|
Goslar
Goslar (; Eastphalian dialect, Eastphalian: ''Goslär'') is a historic town in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is the administrative centre of the Goslar (district), district of Goslar and is located on the northwestern wikt:slope, slopes of the Harz mountain range. The Old Town of Goslar with over 1.500 Timber framing, timber houses and the Mines of Rammelsberg are UNESCO World Heritage Sites for their millennium-long testimony to the history of ore mining and their political importance for the Holy Roman Empire and Hanseatic League. Each year Goslar awards the Goslarer Kaiserring, Kaiserring to an international artist, called the "Nobel Prize" of the art world. Geography Goslar is situated in the middle of the upper half of Germany, about south of Braunschweig, Brunswick and about southeast of the state capital, Hannover, Hanover. The Schalke (Harz), Schalke mountain is the highest elevation within the municipal boundaries at . The lowest point of is near the Oker river. Geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Palace Of Goslar
The Imperial Palace of Goslar () is a historical building complex at the foot of the Rammelsberg hill in the south of the town of Goslar north of the Harz mountains, central Germany. It covers an area of about 340 by 180 metres. The palace grounds originally included the ''Kaiserhaus'', the old collegiate church of St. Simon and St. Jude, the palace chapel of St. Ulrich and the Church of Our Lady (''Liebfrauenkirche''). The ''Kaiserhaus'', which has been extensively restored in the late 19th century, was a favourite imperial residence, especially for the Salian emperors. As early as the 11th century, the buildings of the imperial palace had already so impressed the chronicler Lambert of Hersfeld that he described it as the "most famous residence in the empire". Since 1992, the palace site, together with the Goslar's Old Town and the Rammelsberg has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its millennium-long association with mining and testimony to the exchange and advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
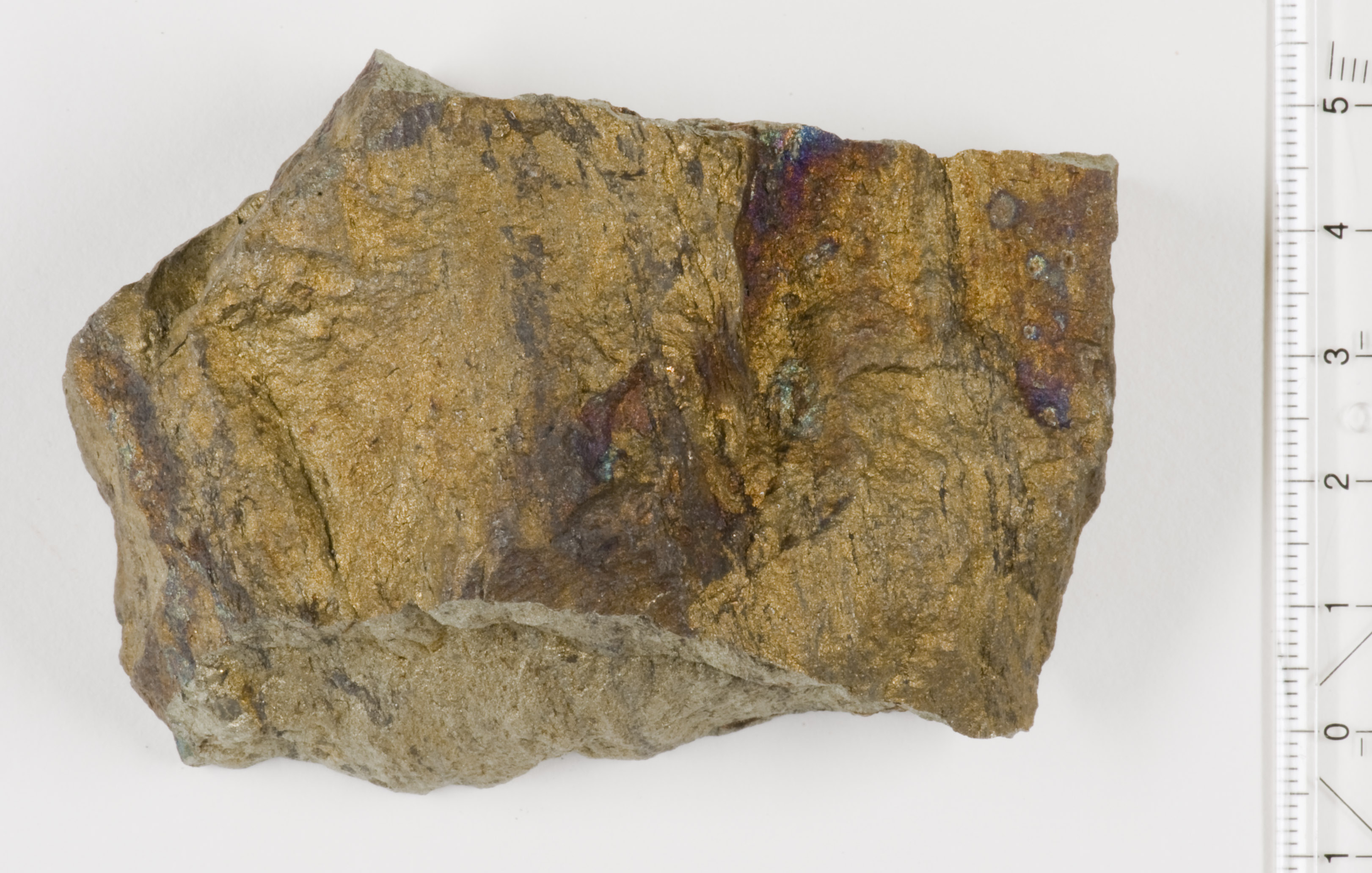
Rammelsberg
The Rammelsberg is a mountain, high, on the northern edge of the Harz range, south of the historic town of Goslar in the North German state of Lower Saxony. The mountain is the location of an important silver, copper, and lead mine. When it closed in 1988, it had been the only mine still working continuously for over 1,000 years. Because of its long history of mining and testimony to the advancement and exchange of technology over many centuries, the visitor mine of Rammelsberg was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1992. Name According to legend, the mountain was named after a knight called "Ramm", who was a henchman of Emperor Otto the Great. In 968, whilst out hunting, the knight tied his horse to a tree, in order to pursue some deer through almost impassable terrain. His charger impatiently pawed the ground with its hooves whilst waiting for his master to return and so exposed a vein of silver ore. According to another explanation, the name may be derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslar (district)
Goslar () is a district in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is bounded by (from the south and clockwise) the districts of Göttingen, Northeim, Hildesheim and Wolfenbüttel, the city of Salzgitter, and by the states of Saxony-Anhalt (district of Harz) and Thuringia ( Nordhausen). History The history of the district is linked with the city of Goslar. The district of Goslar was established in the 19th century by the Prussian government. The city of Goslar did not belong to the district until 1972, when it was eventually incorporated into the district. Langelsheim merged 1 November 2021 with the three municipalities of the Samtgemeinde Lutter am Barenberge, which was abolished. Geography The region comprises the northwestern part of the Harz mountains. The Harz National Park is part of this district. The highest peak is the Wurmberg (971 m) near Braunlage, also being the highest elevation of Lower Saxony. Above the small town of Altenau there is the source of the Oker river, which r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goslarer Kaiserring
Since 1975, the Goslarer Kaiserring award has been given, by the city of Goslar, to a distinguished international artist of modern and contemporary art. The award is for artists whose work has given the contemporary art significant impetus. The prize consists of an aquamarine set in gold, in which the seal of Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor (1050–1106) is engraved. It is made every year by the goldsmith Hadfried Rinke from Worpswede. Recipients Source: * 1975: Henry Moore * 1976: Max Ernst * 1977: Alexander Calder * 1978: Victor Vasarely * 1979: Joseph Beuys * 1980: Jean Tinguely (acceptance refused) * 1981: Richard Serra * 1982: Max Bill * 1983: Günther Uecker * 1984: Willem de Kooning * 1985: Eduardo Chillida * 1986: Georg Baselitz * 1987: Christo * 1988: Gerhard Richter * 1989: Mario Merz * 1990: Anselm Kiefer * 1991: Nam June Paik * 1992: Rebecca Horn * 1993: Roman Opalka * 1994: Bernd and Hilla Becher * 1995: Cy Twombly * 1996: Dani Karavan * 1997: Franz Gertsch * 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harz
The Harz (), also called the Harz Mountains, is a highland area in northern Germany. It has the highest elevations for that region, and its rugged terrain extends across parts of Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Thuringia. The name ''Harz'' derives from the Middle High German word ''Hardt'' or ''Hart'' (hill forest). The name ''Hercynia'' derives from a Celtic name and could refer to other mountain forests, but has also been applied to the geology of the Harz. The Brocken is the highest summit in the Harz with an elevation of above sea level. The Wurmberg () is the highest peak located entirely within the state of Lower Saxony. Geography Location and extent The Harz has a length of , stretching from the town of Seesen in the northwest to Eisleben in the east, and a width of . It occupies an area of , and is divided into the Upper Harz (''Oberharz'') in the northwest, which is up to 800 m high, apart from the 1,100 m high Brocken massif, and the Lower Harz (''Unterhar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
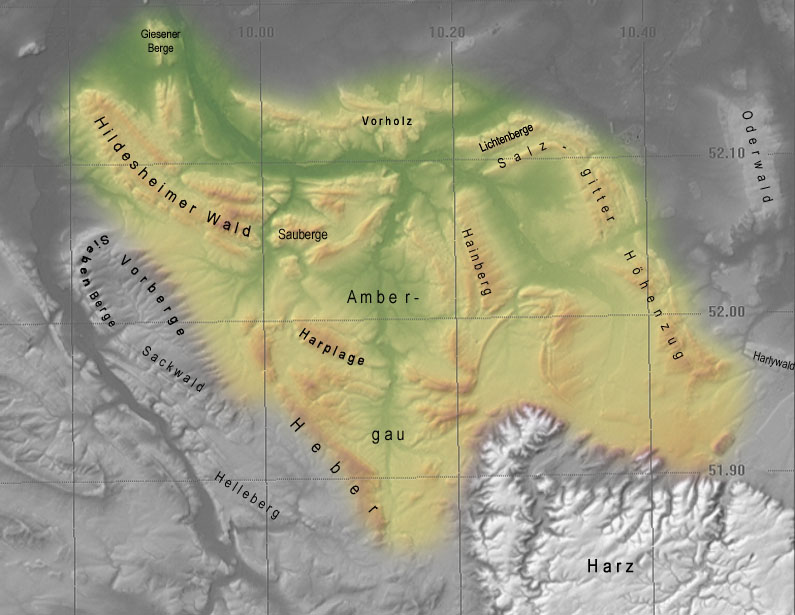
Salzgitter Hills
The Salzgitter Hills (, also ''Salzgitterscher Höhenzug'') is an area of upland up to in height, in the Lower Saxon Hills between Salzgitter and Goslar in the districts of Landkreis Wolfenbüttel, Wolfenbüttel and Landkreis Goslar, Goslar and in the territory of the independent town of Salzgitter. The hills lie in the German federal state of Lower Saxony. The German name of is a term used in the northern Harz Foreland, albeit not found on maps, and is used to mean the string of hills north of the Harz Mountains between the towns mentioned above. The state forest of the Salzgitter Hills is managed by several Lower Saxony forestry offices, including the in Salzgitter-Salder. The Salzgitter Hills can be divided into these four unnamed sections: * Northwest section (mainly comprising the Lichtenberge)(up to 254.2 m high; between Holle and Salzgitter-Gebhardshagen) * North-central section(up to 275.3 m high; between Salzgitter-Gebhardshagen and Salzgitter-Bad) * South-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony is a States of Germany, German state (') in Northern Germany, northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ' of the Germany, Federal Republic of Germany. In rural areas, Northern Low Saxon and Saterland Frisian language, Saterland Frisian are still spoken, though by declining numbers of people. Lower Saxony borders on (from north and clockwise) the North Sea, the states of Schleswig-Holstein, Hamburg, , Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, Hesse and North Rhine-Westphalia, and the Netherlands. Furthermore, the Bremen (state), state of Bremen forms two enclaves within Lower Saxony, one being the city of Bremen, the other its seaport, Bremerhaven (which is a semi-exclave, as it has a coastline). Lower Saxony thus borders more neighbours than any other single '. The state's largest cities are the state capital Hanover, Braunschweig (Brunswick), Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the late 12th century, the League expanded between the 13th and 15th centuries and ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across eight modern-day countries, ranging from Tallinn in Estonia in the east, Bergen (Bjørgvin) in Norway to the North to the Netherlands in the west, and extended inland as far as Cologne, Prussia (region), the Prussian regions and Kraków, Poland. The League began as a collection of loosely associated groups of German traders and towns aiming to expand their commercial interests, including protection against robbery. Over time, these arrangements evolved into the League, offering traders toll privileges and protection on affiliated territory and trade routes. Economic interdependence and familial connections am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oker
The Oker () is a river in Lower Saxony, Germany, that has historically formed an important political boundary. It is a left tributary of the River Aller (Germany), Aller, in length and runs in a generally northerly direction. Origin and meaning of the name The river's name was recorded around 830 as ''Obacra'' and, later, as ''Ovokare'' und ''Ovakara''.H. Blume: ''Oker, Schunter, Wabe.'' In: ''Braunschweigisches Jahrbuch für Landesgeschichte'', vol. 86, 2005, p. 14 sqq. The origin of the name is derived from the root (linguistics), roots ''ov-'' and ''-akara'' meaning “upper” (cf. New High German ''ober-'') and “onward rushing” (rendered in German as “Vorwärtsdrängende”) as distinct from its tributary, the Ecker, whose name means only “onward rushing”. Course The Oker rises at about 910 metres in the Harz National Park in a boggy area on the Bruchberg in the Harz mountains of Central Germany (geography), central Germany. This early section is known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Harz Water Regale
The Upper Harz Water Regale (, ) is a system of dams, reservoirs, ditches and other structures, much of which was built from the 16th to 19th centuries to divert and store the water that drove the water wheels of the mines in the Upper Harz region of Germany. The term ''regale'', here, refers to the granting of royal privileges or rights (''droit de régale'') in this case to permit the use of water for mining operations in the Harz mountains of Germany. The Upper Harz Water Regale is one of the largest and most important historic mining water management systems in the world. The facilities developed for the generation of water power have been placed under protection since 1978 as cultural monuments. The majority are still used, albeit nowadays their purpose is primarily to support rural conservation (the preservation of a historic cultural landscape), nature conservation, tourism and swimming. From a water management perspective, several of the reservoirs still play a role in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schalke (Harz)
The Schalke is a mountain, , in the Upper Harz in the German state of Lower Saxony. It lies in Goslar district north of Clausthal-Zellerfeld and west of Schulenberg im Oberharz, Schulenberg. From 1959 there was a French listening post on the summit, which was supplemented in 1968 by a 64 m high concrete tower. This tower stood empty from 1993 and was demolished on 11 October 2002; the entire facility being removed in September 2003. Other listening posts in the Harz were located on the Wurmberg (Harz), Wurmberg and the Stöberhai. Towers that still exist include those on the Ravensberg (Harz), Ravensberg and the Bocksberg (Harz), Bocksberg, the latter not far from the Schalke. The observation tower, which was about 10.5 m high, stood about 50 metres southeast of the listening post until 2002 and, following the demolition of the latter, was moved back to its original site on the summit. However it only has good views towards the east and south. The view extends from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |