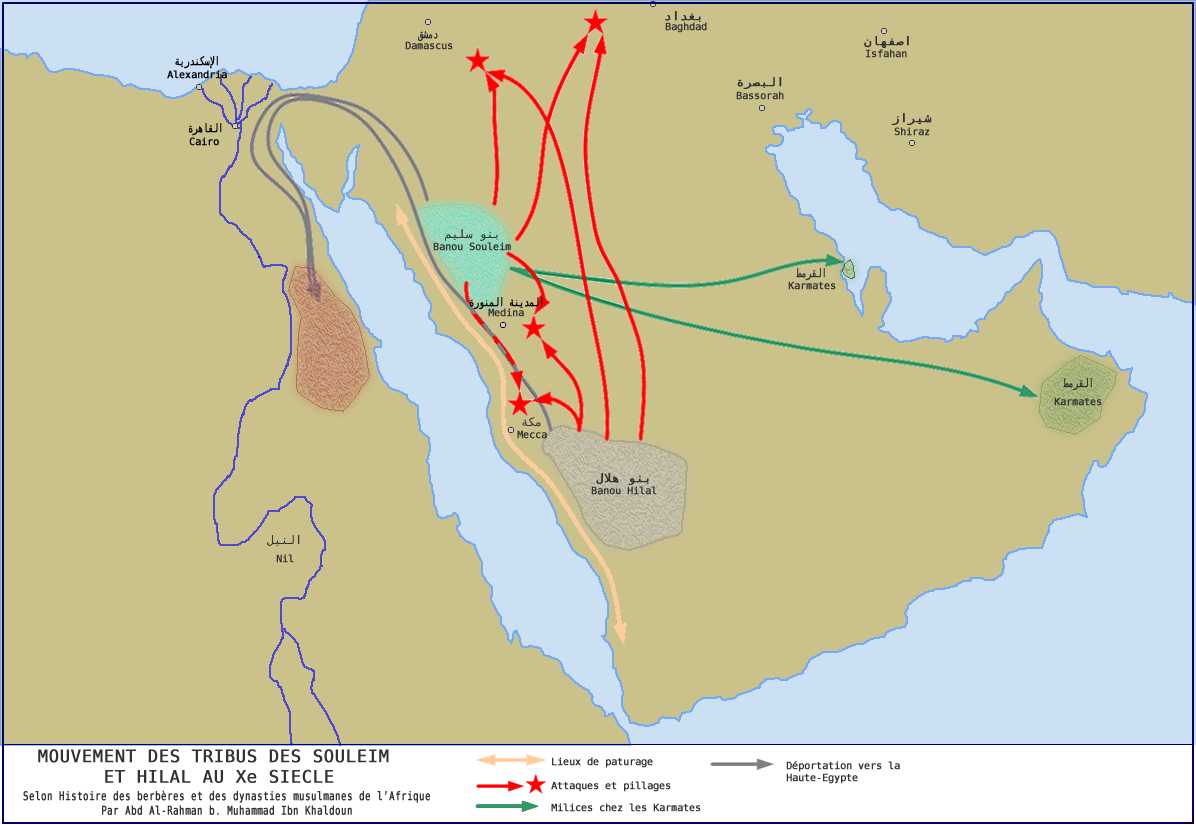
Banu Sulaym
The Banu Sulaym () is an Arab tribe that dominated part of the Hejaz in the pre-Islamic era. They maintained close ties with the Quraysh of Mecca and the inhabitants of Medina, and fought in a number of battles against the Islamic prophet Muhammad before ultimately converting to Islam before his death in 632. They took part in the Muslim conquest of Syria, and established themselves in the Jazira (Upper Mesopotamia), while part of the tribe remained in the Hejaz. During the early Muslim period, the tribe produced notable generals such as Safwan ibn Mu'attal, Abu'l-A'war and Umayr ibn al-Hubab. Those who remained in Arabia were largely absorbed by the Banu Harb of Yemen beginning in the 9th century, while those in Syria and the Jazira were expelled to Upper Egypt by the Fatimid Caliphs in the late 10th century for supporting the Qarmatians. In the mid-11th century, a prolonged famine in Egypt prompted the tribe to migrate westward with the Banu Hilal into Libya. There, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal () was a confederation of Arab tribes from the Najd region of the central Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to the Maghreb region of North Africa in the 11th century. They ruled the Najd, and campaigned in the borderlands between Iraq and Syria. When the Fatimid Caliphate became the rulers of Egypt and the founders of Cairo in 969, they confined the Bedouin in the south before sending them to Central North Africa (Libya, Tunisia and Algeria) and then to Morocco. Historians estimate the total number of Arab nomads who migrated to the Maghreb in the 11th century to be to 500,000 to 700,000 to 1,000,000. Historian Mármol Carvajal estimated that more than a million Hilalians migrated to the Maghreb between 1051 and 1110, and estimated that the Hilalian population in the Maghreb at his time in 1573 was at 4,000,000 individuals, excluding other Arab tribes and other Arabs already present. Origin The Banu Hilal originated in Najd in the central Arabian Peninsula, som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
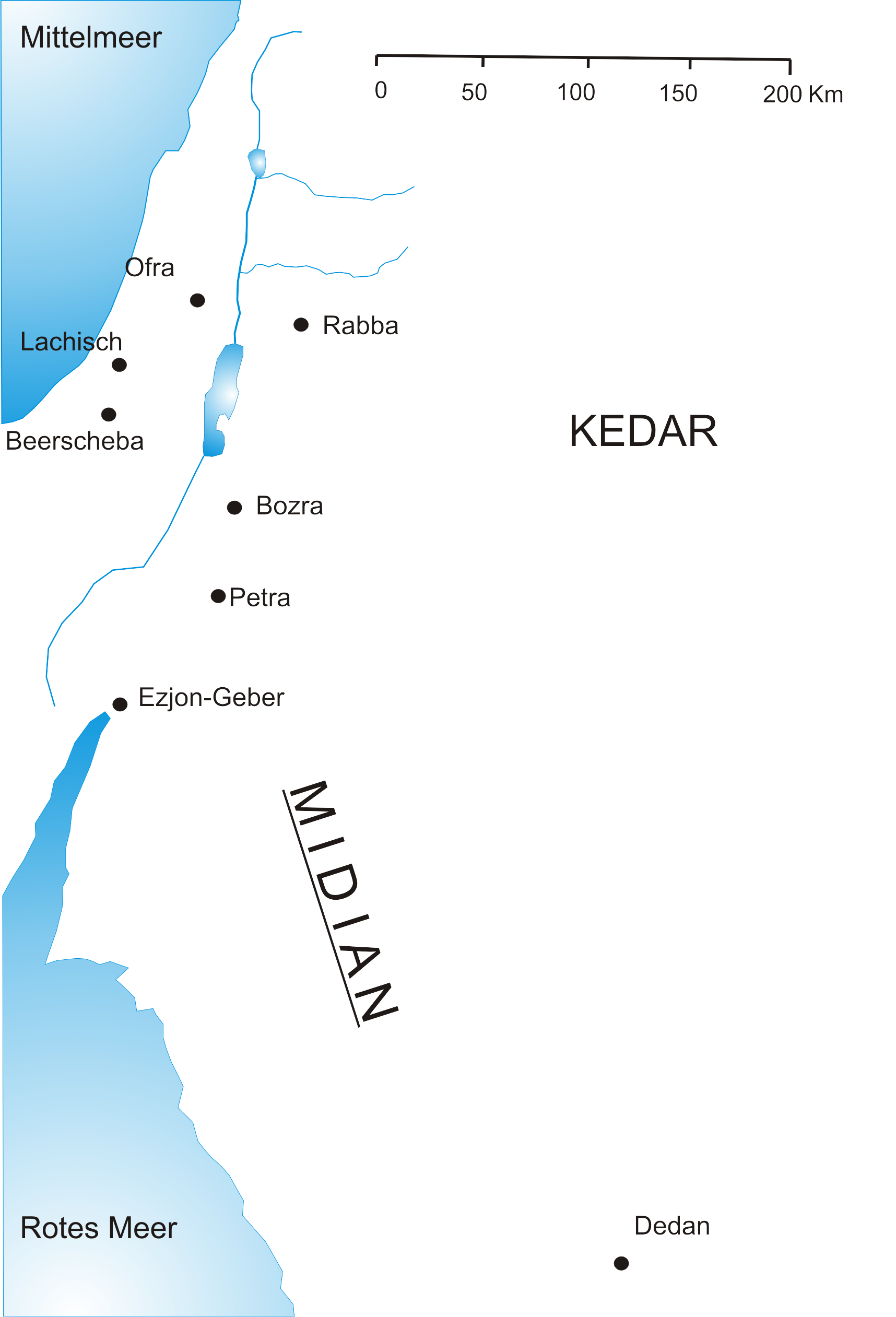
Arabs
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world. Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years. In the 9th century BCE, the Assyrians made written references to Arabs as inhabitants of the Levant, Mesopotamia, and Arabia. Throughout the Ancient Near East, Arabs established influential civilizations starting from 3000 BCE onwards, such as Dilmun, Gerrha, and Magan, playing a vital role in trade between Mesopotamia, and the Mediterranean. Other prominent tribes include Midian, ʿĀd, and Thamud mentioned in the Bible and Quran. Later, in 900 BCE, the Qedarites enjoyed close relations with the nearby Canaanite and Aramaean states, and their territory extended from Lower Egypt to the Southern Levant. From 1200 BCE to 110 BCE, powerful kingdoms emerged such as Saba, Lihyan, Minaean, Qataban, Hadhramaut, Awsan, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |