|
LDAC (codec)
LDAC (Lossless Digital Audio Codec) is a proprietary software, proprietary audio codec, audio coding technology developed by Sony, which allows streaming Lossy compression, lossy audio over Bluetooth connections at up to 990 kbps at 32 bits/96 kHz. Despite this, Sony markets LDAC as "lossless" and "high-resolution," declaring the quality to be better than true lossless, high-resolution audio. It is used by various products, including headphones, earphones, smartphones, portable media players, active speakers, and home theaters. The encoder of LDAC is open-source under Apache License 2.0, so that any device can be coded to transmit LDAC streams without patent or licensing issues. The decoder design remains proprietary. Audio coding LDAC is an alternative to Bluetooth Special Interest Group, Bluetooth SIG's SBC (codec), SBC codec. Its main competitors are Huawei's L2HC, Qualcomm's AptX#aptX HD, aptX-HD/AptX#aptX Adaptive, aptX Adaptive and the HWA Union/Savitech's LHDC (codec) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LDAC Logo
LDAC may refer to: Science and technology * LDAC (codec), an audio codec used in Bluetooth * Linz-Donawitz-Arbed-Centre-National method (LDAC method), at the Minière et Métallurgique de Rodange Organisations * Learning Disabilities Association of Canada, an association in support of children with learning disability#United States and Canada, learning disabilities * Long Distance Advisory Council, of the European Fisheries Control Agency * Land and Building Advisory Committee, in North East New Territories New Development Areas Planning, Hong Kong Other uses * Leader Development and Assessment Course, of the US Army's Reserve Officers' Training Corps * Letterman Digital Arts Center, San Francisco, US {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HWA Union
() are a type of traditional Korean boot, which, along with , is a subdivision of Korean shoes. The refers to all kind of shoes that do not go up to the ankle. are usually made of leather, and artisans who make the shoes are called . were originally worn by the Northern kingdoms of Korea. The horse-riding cultures of the North appear to have typically worn leather boots (), while the farmers of the South wore shoes of leather or straw (). Different types of boots were worn by military and civil officials.Korean Handicrafts: Arts in Everyday Life by Seoul Selection Editorial Team See also *List of shoe styles * *Cowboy boot Cowboy boots are a specific style of riding boot, historically worn by cowboys. They have a High-heeled footwear#Men and heels, high heel that is traditionally made of stacked leather, rounded to pointed toe, high shaft, and, traditionally, no l ... * References Korean footwear Boots Folk footwear Korean words and phrases {{shoe-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AptX Adaptive
aptX (''apt'' stands for ''audio processing technology'') is a family of proprietary audio codec compression algorithms owned by Qualcomm, with a heavy emphasis on wireless audio applications. History The original compression algorithm was developed in the 1980s by Dr. Stephen Smyth as part of his Ph.D. research at Queen's University Belfast School of Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. Its design is based on time domain ADPCM principles without psychoacoustic auditory masking techniques. The algorithm was then commercialized under the name aptX and first introduced to the commercial market as a semiconductor product, a custom programmed DSP integrated circuit with part name APTX100ED, which was initially adopted by broadcast automation equipment manufacturers who required a means to store CD-quality audio on a computer hard disk drive for automatic playout during a radio show, for example, hence replacing the task of the disc jockey. The company was boug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LC3 (codec)
LC3 (Low Complexity Communication Codec) is an audio codec specified by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG) for the LE Audio audio protocol introduced in Bluetooth 5.2. It's developed by Fraunhofer IIS and Ericsson as the successor of the SBC codec. Mono only LC3-SBW is also supported over Bluetooth Classic HFP 1.9, improving on mSBC. It is possible to send 4 LC3 streams to LE audio earbuds, like Samsung's Buds2 Pro. Codec LC3 provides higher audio quality and better packet loss concealment than SBC, G.722 and Opus, according to subjective testing by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group and ETSI. The conclusion regarding Opus is disputed as the test only included speech audio, but the comparison was made to version 1.1.4 of the reference Opus encoder, using complexity level 0 at 32 kbps and relying on CELT (general audio) instead of the FEC-capable SILK (speech); the test also did not take into account the newer version 1.2 of the Opus encoder released in 2017 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
SCL6
Master Quality Authenticated (MQA) is a proprietary system for delivering high-quality digital audio. The system includes audio signal processing, lossy audio compression and authentication. MQA requires licensing fees to use. The system was launched in 2014 by Meridian Audio, and is now owned by Lenbrook. The MQA system is a three-part process applied to digital audio music recordings consisting of 1) modifying and controlling the end-to-end digital filter response; 2) preparing the audio for transfer to a smartphone or audio device using a lossy audio compression format with authentication; and 3) decompressing the recording for playback. There has been controversy regarding several aspects of MQA. These aspects include but are not limited to whether the audio signal processing improves or degrades the sound quality, whether the lossy audio compression degrades the sound quality, the utility of the authentication function, and the effect of licensing fees on music recordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Japan Audio Society
The Japan Audio Society (JAS; Japanese: 一般社団法人日本オーディオ協会) is a non-profit organization based in Japan, dedicated to the advancement of audio technology and the promotion of high-fidelity sound reproduction. Established in 1952, JAS collaborates with audio manufacturers, engineers, and researchers to set standards that ensure high-quality audio experiences for consumers and professionals alike. Hi-Res Audio Certification JAS administers the Hi-Res Audio certification program, which identifies audio devices capable of reproducing high-resolution sound. To qualify for this certification, products must meet specific technical criteria, including: Analog Performance * Microphone frequency response of 40 kHz or higher. * Amplifier performance supporting frequencies of 40 kHz or higher. * Speaker and headphone capabilities extending to 40 kHz or higher. Digital Performance * Recording formats supporting at least 96 kHz/24-bit. * Input/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms. Proprietary software is a subset of non-free software, a term defined in contrast to free and open-source software; non-commercial licenses such as CC BY-NC are not deemed proprietary, but are non-free. Proprietary software may either be closed-source software or source-available software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s, computers—especially large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than Sales, sold. Service and all software available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Android Open Source Project
Android is an operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen-based mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android has historically been developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance, but its most widely used version is primarily developed by Google. First released in 2008, Android is the world's most widely used operating system; the latest version, released on June 10, 2025, is Android 16. At its core, the operating system is known as the Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. However, most devices run the proprietary Android version developed by Google, which ships with additional proprietary closed-source software pre-installed, most notably Google Mobile Services (GMS), which includes core apps such as Google Chrome, the digital distribution platform Google Play, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Android Version History
The version history of the Android mobile operating system began with the public release of its first beta on November 5, 2007. The first commercial version, Android 1.0, was released on September 23, 2008. The operating system has been developed by Google on a yearly schedule since at least 2011. New major releases are announced at Google I/O in May along with beta testing with the stable version usually released to the public between August and October. The first commercially released devices to run the Android operating system were the HTC Dream (marketed as the T-Mobile G1), and the Samsung Galaxy (GT-i7500). Overview The development of Android started in 2003 by Android, Inc., which was purchased by Google in 2005. There were at least two internal releases of the software inside Google and the Open Handset Alliance (OHA) before the beta version was released. The beta was released on November 5, 2007, while the software development kit (SDK) was released on November 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Android 8
Android Oreo ( codenamed Android O during development) is the eighth major release and the 15th version of the Android mobile operating system. It was initially unveiled as an alpha quality developer preview in March 2017 and later made available to the public, on August 21, 2017. It contains a number of major features, including notification channels, picture-in-picture support for video, performance improvements, and battery usage optimization, and support for autofillers, Bluetooth 5, system-level integration with VoIP apps, wide color gamuts, and Wi-Fi Aware. Android Oreo also introduces two major platform features: Android Go – a software distribution of the operating system for low-end devices – and support for implementing a hardware abstraction layer. As of January 2025, Android Oreo (which has ceased receiving security updates as of October 2021) ran on a combined 3.09% of Android devices (2.01% on Android 8.0 and 1.08% on Android 8.1). Android Oreo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Constant Bitrate
Constant bitrate (CBR) is a term used in telecommunications, relating to the quality of service. Compare with variable bitrate. When referring to codecs, constant bit rate encoding means that the rate at which a codec's output data should be consumed is constant. CBR is useful for streaming multimedia content on limited capacity channels since it is the maximum bit rate that matters, not the average, so CBR would be used to take advantage of all of the capacity. CBR is not optimal for storing data as it may not allocate enough data for complex sections (resulting in degraded quality); and if it maximizes quality for complex sections, it will waste data on simple sections. The problem of not allocating enough data for complex sections could be solved by choosing a high bitrate to ensure that there will be enough bits for the entire encoding process, though the size of the file at the end would be proportionally larger. Most coding schemes such as Huffman coding or run-length enc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
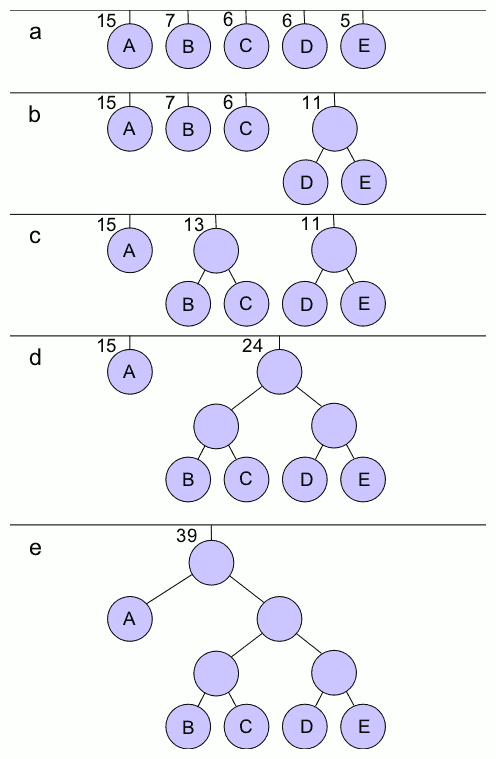
Huffman Coding
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code is Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Doctor of Science, Sc.D. student at Massachusetts Institute of Technology, MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes". The output from Huffman's algorithm can be viewed as a variable-length code table for encoding a source symbol (such as a character in a file). The algorithm derives this table from the estimated probability or frequency of occurrence (''weight'') for each possible value of the source symbol. As in other entropy encoding methods, more common symbols are generally represented using fewer bits than less common symbols. Huffman's method can be efficiently implemented, finding a code in time linear time, linear to the number of input weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |