|
Lavvu
A lavvu (or , , , , (''kåvas''), , , and ) is a temporary dwelling used by the Sami people of northern extremes of Northern Europe. It has a design similar to a Native American tipi but is less vertical and more stable in high winds. It enables the indigenous cultures of the treeless plains of northern Scandinavia and the high arctic of Eurasia to follow their reindeer herds. It is still used as a temporary shelter by the Sami, and increasingly by other people for camping. It should not be confused with the goahti, another type of Sami dwelling, or the Finnish laavu. Historical definition There are several historical references that describe the lavvu structure used by the Sami. These structures have the following in common: # The lavvu is supported by three or more evenly spaced forked or notched poles that form a tripod. # There are upwards of ten or more unsecured straight poles that are laid up against the tripod and which give form to the structure. # The lavvu does ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tipi
A tipi or tepee ( ) is a conical lodge tent that is distinguished from other conical tents by the smoke flaps at the top of the structure, and historically made of animal hides or pelts or, in more recent generations, of canvas stretched on a framework of wooden poles. The loanword came into English usage from the Dakota and Lakota languages. Historically, the tipi has been used by certain Indigenous peoples of the Plains in the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies of North America, notably the seven tribes of the Sioux, as well as among the Iowa people, the Otoe and Pawnee, and among the Blackfeet, Crow, Assiniboines, Arapaho, and Plains Cree. Lewis H. Morgan, "I have seen it in use among seven or eight Dakota sub-tribes, among the Iowas, Otoes, and Pawnees, and among the Black-feet, Crows, Assiniboines, and Crees. In 1878, I saw it in use among the Utes of Colorado. A collection of fifty of these tents, which would accommodate five hundred persons, make a picturesqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succeeding the Second Agricultural Revolution. Beginning in Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain around 1760, the Industrial Revolution had spread to continental Europe and the United States by about 1840. This transition included going from craft production, hand production methods to machines; new Chemical industry, chemical manufacturing and Puddling (metallurgy), iron production processes; the increasing use of Hydropower, water power and Steam engine, steam power; the development of machine tools; and rise of the mechanisation, mechanised factory system. Output greatly increased, and the result was an unprecedented rise in population and population growth. The textile industry was the first to use modern production methods, and textiles b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sami Parliament Of Norway
Acronyms * SAMI, ''Synchronized Accessible Media Interchange'', a closed-captioning format developed by Microsoft * Saudi Arabian Military Industries, a government-owned defence company * South African Malaria Initiative, a virtual expertise network of malaria researchers People * Sami (name), including lists of people with the given name or surname * Sámi people, the indigenous people of Norway, Sweden, the Kola Peninsula and Finland * Samantha Shapiro (born 1993), American gymnast nicknamed "Sami" Places * Sami (ancient city), an ancient Greek city in the Peloponnese * Sami, Burkina Faso, a district * Sämi, a village in Lääne-Viru County in northeastern Estonia * Sami District, Gambia * Sami, Cephalonia, Greece, a municipality ** Sami Bay, east of Sami, Cephalonia * Sami, Gujarat, India, a town * Sami, Paletwa, Myanmar, a town Other uses * Sámi languages, languages spoken by the Sámi * Sami (chimpanzee), kept at the Belgrade Zoo * Sami, a common name for ''P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Máze
, , or is a village in Kautokeino Municipality in Finnmark county, Norway. The village is located along the river Kautokeinoelva, a tributary of the Alta river. about south of the town of Alta and about 60 kilometres north of the village of Kautokeino. The village is made up predominantly of Sami people, a non-Norwegian group indigenous to the Fennoscandinavian peninsula . Masi Church has stood in the town since the 17th century. The present church building is a reconstruction built after the original was torched by German soldiers during the Nazi occupation of Norway in World War II. During the late 1970s, the Norwegian government planned to construct the Alta Hydroelectric Power Station downstream, which was expected to flood Masi, upstream Kautokeino, and the surrounding reindeer pasture and disrupt reindeer migration and wild salmon Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storting
The Storting ( ; ) is the supreme legislature of Norway, established in 1814 by the Constitution of Norway. It is located in Oslo. The Unicameralism, unicameral parliament has 169 members and is elected every four years based on party-list proportional representation in nineteen Voting systems#Multiple-winner methods, multi-seat constituencies. A member of the Storting is known in Norwegian as a ''stortingsrepresentant'', literally "Storting representative". The assembly is led by a president and, since 2009, five vice presidents: the presidium. The members are allocated to twelve standing committees as well as four procedural committees. Three ombudsmen are directly subordinate to parliament: the Norwegian Parliamentary Intelligence Oversight Committee, Parliamentary Intelligence Oversight Committee and the Office of the Auditor General of Norway, Office of the Auditor General. Parliamentary system, Parliamentarianism was established in 1884, with the Storting operating a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alta Controversy
The Alta conflict or Alta controversy was a series of protests in Norway in the late 1970s and early 1980s against the construction of a hydroelectric power plant on the Alta River in Finnmark, Northern Norway. Timeline *Inhabitants of the village of Máze rallied and formed (Action Committee Against the Damming of Masi) on 15 August 1970. *Starting in 1973, the (Alta Committee for the Conservation of the Alta-Kautokeino River Basin) documented the detrimental effects of the project on salmon and "the nature" of the Alta river basin. The group is credited, in large part, for influencing the municipal council of Alta's opposition to the construction project. *On 12 July 1978, about 80 protestors form ' (People's Action Against the Development of the Alta-Kautokeino River Basin) assembled at Alta gymnas, the local high school. *The was established in the summer of 1979. It received 6,500 visitors from 20 nations; a number of the visitors were demonstrators. *Later in 1979, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sami Siida Of North America
The Sami Siida of North America () is a loosely organized group of regional communities, primarily in Canada and the United States, who share the Sámi culture and heritage from the arctic and sub-arctic regions of Norway, Sweden, Finland and the Kola Peninsula of Russia. This area has traditionally been referred to using the endonyms Sápmi and ''Samiland'' as well as the exonym ''Lapland''. Individuals within the North American Siida are immigrants, descendants of immigrants, or are supporters of the Sami culture, although may not have any family lineage from Sápmi. Purpose The North American Siida often performs educational shows, Sami community get-togethers, and related events over the course of the year, often with other Scandinavian events such as FinnFestUSA, American Swedish Institute, and the Norwegian-American Bygdelagenes Fellesraad (NABF). The Siida also hosts a larger gathering approximately every two years called the "Siiddastallen." Within the NABF, the Siida has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People's Commissars to oppose the military forces of the new nation's adversaries during the Russian Civil War, especially the various groups collectively known as the White Army. In February 1946, the Red Army (which embodied the main component of the Soviet Armed Forces alongside the Soviet Navy) was renamed the "Soviet Army". Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union it was split between the post-Soviet states, with its bulk becoming the Russian Ground Forces, commonly considered to be the successor of the Soviet Army. The Red Army provided the largest land warfare, ground force in the Allies of World War II, Allied victory in the European theatre of World War II, and its Soviet invasion of Manchuria, invasion of Manchuria assisted the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troms
Troms (; ; ; ) is a Counties of Norway, county in northern Norway. It borders Finnmark county to the northeast and Nordland county in the southwest. Norrbotten Län in Sweden is located to the south and further southeast is a shorter border with Lapland (Finland), Lapland Province in Finland. To the west is the Norwegian Sea (Atlantic Ocean). The county had a population of 169,610 in 2024. The entire county, which was established in 1866, is located north of the Arctic Circle. The Troms County Municipality is the governing body for the county, elected by the people of Troms, while the Troms County governor (Norway), county governor is a representative of the King of Norway, King and Government of Norway. From 1 January 2020 to 31 December 2023 Troms was merged with the neighboring Finnmark county to create the new Troms og Finnmark county. This merger was reversed by the government resulting from the 2021 Norwegian parliamentary election. General information Name Until 1919, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
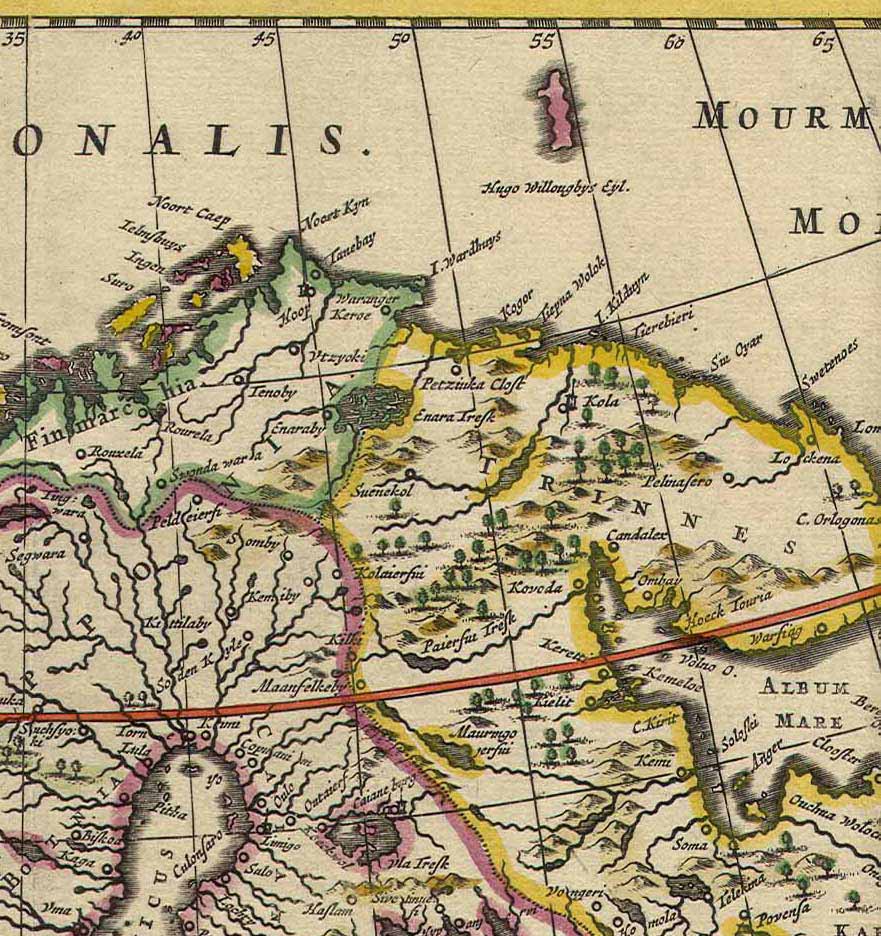
Finnmark
Finnmark (; ; ; ; ) is a counties of Norway, county in northern Norway. By land, it borders Troms county to the west, Finland's Lapland (Finland), Lapland region to the south, and Russia's Murmansk Oblast to the east, and by water, the Norwegian Sea (Atlantic Ocean) to the northwest, and the Barents Sea (Arctic Ocean) to the north and northeast. The county was formerly known as ''Finmarkens amt'' or ''Vardøhus amt''. Since 2002, it has had two official names: Finnmark (Norwegian language, Norwegian) and Finnmárku (Northern Sami language, Northern Sami). It is part of the Sápmi region, which spans four countries, as well as the Barents Region, and is Norway's second-largest and least populous county. Situated at the northernmost part of continental Europe, where the Norwegian coastline swings eastward, Finnmark is an area "where East meets West" in culture as well as in nature and geography. Vardø Municipality, Norway's easternmost municipality, is farther east than Saint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |