|
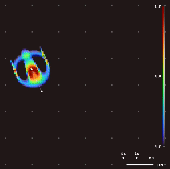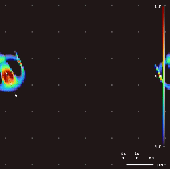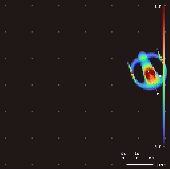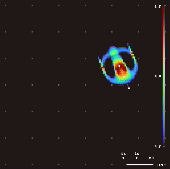
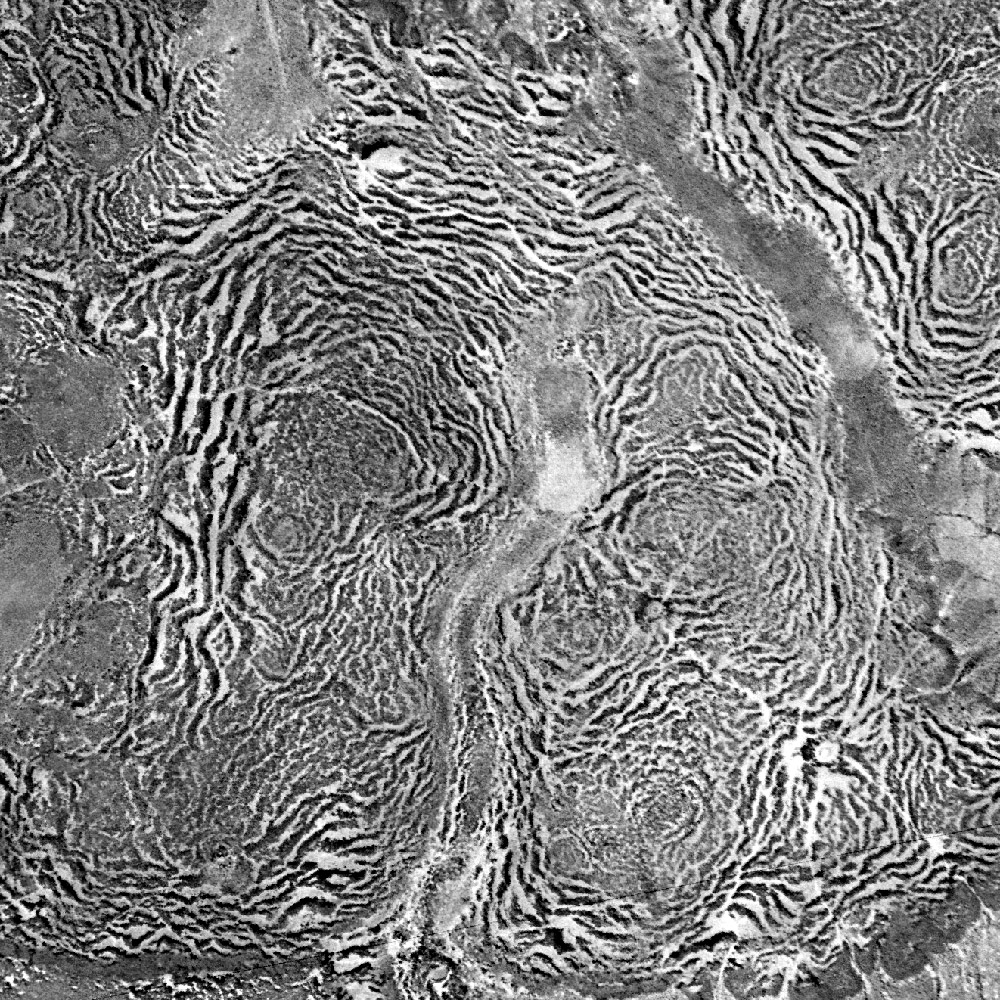
Lenia
Lenia is a family of cellular automaton, cellular automata created by Bert Wang-Chak Chan. It is intended to be a Continuous function, continuous generalization of Conway's Game of Life, with Continuous automaton, continuous states, Continuous spatial automaton, space and time. As a consequence of its continuous, high-resolution domain, the complex autonomous patterns ("lifeforms" or "Spaceship (cellular automaton), spaceships") generated in Lenia are described as differing from those appearing in other cellular automata, being "geometric, Metamerism (biology), metameric, fuzzy, resilient, adaptive, and rule-generic". Lenia won the 2018 Virtual Creatures Contest at the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference in Kyoto, an honorable mention for the ALIFE Art Award at ALIFE 2018 in Tokyo, and Outstanding Publication of 2019 by the International Society for Artificial Life (ISAL). Rules Iterative updates Let \mathcal be the ''lattice'' or ''grid'' containing a set of stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenia Species
Lenia is a family of cellular automata created by Bert Wang-Chak Chan. It is intended to be a continuous generalization of Conway's Game of Life, with continuous states, space and time. As a consequence of its continuous, high-resolution domain, the complex autonomous patterns ("lifeforms" or " spaceships") generated in Lenia are described as differing from those appearing in other cellular automata, being "geometric, metameric, fuzzy, resilient, adaptive, and rule-generic". Lenia won the 2018 Virtual Creatures Contest at the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference in Kyoto, an honorable mention for the ALIFE Art Award at ALIFE 2018 in Tokyo, and Outstanding Publication of 2019 by the International Society for Artificial Life (ISAL). Rules Iterative updates Let \mathcal be the ''lattice'' or ''grid'' containing a set of states S^\mathcal. Like many cellular automata, Lenia is updated iteratively; each output state is a pure function of the previous state, such tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lenia Icon4
Lenia is a family of cellular automata created by Bert Wang-Chak Chan. It is intended to be a continuous generalization of Conway's Game of Life, with continuous states, space and time. As a consequence of its continuous, high-resolution domain, the complex autonomous patterns ("lifeforms" or " spaceships") generated in Lenia are described as differing from those appearing in other cellular automata, being "geometric, metameric, fuzzy, resilient, adaptive, and rule-generic". Lenia won the 2018 Virtual Creatures Contest at the Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference in Kyoto, an honorable mention for the ALIFE Art Award at ALIFE 2018 in Tokyo, and Outstanding Publication of 2019 by the International Society for Artificial Life (ISAL). Rules Iterative updates Let \mathcal be the ''lattice'' or ''grid'' containing a set of states S^\mathcal. Like many cellular automata, Lenia is updated iteratively; each output state is a pure function of the previous state, such that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Function
In mathematics, a radial function is a real-valued function defined on a Euclidean space R''n'' whose value at each point depends only on the distance between that point and the origin. The distance is usually the Euclidian distance. For example, a radial function Φ in two dimensions has the form :\Phi(x,y) = \varphi(r), \quad r = \sqrt where φ is a function of a single non-negative real variable. Radial functions are contrasted with spherical functions, and any descent function (e.g., continuous and rapidly decreasing) on Euclidean space can be decomposed into a series consisting of radial and spherical parts: the solid spherical harmonic expansion. A function is radial if and only if it is invariant under all rotations leaving the origin fixed. That is, ''ƒ'' is radial if and only if :f\circ \rho = f\, for all , the special orthogonal group in ''n'' dimensions. This characterization of radial functions makes it possible also to define radial distributions. These are di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Formation
The science of pattern formation deals with the visible, (statistically) orderly outcomes of self-organization and the common principles behind similar patterns in nature. In developmental biology, pattern formation refers to the generation of complex organizations of cell fates in space and time. The role of genes in pattern formation is an aspect of morphogenesis, the creation of diverse anatomies from similar genes, now being explored in the science of evolutionary developmental biology or evo-devo. The mechanisms involved are well seen in the anterior-posterior patterning of embryos from the model organism ''Drosophila melanogaster'' (a fruit fly), one of the first organisms to have its morphogenesis studied, and in the eyespots of butterflies, whose development is a variant of the standard (fruit fly) mechanism. Patterns in nature Examples of pattern formation can be found in biology, physics, and science, and can readily be simulated with computer graphics, as desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-replication
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and can be transmitted to offspring during reproduction. Biological viruses can replicate, but only by commandeering the reproductive machinery of cells through a process of infection. Harmful prion proteins can replicate by converting normal proteins into rogue forms. Computer viruses reproduce using the hardware and software already present on computers. Self-replication in robotics has been an area of research and a subject of interest in science fiction. Any self-replicating mechanism which does not make a perfect copy (mutation) will experience genetic variation and will create variants of itself. These variants will be subject to natural selection, since some will be better at surviving in their current environment than others and will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Automaton
A cellular automaton (pl. cellular automata, abbrev. CA) is a discrete model of computation studied in automata theory. Cellular automata are also called cellular spaces, tessellation automata, homogeneous structures, cellular structures, tessellation structures, and iterative arrays. Cellular automata have found application in various areas, including physics, theoretical biology and microstructure modeling. A cellular automaton consists of a regular grid of ''cells'', each in one of a finite number of '' states'', such as ''on'' and ''off'' (in contrast to a coupled map lattice). The grid can be in any finite number of dimensions. For each cell, a set of cells called its ''neighborhood'' is defined relative to the specified cell. An initial state (time ''t'' = 0) is selected by assigning a state for each cell. A new ''generation'' is created (advancing ''t'' by 1), according to some fixed ''rule'' (generally, a mathematical function) that determines the new state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recurrent Neural Network
A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a class of artificial neural networks where connections between nodes can create a cycle, allowing output from some nodes to affect subsequent input to the same nodes. This allows it to exhibit temporal dynamic behavior. Derived from feedforward neural networks, RNNs can use their internal state (memory) to process variable length sequences of inputs. This makes them applicable to tasks such as unsegmented, connected handwriting recognition or speech recognition. Recurrent neural networks are theoretically Turing complete and can run arbitrary programs to process arbitrary sequences of inputs. The term "recurrent neural network" is used to refer to the class of networks with an infinite impulse response, whereas "convolutional neural network" refers to the class of finite impulse response. Both classes of networks exhibit temporal dynamic behavior. A finite impulse recurrent network is a directed acyclic graph that can be unrolled and replace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolutional Neural Network
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of artificial neural network (ANN), most commonly applied to analyze visual imagery. CNNs are also known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Networks (SIANN), based on the shared-weight architecture of the convolution kernels or filters that slide along input features and provide translation- equivariant responses known as feature maps. Counter-intuitively, most convolutional neural networks are not invariant to translation, due to the downsampling operation they apply to the input. They have applications in image and video recognition, recommender systems, image classification, image segmentation, medical image analysis, natural language processing, brain–computer interfaces, and financial time series. CNNs are regularized versions of multilayer perceptrons. Multilayer perceptrons usually mean fully connected networks, that is, each neuron in one layer is connected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cellular Automata And Convnets
Cellular may refer to: *Cellular automaton, a model in discrete mathematics *Cell biology, the evaluation of cells work and more * ''Cellular'' (film), a 2004 movie *Cellular frequencies, assigned to networks operating in cellular RF bands *Cellular manufacturing *Cellular network, cellular radio networks * U.S. Cellular Field, also known as "The Cell", a baseball stadium in Chicago * U.S. Cellular Arena, an arena in Milwaukee, Wisconsin Terms such as cellular organization, cellular structure, cellular system, and so on may refer to: *Cell biology, the evaluation of how cells work and more *Cellular communication networks, systems for allowing communication through mobile phones and other mobile devices *Cellular organizational structures, methods of human organization in social groups *Clandestine cell organizations A clandestine cell system is a method for organizing a group of people (such as resistance fighters, sleeper agents, mobsters, or terrorists) such that such p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonic Function
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if and only if it is either entirely non-increasing, or entirely non-decreasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is called ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Function
In artificial neural networks, the activation function of a node defines the output of that node given an input or set of inputs. A standard integrated circuit can be seen as a digital network of activation functions that can be "ON" (1) or "OFF" (0), depending on input. This is similar to the linear perceptron in neural networks. However, only ''nonlinear'' activation functions allow such networks to compute nontrivial problems using only a small number of nodes, and such activation functions are called nonlinearities. Classification of activation functions The most common activation functions can be divided in three categories: ridge functions, radial functions and fold functions. An activation function f is saturating if \lim_ , \nabla f(v), = 0. It is nonsaturating if it is not saturating. Non-saturating activation functions, such as ReLU, may be better than saturating activation functions, as they don't suffer from vanishing gradient. Ridge activation functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |