|
Levantine Bronze Age
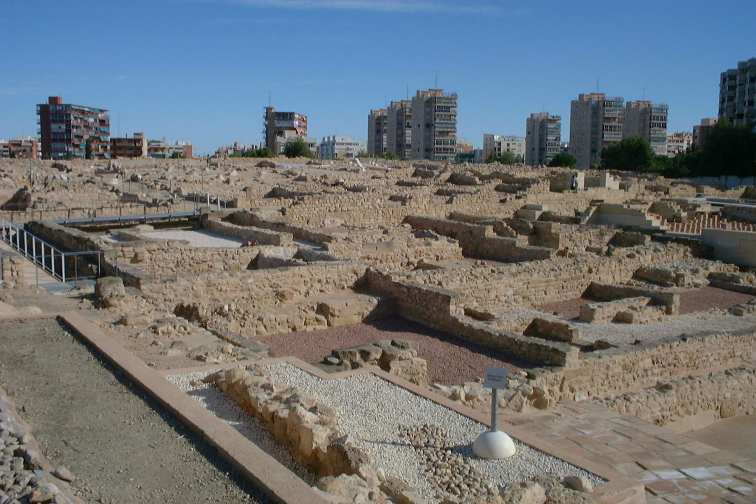
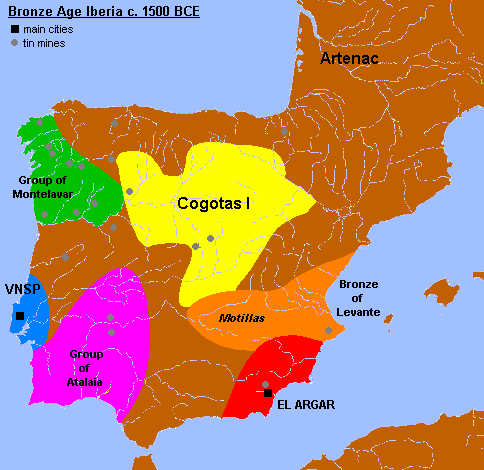
Named after its regional range, the Levantine Bronze Age (or Bronze of Levant, or Valencian Bronze) refers to a culture extended over the actual territory of the Valencian Community, in the "Levante" or eastern side of the Iberian peninsula. Its chronological range was between 2200 BC and 1500 BC. It is considered an autonomous culture in relation to the Argaric culture by Miquel Tarradell in the sixties. The main aspects that allow the distinction of the Valencian Bronze from that of El Argar are the scarcity of metallic objects, the lack of carinated cups and ceramics, and the lack of the rite involving the inhumation of the deceased under its home floor. The economy was involved mainly in agriculture and herding. The metallurgy was much more developed in the southern part by the influence of the near Argaric culture. Oppida were defended by natural elements, tenches, walls and towers. The houses were rectangular and the walls had stone basements. Caves were used as funera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Europe and the fourth-most populous European Union member state. Spanning across the majority of the Iberian Peninsula, its territory also includes the Canary Islands, in the Eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Balearic Islands, in the Western Mediterranean Sea, and the Autonomous communities of Spain#Autonomous cities, autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla, in mainland Africa. Peninsular Spain is bordered to the north by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; to the east and south by the Mediterranean Sea and Gibraltar; and to the west by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean. Spain's capital and List of largest cities in Spain, largest city is Madrid, and other major List of metropolitan areas in Spain, urban areas include Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Bronze Age
The Atlantic Bronze Age is a term that has never been formally defined. Some take its meaning to be a label for the period spanning approximately 1300–700 BC in Britain, France, Ireland, Portugal and Spain; that is, the Atlantic coast of Europe. Others assign it to a cultural complex of the Bronze Age period in prehistoric Europe that is defined by the culture prevalent at this time and location. Trade The Atlantic Bronze Age is characterized by economic and cultural exchange between far-flung communities, resulting in a high degree of cultural similarity seen in coastal communities ranging from central Portugal in the south of coastal Europe, through Galicia (Spain), the Atlantic coast of France, including Armorica (Brittany) to Cornwall in southwest England and as far north as Scotland. This is evidenced by the frequent use of stone as chevaux-de-frise, the construction of cliff castles, and a similarity of domestic architecture and living spaces, sometimes characterize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures In Spain
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves Survey (archaeology), surveying, Archaeological excavation, excavation, and eventually Post excavation, analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Cultures Of Europe
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloids (such as arsenic or silicon). These additions produce a range of alloys some of which are harder than copper alone or have other useful properties, such as ultimate tensile strength, strength, ductility, or machinability. The three-age system, archaeological period during which bronze was the hardest metal in widespread use is known as the Bronze Age. The beginning of the Bronze Age in western Eurasia is conventionally dated to the mid-4th millennium BCE (~3500 BCE), and to the early 2nd millennium BCE in China; elsewhere it gradually spread across regions. The Bronze Age was followed by the Iron Age, which started about 1300 BCE and reaching most of Eurasia by about 500 BCE, although bronze continued to be much more widely used than it is in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Valencian Community
The Valencian Community is an autonomous community of Spain. It is the fourth most populous Spanish autonomous community after Andalusia, Catalonia and the Community of Madrid with more than five million inhabitants.Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Madrid, 2020. Its eponymous capital Valencia is the third largest city and metropolitan area in Spain. It is located along the Mediterranean coast on the east side of the Iberian Peninsula. It borders Catalonia to the north, Aragon and Castilla–La Mancha to the west, and Murcia to the south, and the Balearic Islands are to its east. The Valencian Community is divided into three provinces: Castellón, Valencia and Alicante. According to Valencia's Statute of Autonomy, the Valencian people are a '' "historical nationality"''. Their origins date back to the 1238 Aragonese conquest of the Taifa of Valencia. The newly-founded Kingdom of Valencia enjoyed its own legal entity and administrative institutions as a component of the Crown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Raboses
The archaeological site of Les Raboses is located on the mountain with the same name in the municipality of Albalat dels Tarongers (Baix Palancia). This deposit is framed chronologically in the Bronze Age. History The site was found by the prospecting works carried out in the 1940s, by Andrés Monzo Nogues. The materials found in these surveys are being investigated and preserved by the '' Servicio de Investigación Prehistórica'' (SIP) de Valencia. The site was prospected and excavated again in 1987-89 by Eva Ripollés. Location and environment The site of Les Raboses is inside the Camp de Morvedre region. Its location, on a hilltop is characteristic of the Bronze Age culture. Its environment is hilly and also frames the Palancia river basin, which has served as a communication hub between the interior and the coast since ancient times. It is delimited by the Garbí on the west and the mountains of Sant Esperit on the east. Their lithologies are formed by limestone ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloma De Betxí
The Lloma de Betxí is a Bronze Age archaeological site in the municipality of Paterna (Valencian Community (Spain). It is on the top of a hill at 99m over the sea level and 30m over the surroundings. It is in the county of Paterna, nearby the Turia river, close to Valencia city. The chronology of the site: 1800 – 1300 B.C., part of the Valencian Bronze Age. Historiography and Excavation The first information about the site appeared in 1928 and the author was Gómez Serrano. The next reference was included in the Enciclopedia de la Región Valenciana, in 1973. The first excavation was carried out in 1984 by Helena Bonet, Joan Bernabeu and María Jesús de Pedro. The excavations continued since 1985, under the management of María Jesús de Pedro, and ended in 2013. The recovered material was placed into the Museo de Prehistoria and Servicio de Investigación Prehistórica of the Valencian government. Chronology Establishing the time frames for the Valencian Bronze Age is di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenean Bronze
The Pyrenean Bronze (also known as Northeastern Bronze) is a regional European Bronze Age culture, known from archaeological facies, that spread through the Spanish provinces of Girona, Barcelona, Lleida and the eastern half of Huesca; also it spread through the French departments of the Pyrenees-Orientales and Aude. From the Bell Beaker culture (2750-2300 BC), two regional styles appeared in Catalonia, one being the Pyrenean and the other the Salomó (from which the North-East Group was derived). These two styles coexisted at the same time in the provinces of Barcelona and the south of Lleida. From 1650 A.C. the Pyrenean ceramic style gave way to carinated cups, to pots with smooth or digitated cords, as well as to vessels with button appendages on the handle. Few settlements are known: Lo Lladre (Llo, Pyrenees-Orientales), Collet de Brics (Ardèvol, Lleida), Institut A. Pous (Manlleu, Barcelona), Roques del Sarró (Lleida), Cedre (Santa Coloma, Andorra). Advanced bronze met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motillas
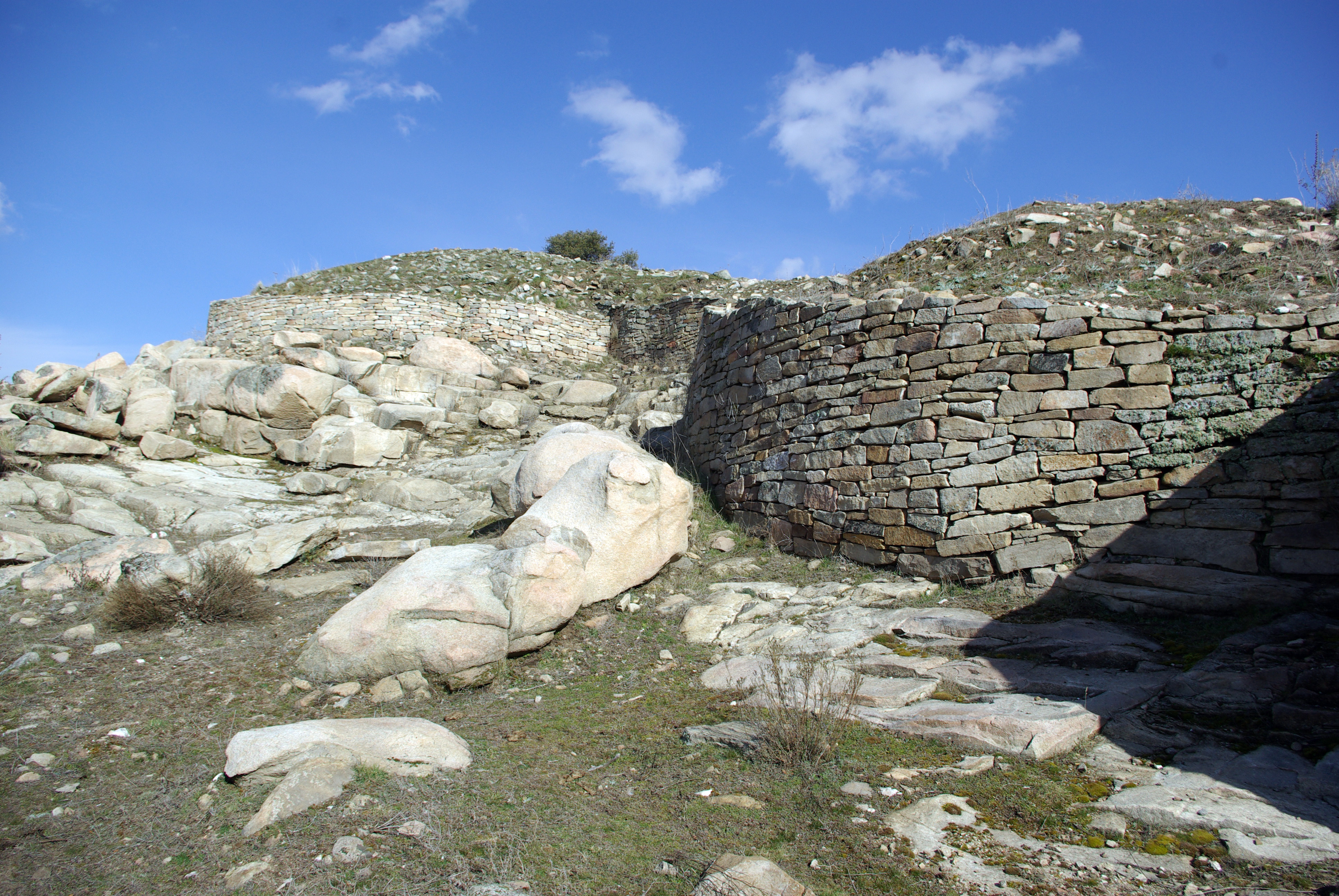
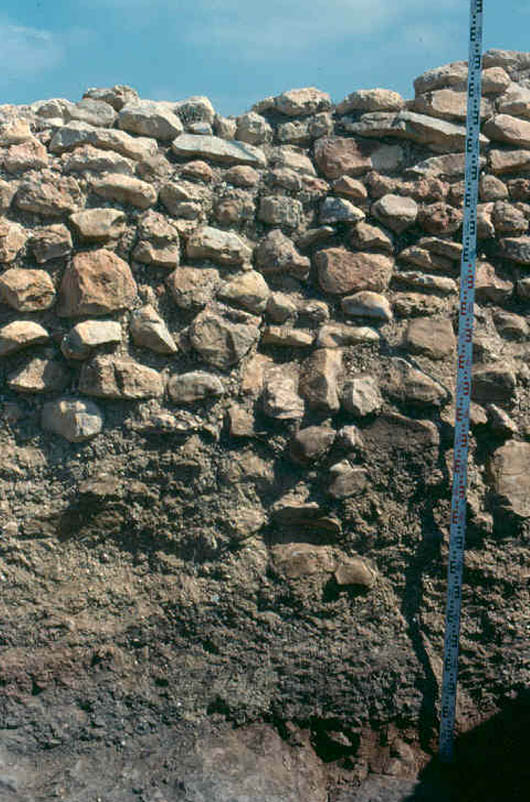
The ''motillas'' were the early settlements of La Mancha (Spain) belonging to the Middle Bronze Age, and connected to the Bronze of Levante culture. These were human-made hills atop of which are placed fortified settlements. Their height is usually between four and five meters and the ''motillas'' are separated from each other by a distance of four to five kilometers. Their construction started BCE and they were used for about 1000 years. History of research The ''motillas'' were first believed to be antique burial mounds. However, this hypothesis was ruled out when an excavation at the Motilla del Azuer that took place in the seventies proved their defensive and management faculties. This way, a wide area could be controlled easily. Some similar sites in the foothills of Sierra Morena mountains are fortified towns of larger size. Construction and use The ''motillas'' were constructed in the period of BCE–1200 BCE. Their use started at the time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Cogotas
Las Cogotas () is an archaeological site in Spain in Cardenosa municipality, province of Avila. The site was researched by the Galician archaeologist Juan Cabré in 1920s. It is namesake for two different archaeological cultures known from this site: Cogotas I (pre-Celtic) of the Late Bronze Age and Cogotas II (most probably Celtic) of the Iron Age. The latter is known from the upper layer of Las Cogotas, which represents a classical settlement of Vettones, which inhabited the territory of modern provinces of Avila and Salamanca, as well as parts of Toledo, Zamora, Cáceres and Tras-os-Montes in Portugal. Protocogotas culture This stage of the Meseta history is the least known, although a series of archeological sites, such as ''Los Tolmos de Caracena'' in Soria, Cogeces del Monte in Valladolid, Abia de la Obispalia in Cuenca, and some others, allow to describe Protocogotas culture as a formation stage of Cogotas I culture. This culture, which existed around 1700� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muntanya Assolada
Muntanya Assolada is a Bronze Age settlement located on the right bank of the Xúquer river, in Spain, built on the top of a spur of the Corbera mountain range, dominating the river plain from a height of above sea level. It is located in the municipality of Alzira, Valencia, Spain. Excavation campaigns began in 1978, under the direction of Bernat Martí Oliver, and continued until 1996, and work on the site was resumed in 2004. From the 1990s Rosa Enguix Alemany and María Jesús de Pedro joined the direction of the site. At present the excavated area covers and includes different structures, like a central street and rectangular departments on both sides; a wall of two meters wide that preserves almost three meters of height (); occupancy soils and abandonment episodes; livestock stabling; and terracing of the slopes to expand its surface. At present the site is property of the Alzira City council, and the new beginning of the excavations by the Servei d'Investigació Prehistò ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |