|
Lars Nilson
Lars Fredrik Nilson (27 May 1840 – 14 May 1899) was a Swedish chemist, professor at Uppsala University, and later Director of the Agricultural Chemical Experiment Station at the Royal Swedish Academy of Agriculture and Forestry in Stockholm. He discovered the element scandium in 1879, by separating out scandium(III) oxide, also known as scandia. In addition to his work concerning the analytic chemistry of elements and rare earths, he made substantial contributions to Swedish agriculture, including methods of fertilization and the introduction of sugar beets as a crop. Education Nilson was born in Skönberga parish in Östergötland, Sweden. Later his family relocated to the island of Gotland, where his father, Nikolaus, owned the farm Rosendal in Follingbo. During later life, Lars Fredrik Nilson retained a small holding on Gotland, which he visited yearly. After graduating from Wisby high school on Gotland, Lars Fredrik Nilson enrolled at Uppsala University in 1859. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Sciences
Natural science or empirical science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer review and reproducibility of findings are used to try to ensure the validity of scientific advances. Natural science can be divided into two main branches: life science and physical science. Life science is alternatively known as biology. Physical science is subdivided into branches: physics, astronomy, Earth science and chemistry. These branches of natural science may be further divided into more specialized branches (also known as fields). As empirical sciences, natural sciences use tools from the formal sciences, such as mathematics and logic, converting information about nature into measurements that can be explained as clear statements of the " laws of nature". Modern natural science succeeded more classical approaches to natura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euxenite - Vegusdal, Norvegia 01
Euxenite, or euxenite-(Y) (the official mineralogical name), is a brownish black mineral with a metallic luster. Chemistry It contains calcium, niobium, tantalum, cerium, titanium, yttrium, and typically uranium and thorium, with some other metals. The chemical formula is . It is commonly partially amorphous due to radiation damage. Euxenite forms a continuous series with the titanium rich polycrase-(Y) having the formula . Name and discovery It was first described in 1870 and named for from the Greek (εὔξενος), ''hospitable'' or ''friendly to strangers'', in allusion to the many rare elements that it contains. Occurrence It occurs in granite pegmatites and detrital black sands. It is found in many locations worldwide, notably its type locality in Jølster, Sunnfjord, Norway. Other locations include the Ural Mountains of Russia; Sweden; Minas Gerais, Brazil; Ampangabe, Madagascar; Ontario, Canada; and in Arizona, Wyoming and Colorado in the US.http://www.galleries.c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
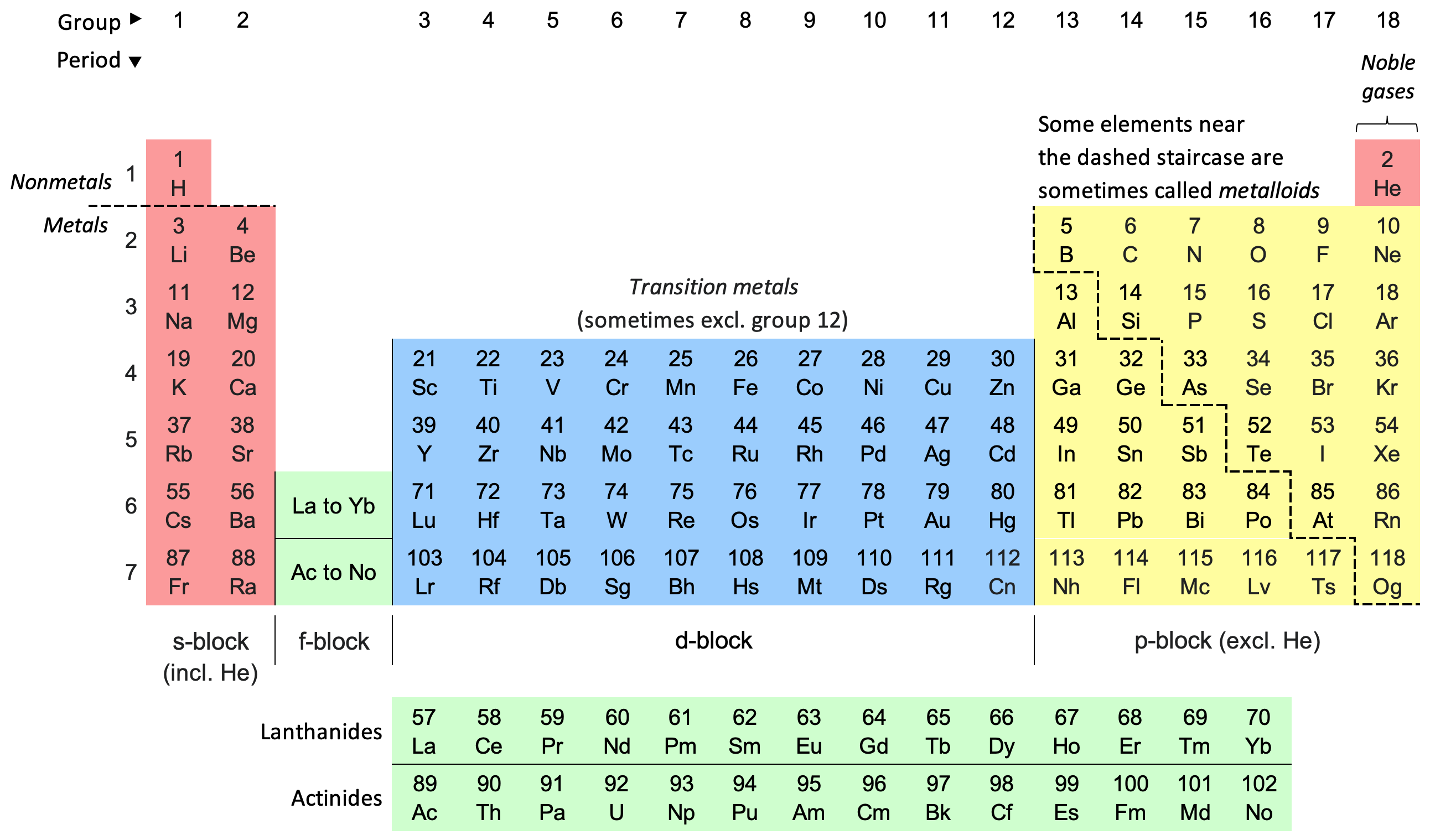
Periodic System
The periodic table, also known as the periodic table of the elements, is an ordered arrangement of the chemical elements into rows ("Period (periodic table), periods") and columns ("Group (periodic table), groups"). It is an Cultural icon, icon of chemistry and is widely used in physics and other sciences. It is a depiction of the Periodic trends, periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged in order of their atomic numbers an approximate periodic function, recurrence of their properties is evident. The table is divided into four roughly rectangular areas called block (periodic table), blocks. Elements in the same group tend to show similar chemical characteristics. Vertical, horizontal and diagonal Periodic trends, trends characterize the periodic table. Metallic character increases going down a group and from right to left across a period. Nonmetal (chemistry), Nonmetallic character increases going from the bottom left of the periodic table to the top r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Element
A chemical element is a chemical substance whose atoms all have the same number of protons. The number of protons is called the atomic number of that element. For example, oxygen has an atomic number of 8: each oxygen atom has 8 protons in its atomic nucleus, nucleus. Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei, known as isotopes of the element. Two or more atoms can combine to form molecules. Some elements form Homonuclear molecule, molecules of atoms of said element only: e.g. atoms of hydrogen (H) form Diatomic molecule, diatomic molecules (H). Chemical compounds are substances made of atoms of different elements; they can have molecular or non-molecular structure. Mixtures are materials containing different chemical substances; that means (in case of molecular substances) that they contain different types of molecules. Atoms of one element can be transformed into atoms of a different element in nuclear reactions, which change an atom's at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |