|
Laranjal Do Jari
Laranjal do Jari () (''Jari Orangery'') is a Municipalities of Brazil, municipality located in the west of the state of Amapá in Brazil. It is the only municipality in the west boundaries of Amapá, except for a small part of Vitória do Jari. Its population is 35,114 and its area is 30,783 km2, which makes it the largest municipality of Amapá. History The land was originally inhabited by Amerindians. Later businessmen set up Natural rubber, rubber plantations. The largest plantation was owned by who owned of land which made him the biggest landowner at the time. In 1948, his tenants revolted and he was forced to sell the land to Portuguese businessmen who sold it to Daniel K. Ludwig, an American billionaire, in 1964. In 1967, Ludwig conceived the Jari project. He wanted to replace the rainforest with ''Gmelina arborea'' for the Pulp (paper), pulp industry. A planned city called Monte Dourado was built in Almeirim, Pará, Almeirim, however it was unable to provide hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Municipalities In Amapá
This is a list of the municipalities in the state of Amapá (AP), located in the North Region of Brazil. Amapá is divided into 16 municipalities. Municipalities See also *Geography of Brazil The country of Brazil occupies roughly half of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. Brazil covers a total area of which includes of land and of water. The highest point in Brazil is Pico da Neblina at . Brazil is bordered by the count ... * List of cities in Brazil References {{DEFAULTSORT:List of municipalities in Amapa Amapa * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (; IBGE) is the agency responsible for official collection of statistical, geographic, cartographic, geodetic and environmental information in Brazil. IBGE performs a decennial national census; questionnaires account for information such as age, household income, literacy, education, occupation and hygiene levels. IBGE is a public institute created in 1936 under the name ''National Institute of Statistics''. Its founder and chief proponent was statistician Mário Augusto Teixeira de Freitas. The current name dates from 1938. Its headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro, and its current president is Marcio Pochmann, replacing Eduardo Rios Neto. It was made a federal agency by Decree-Law No. 161 on February 13, 1967, and is linked to the Ministry of the Economy, inside the Secretariat of Planning, Budget and Management. Structure IBGE has a network of national research and dissemination components, comprising: * 27 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve
The Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve () is a sustainable development reserve in the state of Amapá, Brazil. It contains a well-preserved area of terra firme forest with rich fauna. The local communities that surround the reserve use it for sustainable extraction of products such as Brazil nuts. Location The Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve is divided between the municipalities of Laranjal do Jari (69.01%), Mazagão (18.68%) and Pedra Branca do Amapari (12.1%) in Amapá. It has an area of . The Jari River forms the western boundary. The Iratapuru River, a tributary of the Jari, crosses the reserve from north to south and is fed by many tributaries. The reserve is bounded by the Waiãpi Indigenous Territory to the north and part of the Jari Ecological Station to the south. The Amapá State Forest adjoins the reserve to the east. The Jari River also forms the western boundary of the Tumucumaque Mountains National Park, just north of the reserve. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Cajari Extractive Reserve
The Rio Cajari Extractive Reserve () is an extractive reserve in the state of Amapá, Brazil. It protects a region of dense rainforest, ''cerrado'' fields and flooded riparian zones that is rich in biodiversity. Formerly it was used for rubber extraction, and later efforts were made to develop a pulp industry. Extraction of timber for sale is now prohibited. The residents, who are poorly educated and suffer poor health, engage in subsistence hunting, fishing and farming, and extract forest products such as Brazil nuts, açaí palm fruit and heart of palm. Location The Rio Cajari Extractive Reserve is divided between the municipalities of Mazagão (44.44%), Vitória do Jari (16.88%) and Laranjal do Jari (38.67%) in Amapá. It has an area of . The Cajari River, which gives its name to the reserve, drains the center of the reserve. The Amazon River forms the southeast boundary of the reserve, and the Ajuruxi River defines the northeastern boundary. Highway BR-156 runs through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BR-210
BR-210 is a federal highway of Brazil. The 411.7 kilometre road, popularly known as ' ("north perimeter"), is primarily located in the North Region, Brazil, Northern Brazilian state of Roraima, with other segments in Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas, Pará, and Amapá. The planning of the highway would consist of connecting Macapá, Amapá with the Brazil-Colombia border in the municipality of São Gabriel da Cachoeira, Amazonas (Brazilian state), Amazonas. The highway would have 2,454.7 km (1,525.3 mi) in total. However, only small stretches of it have been implemented. In 1976, the highway entered the Wajãpi Indigenous Territory in Amapá. The invasion was repelled by the indigenous leadership who expelled the intruders between the 1980s and the 1990s, and therefore, the highway will probably never be completely built. References Federal highways in Brazil Transport in Roraima Transport in Amapá Transport in Amazonas (Brazilian state) Transport in Pará {{Braz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BR-156
BR-156 is a federal highway of Brazil. The road consists of 552 km between Oiapoque and Macapá, and 271 km between Macapá and Laranjal do Jari (except via Santana city), totalling 823 km of road through forest and savannah. Only the road between Macapá and Calçoene is paved with asphalt. The rest of the road has a dirt surface. Because of the road conditions, it takes around 10-12 hours to drive between Oiapoque and Macapá. With the Oyapock River Bridge (linking the cities of Oiapoque in Brazil and Saint-Georges-de-l'Oyapock in French Guiana) open to traffic starting from 20 March 2017, it is now possible to drive from Macapá to Cayenne, the capital city of French Guiana French Guiana, or Guyane in French, is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France located on the northern coast of South America in the Guianas and the West Indies. Bordered by Suriname to the west .... References Federal highways in Brazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jari River
The Jari River, or Jary River (), is a northern tributary of the Amazon River on the border between the states of Pará and Amapá in northeastern Brazil. It is in the most downstream regions of the Amazon Basin and borders the Guiana Highlands and the Guianas to the northwest. Course The river flows through the Uatuma-Trombetas moist forests ecoregion. The source of the Jari is in the south of the Tumuk Humak Mountains, and its mouth is at the Amazon River between the municipalities of Almeirim in Pará and Vitória do Jari in Amapá. Ilha Grande de Gurupá, the second-largest island of the Amazon River Delta, is opposite of the mouth of the Jari River. Part of the river's basin is in the Maicuru Biological Reserve. The Jari River forms the western boundary of the Tumucumaque Mountains National Park. Below the park it forms the western boundary of the Rio Iratapuru Sustainable Development Reserve, created in 1997. For part of its course it runs through the Jari Ecol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanty Town
A shanty town, squatter area, squatter settlement, or squatter camp is a settlement of improvised buildings known as shanties or shacks, typically made of materials such as mud and wood, or from cheap building materials such as corrugated iron sheets. A typical shanty town is squatted and, at least initially, lacks adequate infrastructure, including proper sanitation, safe water supply, electricity and street drainage. Over time, shanty towns may develop their infrastructure and even change into middle class neighbourhoods. They can be small informal settlements or they can house millions of people. First used in North America to designate a shack, the term ''shanty'' is likely derived from French ''chantier'' (construction site and associated low-level workers' quarters), or alternatively from Scottish Gaelic ''sean'' () meaning 'old' and ''taigh'' () meaning 'house old. Globally, some of the largest shanty towns are Ciudad Neza in Mexico, Orangi in Pakistan and Dharavi i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almeirim, Pará
Almeirim is a city on the Amazon River, Amazon and the northernmost municipality in the Brazilian States of Brazil, state of Pará. It is also the fourth largest municipality in that state and the eighth largest in Brazil (by area). The municipality is crossed by the Equator. History Almeirim was first inhabited by the Amerindians. Manoel da Mota e Siqueira constructed the Paru Fort which was designated a village in 1758, and named Almerim. In 1835, the Cabanagem Revolt started in Almeirim which resulted in widespread devastation. In 1890, Almeirim became an independent municipality. The Santo Antonio do Jari hydroelectric system is located on the Jari River and provides 373.4 MW of hydro electricity. Construction began in 2011 and was completed in 2014. Nature The municipality includes a large part (94.49%) of the Maicuru Biological Reserve. It also contains part of the Jari Ecological Station. Transport The city is served by Almeirim Airport. Monte Dourado Airport, Serra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monte Dourado
Monte Dourado is a town and district in the Brazilian municipality of Almeirim, in the state of Pará. Monte Dourando is a planned town established in 1967 to house the workers for the Jari project. The city is located on the Jari River. History In 1964, Daniel K. Ludwig, an American billionaire, purchased of rainforest in Brazil. In 1967, he conceived the Jari project. The plan was to replace the rainforest with ''Gmelina arborea'' for the pulp industry. A planned city called Monte Dourado (English: Golden Mountain) was built in Almeirim to house the workers. Ludwig started building schools, hospitals, roads, and ports. He wanted the Brazilian government to finance the construction of the city, but they refused. The city was unable to provide housing for all the workers, and a shanty town called Beiradão (nowadays: Laranjal do Jari) emerged on the other side of the Jari River. The project turned into a major money-losing failure, and in 1982, the land was sold. In 1983, Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
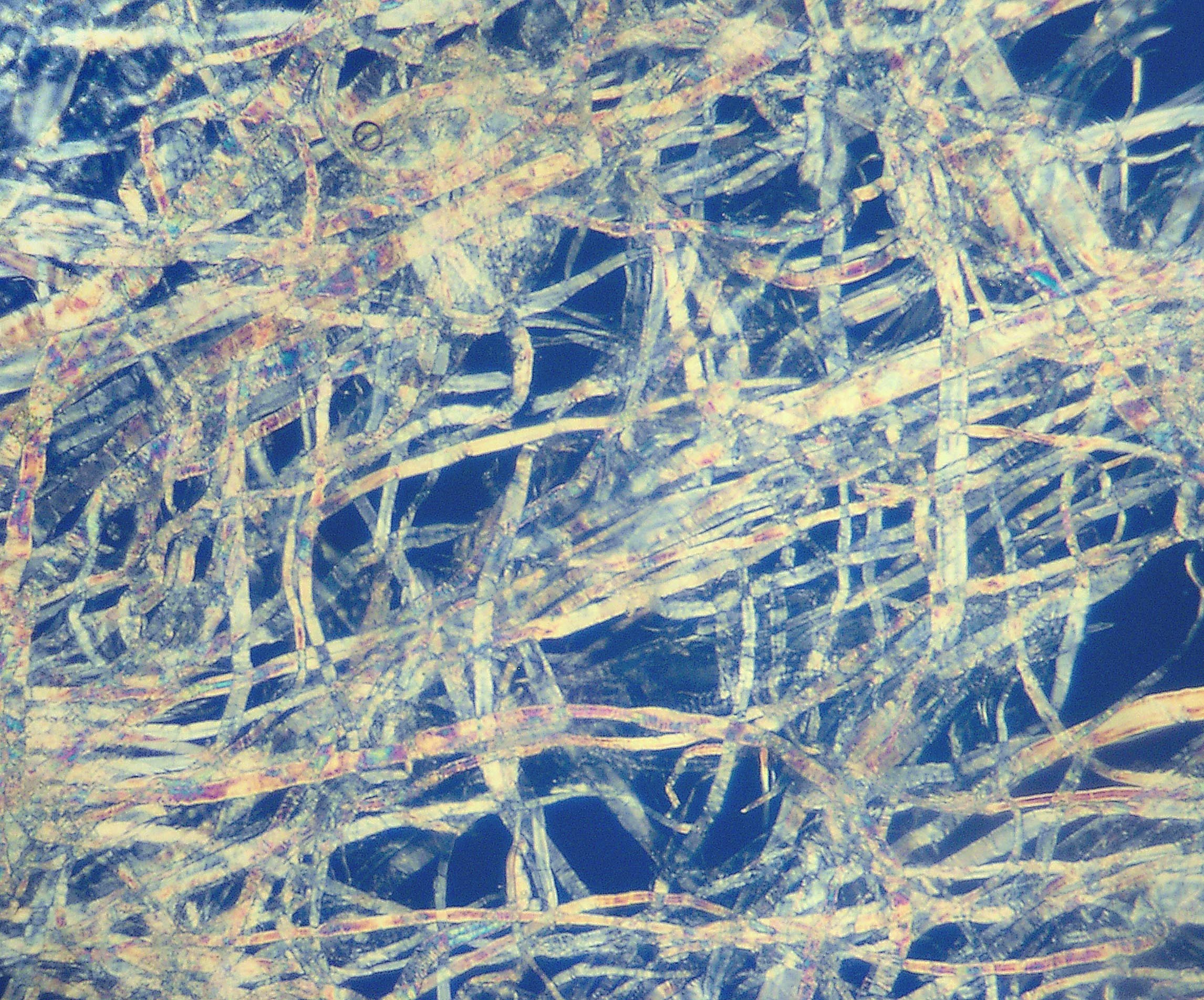
Pulp (paper)
Pulp is a fibrous Lignocellulosic biomass, lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically, or mechanically isolating the cellulose fiber, cellulosic fibers of wood, fiber crops, Paper recycling, waste paper, or cotton paper, rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other Pulp and paper industry, paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around AD 105, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of Bark (botany), bark or Bast fibre, bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmelina Arborea
''Gmelina arborea'', (in English beechwood, gmelina, goomar teak, Kashmir tree, Malay beechwood, white teak, yamane ), locally known as gamhar, is a fast-growing deciduous tree in the family Lamiaceae. Distribution and habitat ''Gmelina arborea'' grows naturally throughout India, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam and in southern provinces of China. It is found at altitudes from sea level to . Since the 1960s, it has been introduced extensively as fast-growing timber trees in Brazil, Gambia, Honduras, Ivory Coast, Malaysia, Malawi, Nigeria, the Philippines, and Sierra Leone. It is also planted in gardens and avenues. Utilization The species is fast-growing and thus raised in large-scale plantations to produce wood for construction, crafts, paper pulp, fuel, and charcoal. It produces high-quality wood used in the manufacture of furniture and to make plywood, matches and agricultural implements. The nectar of the flowers yields high-quality honey. The Lion Throne of Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |