|
Leverhulmia
''Leverhulmia'' is an extinct genus of probable hexapod, known from a single partial specimen with preserved gut contents, found in the Windyfield (Rhynie) chert. Description ''Leverhulmia'' is an arthropod roughly long, with at least five pairs of uniramous limbs, split into six podomeres, and an unknown number of segments. As the head is not preserved, it could not be firmly classified into or excluded from any group within Myriapoda, although a position within Diplopoda, or as a relative of ''Kampecaris'', was hypothesised. Therefore, it was classed as Myriapoda ''incertae sedis''. A later paper suggests it was a hexapod, specifically a relative of Zygentoma or Archaeognatha instead, after the discovery of thoracic leg segments which suggest the type specimen is part of the abdomen. Unlike '' Rhyniognatha'' and '' Strudiella'', its interpretation as insect is not questioned yet, but it is not easy to interpret. Etymology ''Leverhulmia'' is named after the Leverhul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynie Chert
The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian Sedimentary rock, sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness (a Lagerstätte). It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located some 700 m away. The Rhynie chert contains exceptionally preserved plant, fungus, lichen and animal material preserved in place by an overlying Volcanic rock, volcanic deposit. The bulk of the Devonian fossil bed consists of primitive plants (which had xylem, water-conducting cells and spores, sporangia, but no true leaf, leaves), along with arthropods, lichens, algae and fungi. This fossil bed is remarkable for two reasons. First, the age of the site (Pragian, Early Devonian, formed about ) places it at an early stage in the colonisation of land. Second, these cherts are famous for their exceptional state of ultrastructure, ultrastructural preservation, with individual cell walls easily visible in polished specimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strudiella
''Strudiella devonica'' is a species of extinct arthropod from the Devonian.Garrouste, Romain; Clément, Gaël; Nel, Patricia; Engel, Michael S.; Grandcolas, Philippe; D’Haese, Cyrille; Lagebro, Linda; Denayer, Julien; Gueriau, Pierre; Lafaite, Patrick; Olive, Sébastien; Prestianni, Cyrille; Nel, André (2012). "A complete insect from the Late Devonian period". Nature. 488 (7409): 82–85. , It was recovered in the Strud (Gesves, Belgium) environment from the Bois des Mouches Formation, Upper Famennian. It was originally described as the first complete Late Devonian terrestrial insect, but due to its poor state of preservation, its affinity is discussed. Description ''Strudiella'' is known from a single specimen. It is a small arthropod with length about . Structures like antennae and a number of pairs of legs can be seen. Due to the poorly preserved nature of this fossil, its interpretation and classification depend on the authors. Garrouste et al. (2012) In the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
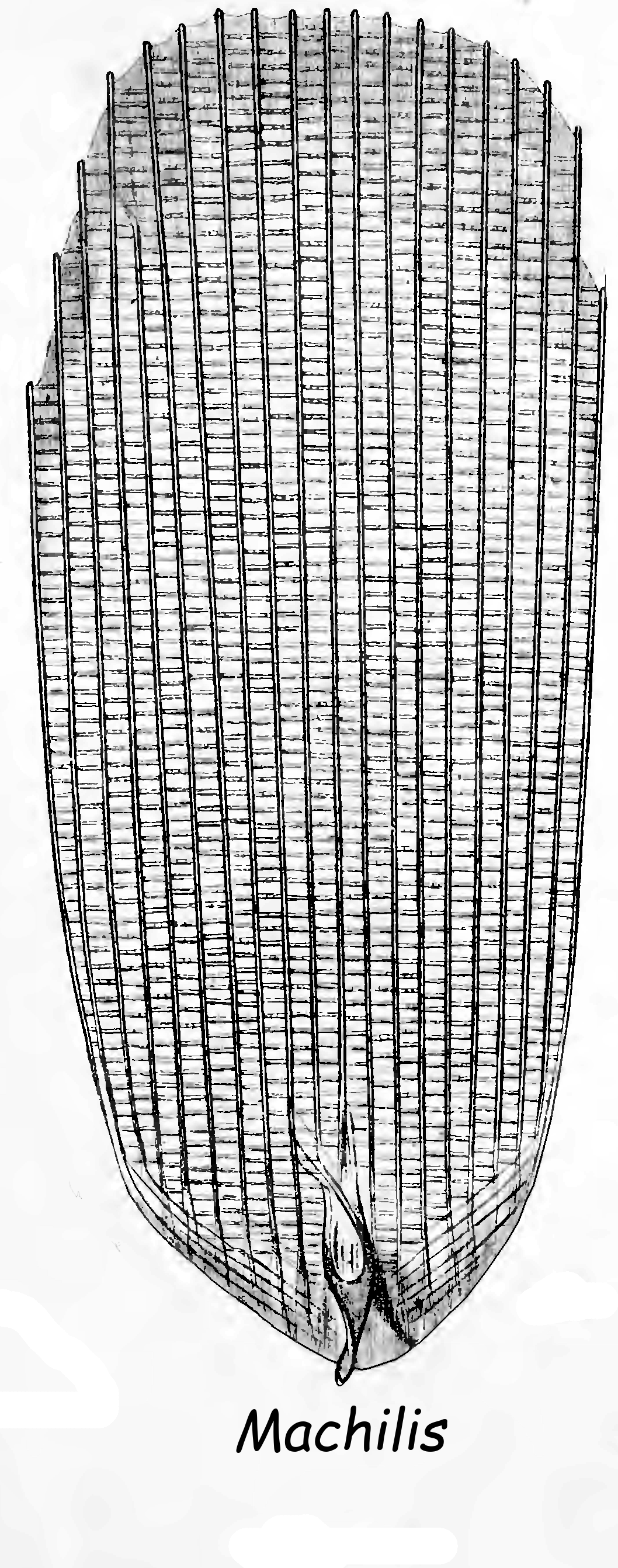
Zygentoma
Zygentoma are an order in the class Insecta, and consist of about 550 known species. The Zygentoma include the so-called silverfish or fishmoths, and the firebrats. A conspicuous feature of the order are the three long caudal filaments. The two lateral filaments are cerci, and the medial one is an epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. In this they resemble the Archaeognatha, although the cerci of Zygentoma, unlike in the latter order, are nearly as long as the epiproct. Until the late twentieth century the Zygentoma were regarded as a suborder of the Thysanura, until it was recognized that the order Thysanura was paraphyletic, thus raising the two suborders to the status of independent monophyletic orders, with Archaeognatha as sister group to the Dicondylia, including the Zygentoma. Etymology The name "Zygentoma" is derived from the Greek ('), in context meaning "yoke" or "bridge"; and ('), "insects" (literally meaning "cut into", in reference to the segmented anatomy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Devonian
The Early Devonian is the first of three Epoch (geology), epochs comprising the Devonian period, corresponding to the Lower Devonian Series (stratigraphy), series. It lasted from and began with the Lochkovian Stage , which was followed by the Pragian from and then by the Emsian, which lasted until the Middle Devonian began, . During this time, the first Ammonoidea, ammonoids appeared, descending from Bactritida, bactritoid Nautiloidea, nautiloids. Ammonoids during this time period were simple and differed little from their nautiloid counterparts. These ammonoids belong to the order Agoniatitida, which in later epochs evolved to new ammonoid orders, for example Goniatite, Goniatitida and Clymeniida. This class of cephalopod molluscs would dominate the marine fauna until the beginning of the Mesozoic Era. References Early Devonian, Geological epochs Devonian geochronology, *01 {{Geochronology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian Arthropods Of Europe
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago ( Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at Ma. It is the fourth period of both the Paleozoic and the Phanerozoic. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant evolutionary radiation of life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free- sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants ( pteridospermatophytes) appeared. This rapid evolution and colonization process, which had begun during the Silurian, is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enigmatic Arthropod Taxa
Enigmatic is an adjective meaning "mysterious" or "puzzling". It may also refer to: * ''Enigmatic'' (album), a 1970 album by Czesław Niemen * '' Enigmatic: Calling'', a 2005 album by Norwegian progressive metal band Pagan's Mind * Enigmatic scale, musical scale used by Verdi and others * "The Enigmatic", a song by Joe Satriani on the album '' Not of This Earth'' See also * Enigmatic leaf turtle, a species of Asian leaf turtle * Enigmatic moray eel, a species found in the Pacific and Indian Oceans * ''Glaresis ''Glaresis'' is a genus of beetles, sometimes called "Enigmatic scarab beetles", in its own family, Glaresidae. It is closely related to, and was formerly included in, the family Scarabaeidae. Although its members occur in arid and sandy areas wo ...'', a genus of beetles sometimes called "enigmatic scarab beetles" * Enigma (other) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detritivore
Detritivores (also known as detrivores, detritophages, detritus feeders or detritus eaters) are heterotrophs that obtain nutrients by consuming detritus (decomposing plant and animal parts as well as feces). There are many kinds of invertebrates, vertebrates, and plants that eat detritus or carry out coprophagy. By doing so, all these detritivores contribute to decomposition and the nutrient cycles. Detritivores should be distinguished from other decomposers, such as many species of bacteria, fungi and protists, which are unable to ingest discrete lumps of matter. Instead, these other decomposers live by absorbing and metabolizing on a molecular scale (saprotrophic nutrition). The terms ''detritivore'' and ''decomposer'' are often used interchangeably, but they describe different organisms. Detritivores are usually arthropods and help in the process of remineralization. Detritivores perform the first stage of remineralization, by fragmenting the dead plant matter, allowing decomp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus (: fungi , , , or ; or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as one of the kingdom (biology)#Six kingdoms (1998), traditional eukaryotic kingdoms, along with Animalia, Plantae, and either Protista or Protozoa and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of motility, mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leverhulme Trust
The Leverhulme Trust () is a large national grant-making organisation in the United Kingdom. It was established in 1925 under the will of the 1st Viscount Leverhulme (1851–1925), with the instruction that its resources should be used to cover certain trade charities and support "scholarships for the purposes of research and education." Over time, it has come to focus on the latter aim. The Trust is based in London and is a registered charity under English law. The current Chair of the Trust is Alan Jope CBE. Activities Since its foundation in 1925, the Trust has provided funding for research projects, fellowships, studentships, bursaries and prizes. It operates across all academic disciplines with the intention of supporting individuals in research and professional training. Dispensing over £100 million a year, the Trust is one of the largest providers of research funding in the UK. The Trust places special weight on: * the originality of the projects put to them; * th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeognatha
The Archaeognatha are an order of apterygotes, known by various common names such as jumping bristletails. Among extant insect taxa they are some of the most evolutionarily primitive; they appeared in the Middle Devonian period at about the same time as the arachnids. Specimens that closely resemble extant species have been found as both body and trace fossils (the latter including body imprints and trackways) in strata from the remainder of the Paleozoic Era and more recent periods. For historical reasons an alternative name for the order is Microcoryphia. Until the late 20th century the suborders Zygentoma and Archaeognatha comprised the order Thysanura; both orders possess three-pronged tails comprising two lateral cerci and a medial epiproct or ''appendix dorsalis''. Of the three organs, the appendix dorsalis is considerably longer than the two cerci; in this the Archaeognatha differ from the Zygentoma, in which the three organs are subequal in length. In the late 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyniognatha
''Rhyniognatha'' is an extinct genus of arthropod of disputed placement. It has been considered in some analyses as the oldest insect known, as well as possibly being a flying insect. ''Rhyniognatha'' is known from a partial head with preserved mouthparts from the Early Devonian aged Rhynie chert around 400 million years ago, when Earth’s first terrestrial ecosystems were being formed. The type, and only species is ''R. hirsti'', which was named and described in 1928.R. J. Tillyard. 1928. Some remarks on the Devonian fossil insects from the Rhynie chert beds, Old Red Sandstone. ''Transactions of the Entomological Society of London'' 76:65-71 Other analyses have interpreted the specimen as a myriapod. Evidence The head part of a specimen, preserved in a fragment of Rhynie Chert, was collected in 1919 by the Reverend W. Cran, who provided it to S. Hirst, Samarendra Maulik and D.J. Scourfield. Hirst and Maulik published a report in 1926; in it they described ''Rhyniella praecurs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapoda
The subphylum Hexapoda (from Greek for 'six legs') or hexapods comprises the largest clade of arthropods and includes most of the extant arthropod species. It includes the crown group class Insecta (true insects), as well as the much smaller clade Entognatha, which includes three classes of wingless arthropods that were once considered insects: Collembola (springtails), Protura (coneheads) and Diplura (two-pronged bristletails). The insects and springtails are very abundant and are some of the most important pollinators, basal consumers, scavengers/ detritivores and micropredators in terrestrial environments. Hexapods are named for their most distinctive feature: a three-part body plan with a consolidated thorax and three pairs of legs. Most other arthropods have more than three pairs of legs. Most recent studies have recovered Hexapoda as a subgroup of Pancrustacea. Morphology Hexapods have bodies ranging in length from 0.5 mm to over 300 mm which are divided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |