|
Liebenburg
Liebenburg is a municipality in the Goslar (district), district of Goslar, in Lower Saxony, Germany. Geography The municipal area is situated north of the Harz mountain range, within the eastern Salzgitter Hills of the Innerste Uplands. It borders on the district capital Goslar, approx. in the south; the adjacent municipalities in the north are Salzgitter-Bad and Schladen in Wolfenbüttel (district), Wolfenbüttel District. Subdivisions The municipality comprises Liebenburg proper (with 2,140 inhabitants) and the following nine villages, which were incorporated on 1 July 1972 with the following population as of 30 June 2018: * Dörnten (1,189 inhabitants) with Kunigunde * Groß Döhren (872) * Heißum (301) * Klein Döhren (420) * Klein Mahner (333) * Neuenkirchen (206) * Ostharingen (246) * Othfresen (1,902) with Heimerode and Posthof * Upen (317) History Archaeological excavations of a gallery grave indicate a settlement of the area in the Late Neolithic. The former Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
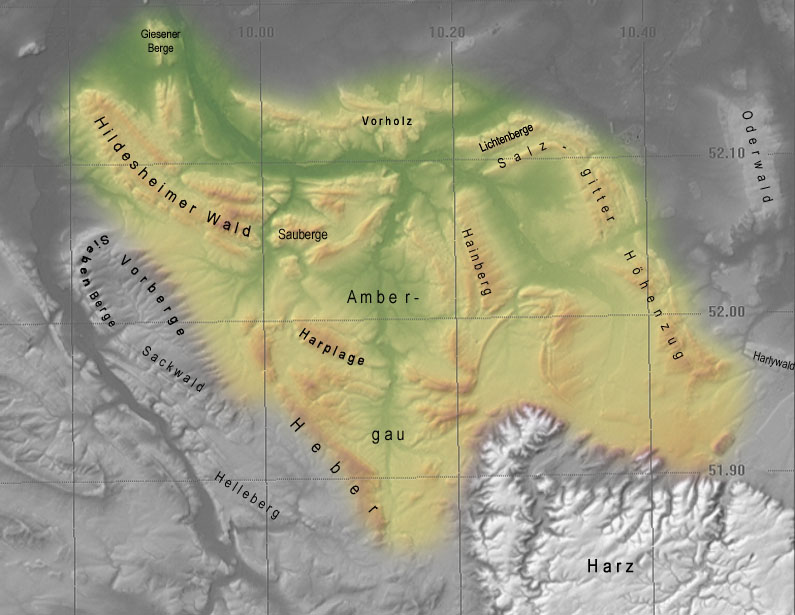
Salzgitter Hills
The Salzgitter Hills (, also ''Salzgitterscher Höhenzug'') is an area of upland up to in height, in the Lower Saxon Hills between Salzgitter and Goslar in the districts of Landkreis Wolfenbüttel, Wolfenbüttel and Landkreis Goslar, Goslar and in the territory of the independent town of Salzgitter. The hills lie in the German federal state of Lower Saxony. The German name of is a term used in the northern Harz Foreland, albeit not found on maps, and is used to mean the string of hills north of the Harz Mountains between the towns mentioned above. The state forest of the Salzgitter Hills is managed by several Lower Saxony forestry offices, including the in Salzgitter-Salder. The Salzgitter Hills can be divided into these four unnamed sections: * Northwest section (mainly comprising the Lichtenberge)(up to 254.2 m high; between Holle and Salzgitter-Gebhardshagen) * North-central section(up to 275.3 m high; between Salzgitter-Gebhardshagen and Salzgitter-Bad) * South-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslar (district)
Goslar () is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by (from the south and clockwise) the districts of Göttingen, Northeim, Hildesheim and Wolfenbüttel, the city of Salzgitter, and by the states of Saxony-Anhalt (district of Harz) and Thuringia ( Nordhausen). History The history of the district is linked with the city of Goslar. The district of Goslar was established in the 19th century by the Prussian government. The city of Goslar did not belong to the district until 1972, when it was eventually incorporated into the district. Langelsheim merged 1 November 2021 with the three municipalities of the Samtgemeinde Lutter am Barenberge, which was abolished. Geography The region comprises the northwestern part of the Harz mountains. The Harz National Park is part of this district. The highest peak is the Wurmberg (971 m) near Braunlage, also being the highest elevation of Lower Saxony. Above the small town of Altenau there is the source of the Oker river, which r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian dialect, Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the Goslar (district), district of Goslar and is located on the northwestern wikt:slope, slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar with over 1.500 Timber framing, timber houses and the Mines of Rammelsberg are UNESCO World Heritage Sites for their millennium-long testimony to the history of ore mining and their political importance for the Holy Roman Empire and Hanseatic League. Each year Goslar awards the Goslarer Kaiserring, Kaiserring to an international artist, called the "Nobel Prize" of the art world. Geography Goslar is situated in the middle of the upper half of Germany, about south of Braunschweig, Brunswick and about southeast of the state capital, Hannover, Hanover. The Schalke (Harz), Schalke mountain is the highest elevation within the municipal boundaries at . The lowest point of is near the Oker river. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishopric Of Hildesheim
The Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim () was an Hochstift, ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the Middle Ages until its dissolution in 1803. The Prince-Bishopric must not be confused with the Roman Catholic Diocese of Hildesheim, Diocese of Hildesheim, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the spiritual authority of an ordinary bishop. History After the Duchy of Saxony had been conquered by the Frankish Kingdom, Emperor Charlemagne in 800 founded a missionary diocese at his eastphalian court in Elze (''Aula Caesaris''), about west of Hildesheim. His son King Louis the Pious established the bishopric at Hildesheim in 815, dedicated to Mary (mother of Jesus), Virgin Mary. According to legend delivered by the Brothers Grimm, the king was hunting in the wintery woods of Elze, when he realized that he had lost his pendant with the relic of Blessed Virgin Mary. Distraught he sent out his attendants who finally discovered a flowering r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry V, Duke Of Brunswick-Lüneburg
Henry V of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel (; 10 November 1489 – 11 June 1568), called the Younger, (''Heinrich der Jüngere''), a member of the House of Welf, was Duke of Brunswick-Lüneburg and ruling Prince of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel from 1514 until his death. The last Catholic of the Welf princes, he was known for the large number of wars in which he was involved and for the long-standing affair with his mistress Eva von Trott. Life Henry was born at Wolfenbüttel Castle, the son of Duke Henry IV of Brunswick-Lüneburg, known as Henry the Elder, and his consort Catherine, a daughter of the Griffin duke Eric II of Pomerania. His father had received the Principality of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel in the course of a subdivision of the Brunswick lands in 1495. Henry succeeded as ruling Prince of Wolfenbüttel when his father was killed in a 1514 battle during the Saxon feud. He soon entered into the Great Diocesan Feud with the Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim under John IV of Saxe-La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hildesheim Diocesan Feud
The Hildesheim Diocesan Feud () or Great Diocesan Feud, sometimes referred to as a "chapter feud", was a conflict that broke out in 1519 between the Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim ('' Hochstift Hildesheim'') and the principalities of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel and Calenberg that were ruled by the House of Welf. Originally just a local conflict between the Hildesheim prince-bishop John IV of Saxe-Lauenburg and his own prince-bishopric's nobility (''Stiftsadel''), it developed into a major dispute between various Lower Saxon territorial princes. The cause was the attempt by Prince-Bishop John to redeem the pledged estates and their tax revenue from the nobles in his temporalities, the prince-bishopric (Hochstift, or simply das Stift). The diocesan feud ended with the Treaty of Quedlinburg in 1523.''Hildesheim Sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried II Of Querfurt
Siegfried II of Querfurt (mid 13th century – 5 May 1310) was the Prince-Bishop of Hildesheim from 1279 to 1310. Biography Siegfried was born to a noble family from the city Querfurt (which now belongs to Saxony-Anhalt). He was head of the chapter at the Cathedral of Magdeburg before he was appointed as bishop on 18 July 1279. He founded the medieval commune of Gronau. This was one part of his defense strategy of the Prince-Bishopric of Hildesheim that he was head of in his role as prince-bishop. Two other parts of this strategy were that he ordered to build a castle in Liebenburg and another one in Ruthe (which now belongs to the municipality of Sarstedt). Both castles were destroyed in the centuries thereafter. In 1302 he bought a castle in Westerhof (which now belongs to the municipality of Kalefeld). In 1310 he bought the County of Dassel in order to enlarge his prince-bishopric. The dukes of Brunswick and Lunenburg were his major opponents. Additionally, the citizen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albrecht Von Wallenstein
Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein, Duke of Friedland (; 24 September 1583 – 25 February 1634), also von Waldstein (), was a Bohemian military leader and statesman who fought on the Catholic side during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). His successful martial career made him one of the richest and most influential men in the Holy Roman Empire by the time of his death. Wallenstein became the supreme commander of the armies of Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II and was a major figure of the Thirty Years' War. Wallenstein was born in the Kingdom of Bohemia into a poor Czech Protestant noble family, affiliated with the Utraquist Hussites, a group of notable anti-German sentiment in some of its circles, and following the teachings of the early reformer Jan Hus. He acquired a multilingual university education across Europe and converted to Catholicism in 1606. A marriage in 1609 to the wealthy widow of a Bohemian landowner gave him access to considerable estates and wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braunschweig
Braunschweig () or Brunswick ( ; from Low German , local dialect: ) is a List of cities and towns in Germany, city in Lower Saxony, Germany, north of the Harz Mountains at the farthest navigable point of the river Oker, which connects it to the North Sea via the rivers Aller (Germany), Aller and Weser. In 2024, it had a population of 272,417. The Braunschweig-Wolfsburg-Salzgitter region had 1.02 million residents including the cities Wolfsburg and Salzgitter, it is the second largest urban center in Lower Saxony after Hanover. The urban agglomeration of Braunschweig had a population of 551,000 with almost 45% having a migration background, making it the most diverse urban agglomeration in the whole Niedersachsen, state. The city consists of 37.5% immigrants (approximately 102,000) with a high amount of migrants coming from other European countries, Asia and Africa. 73% of the Germans residing in Braunschweig come from different parts of the country, particularly North Rhine West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War, fought primarily in Central Europe between 1618 and 1648, was one of the most destructive conflicts in History of Europe, European history. An estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died from battle, famine, or disease, while parts of Germany reported population declines of over 50%. Related conflicts include the Eighty Years' War, the War of the Mantuan Succession, the Franco-Spanish War (1635–1659), Franco-Spanish War, the Torstenson War, the Dutch-Portuguese War, and the Portuguese Restoration War. The war had its origins in the 16th-century Reformation, which led to religious conflict within the Holy Roman Empire. The 1555 Peace of Augsburg attempted to resolve this by dividing the Empire into Catholic and Lutheran states, but the settlement was destabilised by the subsequent expansion of Protestantism beyond these boundaries. Combined with differences over the limits of imperial authority, religion was thus an important factor in star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mühlberg
The Battle of Mühlberg took place near Mühlberg in the Electorate of Saxony in 1547, during the Schmalkaldic War. The Catholic princes of the Holy Roman Empire led by the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V decisively defeated the Lutheran Schmalkaldic League of Protestant princes under the command of Elector John Frederick I of Saxony and Landgrave Philip I of Hesse. The battle ended the Schmalkaldic war and led to the dissolution of the Schmalkaldic League. Background The spread of the Protestant Reformation in Germany after 1517 represented a major obstacle to the universalistic projects of Charles V, the Habsburg emperor. Attempts at reconciliation between Lutherans and Catholics at the diets of Speyer of 1526 and 1529 had failed, sharpening the mutual opposition between the two sides. The Reformation offered to most independent German states the pretext to affirm their autonomy not only on the religious level, but also on the political one. For some of these small st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schmalkaldic League
The Schmalkaldic League (; ; or ) was a military alliance of Lutheranism, Lutheran Prince of the Holy Roman Empire, principalities and cities within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century. It received its name from the town of Schmalkalden, where the group was founded in 1531. Although created for religious motives soon after the start of the Reformation, its members later came to have the intention that the League would replace the Holy Roman Empire as their focus of political allegiance. While it was not the first alliance of its kind, unlike previous formations, such as the League of Torgau, the Schmalkaldic League had a substantial military to defend its political and religious interests. Origins The League was officially established on 27 February 1531 by Philip I, Landgrave of Hesse, and John Frederick I, Elector of Saxony, the two most powerful Protestant rulers in the Holy Roman Empire at the time. It originated as a defensive religious alliance, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |