|
Lanthanotus
The earless monitor lizard (''Lanthanotus borneensis'') is a semiaquatic, brown lizard native to the Southeast Asian island of Borneo. It is the monotypic, only living species in the family Lanthanotidae and it is related to the true monitor lizards. Taxonomy The earless monitor lizard was species description, described in 1878 by Franz Steindachner. The genus name ''Lanthanotus'' means "hidden ear" and the species name ''borneensis'' refers to its home island of Borneo. The uniqueness of the species was immediately recognized and Steindachner placed it in its own family, Lanthanotidae. In 1899, George Albert Boulenger relegated it to the family Helodermatidae, together with the Heloderma, beaded lizards and Gila monster, on the basis of morphological similarities. Further studies were conducted in the 1950s where it was found that although it is related to Helodermatidae, this relationship is relatively distant. The similarity is in part the result of convergent evolution and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanidae
The Varanidae are a family of lizards in the superfamily Varanoidea and order Anguimorpha. The family, a group of carnivorous and frugivorous lizards, includes the living genus '' Varanus'' and a number of extinct genera more closely related to ''Varanus'' than to the earless monitor lizard (''Lanthanotus''). ''Varanus'' includes the Komodo dragon (the largest living lizard), crocodile monitor, savannah monitor, the goannas of Australia and Southeast Asia, and various other species with a similarly distinctive appearance. Their closest living relatives are the earless monitor lizard and Chinese crocodile lizard. The oldest members of the family are known from the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Taxonomy The Varanidae were defined (using morphological characteristics) by Estes, de Queiroz and Gauthier (1988) as the clade containing the most recent common ancestor of '' Lanthanotus'' and ''Varanus'' and all of its descendants. A similar definition was formulated by Conrad ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
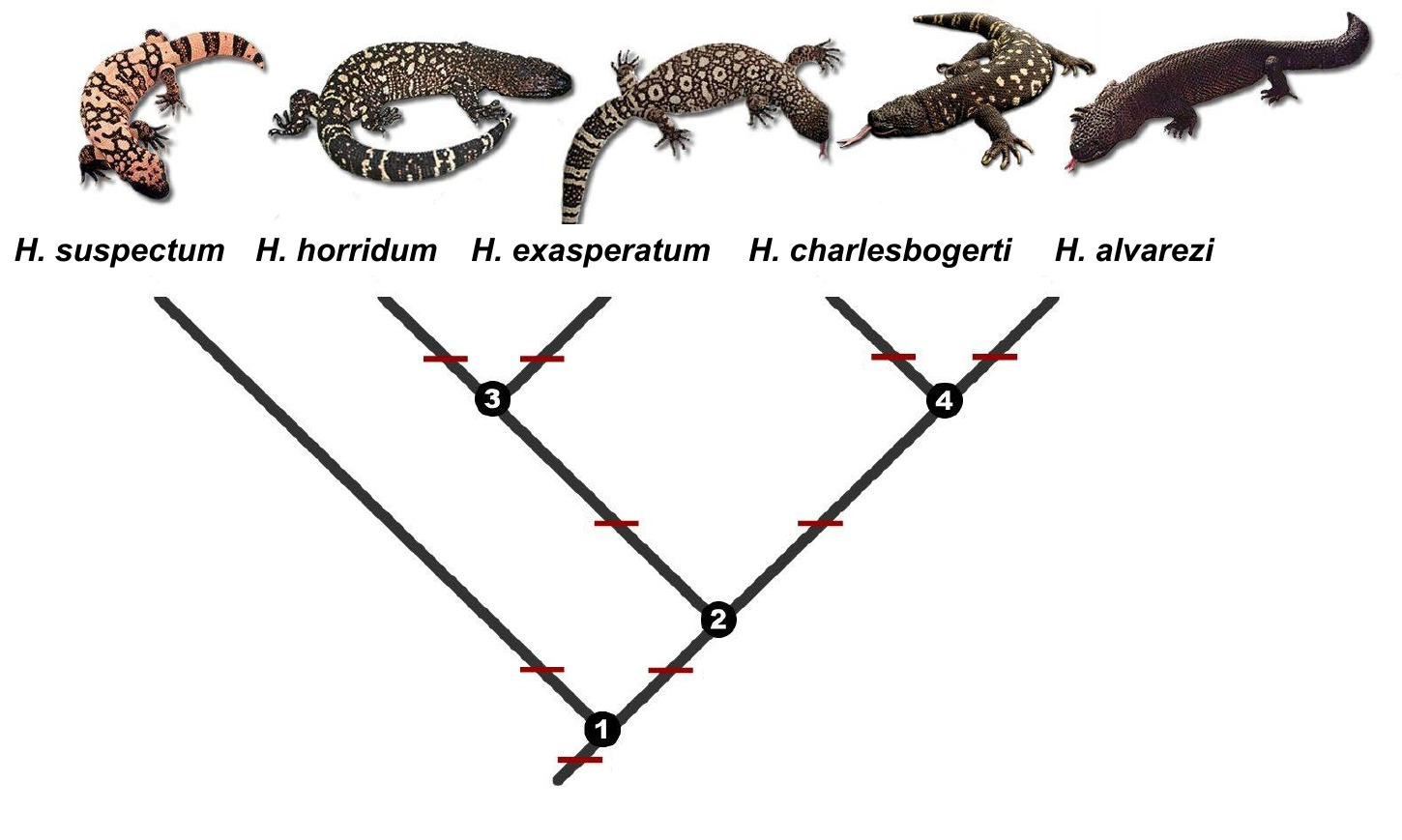
Heloderma
''Heloderma'' is a genus of toxicoferan lizards that contains five species, all of which are venomous. It is the only extant genus of the family Helodermatidae. Description The genus ''Heloderma'' contains the Gila monster (''H. suspectum'') and four species of beaded lizards. Their eyes are immobile and fixed in their heads. The Gila monster is a large, stocky, mostly slow-moving reptile that prefers arid deserts. Beaded lizards are seen to be more agile and seem to prefer more humid surroundings. The tails of all species of ''Heloderma'' are used as fat-storage organs. The scales of the head, back, and tail are bead-like, containing osteoderms for better protection. The scales of the belly are free from osteoderms. Most species are dark in color, with yellowish or pinkish markings. Venom The venom glands of ''Heloderma'' are located at the end of the lower jaws, unlike snakes' venom glands, which are located behind the eyes. Also, unlike snakes, the Gila monster and beaded li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguimorpha
The Anguimorpha is a suborder of Squamata, squamates. The group was named by Fürbringer in 1900 to include all autarchoglossans closer to ''Varanus'' and ''Anguis'' than ''Scincus''. These lizards, along with iguanians and snakes, constitute the proposed "venom clade" Toxicofera of all venomous reptiles. Evolution The oldest widely accepted member of Anguimorpha is ''Dorsetisaurus'' from the Late Jurassic of Europe and North America. In 2022, the genus ''Cryptovaranoides'' was described from the latest Triassic (Rhaetian) of England. ''Cryptovaranoides'' was recovered in the study as a crown-group anguimorph, and therefore the oldest crown group-squamate, 35 million years older than any previously known crown-group squamate. However, a 2023 study found that ''Cryptovaranoides'' most likely represents an Archosauromorpha, archosauromorph that was only distantly related to squamates. Families Anguidae There are 9 genera found within the Anguidae family. They are characteriz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varanoidea
Varanoidea is a superfamily of lizards, including the well-known family Varanidae (the monitors and goannas). Also included in the Varanoidea are the Lanthanotidae ( earless monitor lizards), and the extinct Palaeovaranidae. Throughout their long evolutionary history, varanoids have exhibited great diversity, both in habitat and form. This superfamily includes the largest-known terrestrial lizard, Megalania (~5 meters), and the largest extant lizard, the Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis'', ~3 meters). Evolution Either synonymous with, or a subgroup of, the group Platynota, the varanoids first appear in the fossil record in the latter part of Early Cretaceous, but possible varanoid ancestors have been traced back as far as Early Jurassic times. Among the earliest known varanoids are the monitor-like necrosaurids '' Palaeosaniwa canadensis'' from the Campanian (roughly 71–82 mya) of North America and '' Estesia mongoliensis'' and '' Telmasaurus grangeri'', both from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemism
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population density, most sparsely populated sovereign state. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border an Endorheic basin, inland sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and List of cities in Mongolia, largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, the Second Turkic Khaganate, the Uyghur Khaganate and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest List of largest empires, contiguous land empire i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Aus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geological period of the entire Phanerozoic. The name is derived from the Latin , 'chalk', which is abundant in the latter half of the period. It is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation . The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high Sea level#Local and eustatic, eustatic sea levels that created numerous shallow Inland sea (geology), inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites, and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on land. The world was largely ice-free, although there is some evidence of brief periods of glaciation during the cooler first half, and forests extended to the poles. Many of the dominant taxonomic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Most Recent Common Ancestor
A most recent common ancestor (MRCA), also known as a last common ancestor (LCA), is the most recent individual from which all organisms of a set are inferred to have descended. The most recent common ancestor of a higher taxon is generally assumed to have been a species. The term is also used in reference to the ancestry of groups of genes (haplotypes) rather than organisms. The ancestry of a set of individuals can sometimes be determined by referring to an established pedigree, although this may refer only to patrilineal or matrilineal lines for sexually-reproducing organisms with two parents, four grandparents, etc. However, in general, it is impossible to identify the exact MRCA of a large set of individuals, but an estimate of the time at which the MRCA lived can often be given. Such ''time to most recent common ancestor'' (''TMRCA'') estimates can be given based on DNA test results and established mutation rates as practiced in genetic genealogy, or by reference to a non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarawak
Sarawak ( , ) is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia. It is the largest among the 13 states, with an area almost equal to that of Peninsular Malaysia. Sarawak is located in East Malaysia in northwest Borneo, and is bordered by the Malaysian state of Sabah to the northeast, Kalimantan (the Indonesian portion of Borneo) to the south, and Brunei in the north. The state capital, Kuching, is the largest city in Sarawak, the economic centre of the state, and the seat of the Sarawak state government. Other cities and towns in Sarawak include Miri, Malaysia, Miri, Sibu, and Bintulu. As of 2020 Malaysia census, the population of Sarawak was 2.453 million. Sarawak has an equatorial climate with tropical rainforests and abundant animal and plant species. It has several prominent cave systems at Gunung Mulu National Park. Rajang River is the longest river in Malaysia; Bakun Dam, one of the largest dams in Southeast Asia, is located on one of its tributaries, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |