|
Kyiv (trolleybus Model)
Kyiv (), previously known as KTB () for Kyivan Trolleybus (), is a Soviet and Ukrainian trolleybus model originally designed by Kyiv Electric Transport Plant. KTB-1/Kyiv-2/Kyiv-4 (1960–1969) In 1950's KZET has been producing only SVARZ' trolleybuses until 1959 while attempting to design their own model. In 1958 constructor V. Seriohin designed a four-axle trolleybus KZET 4T concept but the idea was scrapped. In the beginning of 1960 KZET assembled the first trolleybus designed by themselves. The model was equipped with MAZ-200 truck axis and was called 2T. During the testing the front overhang was proved to be too large, severely overloading the front axis. Due to this defect the serial production never started so the plant began to work on the second prototype. Next month KZET assembled the 2Tu trolleybus that was a shortened version of 2T and used a lot of parts from Moscow's MTB-82. The model turned out more successful than its predecessor and in the Autumn of 1960 the plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LAZ-695
The LAZ-695 is a Soviet Union, Soviet/Ukraine, Ukrainian 2 axle urban/suburban bus, which was produced in the Western Ukraine, Western Ukrainian city Lviv from 1965 to 2002. After the production stopped at the main factory in Lviv, the documentation was handed over to the DAZ automotive facility in the Ukrainian city Kamianske, where the production continued up to 2010. In over 50 years of manufacturing there were over 250,000 units of various modifications built. This made the model one of the most widely used buses in the Soviet Union and the LAZ factory the biggest bus manufacturer in Europe in the 1980s. The bus belongs to the model series 69x, which includes also the LAZ-697 "Tourist" and the LAZ-699. History Considerations to build a new factory, specialized on production of spare parts for heavy duty trucks in the Ukrainian city Lviv, were made by the Government of the Soviet Union, Soviet government after the World War II, Second World War The construction was finalized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tatra T3
The T3 is a type of Czech tramcar produced by ČKD Tatra. A late-2000s study conducted on the Prague tram system has shown 98.9% reliability, the best of the Prague tram system fleet. During its period of production between 1960 and 1999, 13,991 powered units and 122 unpowered trailers were sold worldwide. It became the most dominant tramcar model in Eastern Bloc countries, except for Poland, where locally produced trams from Konstal factory are still the mainstay in tram systems there, and Hungary, where ČKD only made inroads to the country's tram market during the late 1970s. Together with Soviet KTM-5 it is among the most produced trams, as of 2022, it is still the most widespread tram car in the world. Types T3 The design of the T3 had to meet difficult specifications. The cars needed to have the same capacity as its predecessor (the Tatra T2), but be easier to build. Some of the things that were done to meet this goal were making the walls thinner, and fitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
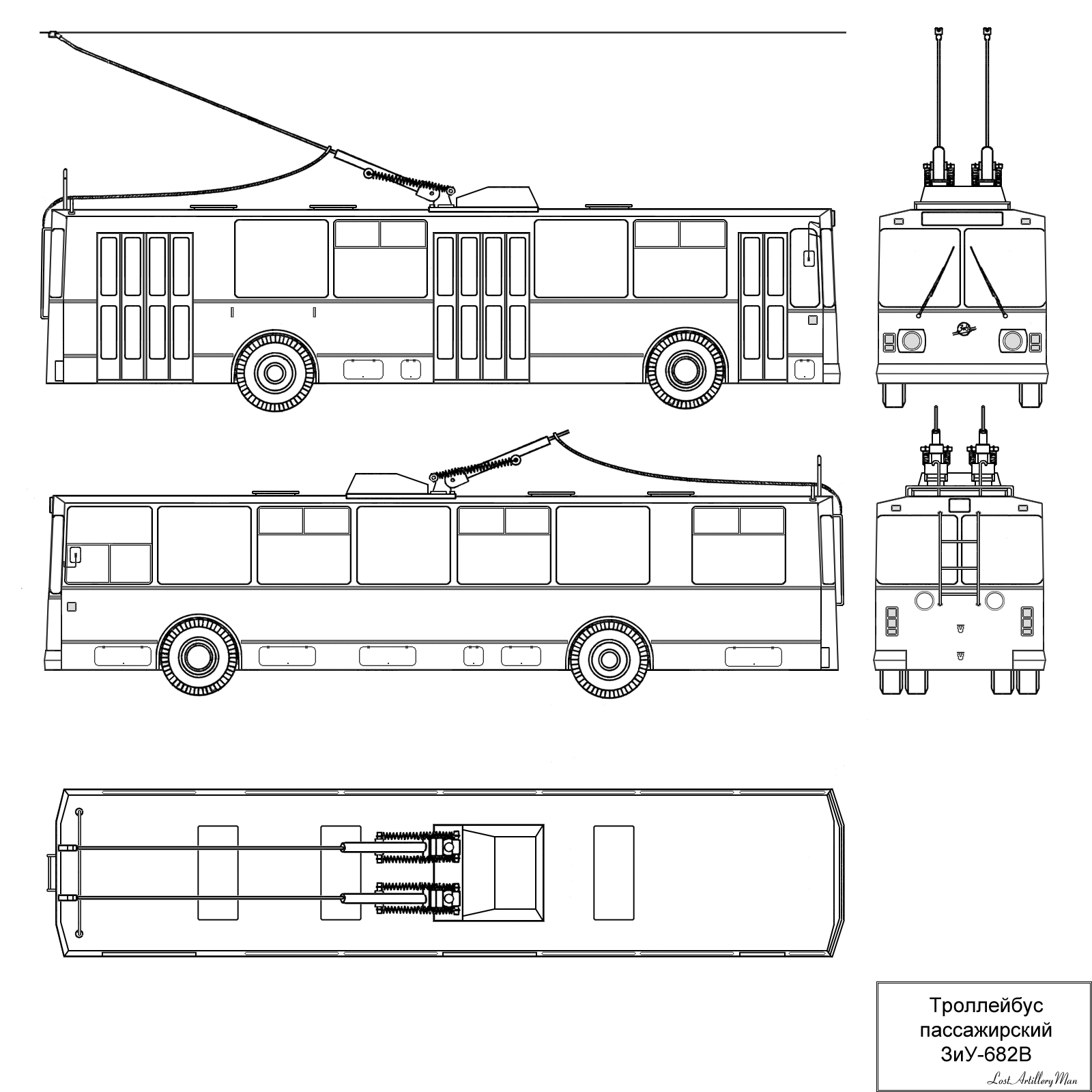
ZiU-9
ZiU-9, or ZIU-9 (Cyrillic: ЗиУ-9) is a Soviet Union, Soviet (and later Russian) trolleybus. Other names for the ZiU-9 are ZiU-682 and HTI-682 (Cyrillic: ЗиУ-682 and ХТИ-682). The ZiU acronym stands for "Zavod imeni Uritskogo", which means a factory named after Moisei Uritsky, the Russian revolutionary. Before 1996 this acronym was also a trademark of the vehicle manufacturer ''Trolza''. The ZiU-9 was first built in 1966, although it was only put into mass production in 1972 and it was still assembled along with other more advanced trolleybus vehicles in the Trolza (former ZiU) factory until 2015. The total number of produced ZiU-9s exceeds 42,000 vehicles making it the most produced trolleybus in the world. Many copies of the ZiU-9 were made in other factories of the former Soviet bloc. Following the Soviet era, many cities still utilize the ZiU-9 as their primary trolleybus; for example Cheboksary, Ryazan, Vinnitsa and others. History and development The explosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rába (company)
The RÁBA Automotive Group (), commonly known as Rába, is a Hungary, Hungarian public limited company, listed on the Budapest Stock Exchange. Rába engineers, manufactures and customizes automotive components, specialty vehicles and axles for commercial vehicles, agri-machinery and earth-movers. The Rába has been building axles as well as complete vehicles since 1902. The company has three strategic business units. The company is headquartered in Győr, employing more than 2000 people. History The company was founded by local investor groups in Győr in 1896. In 1899, the Rába had started to export to foreign countries: it supplied railway passenger carriages to Egypt, the East Indies, Southern Africa, city tramcars to Amsterdam and Antwerp. The carriages of the London underground railway were constructed and manufactured in the Rába company. The London Underground Railway ordered 30 multiple-unit trains, 66 passenger cars for multiple-unit trains and bogies. In 1904, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian People's Republic
The Hungarian People's Republic (HPR) was a landlocked country in Central Europe from its formation on 20 August 1949 until the establishment of the current Hungary, Republic of Hungary on 23 October 1989. It was a professed Communist_state#People's_democratic_state, communist state, governed first by the Hungarian Working People's Party and after the Hungarian Revolution of 1956, the Hungarian Socialist Workers' Party. Both governments were closely tied to the Soviet Union as part of the Eastern Bloc.Rao, B. V. (2006), ''History of Modern Europe A.D. 1789–2002'', Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. The state considered itself the heir to the Hungarian Soviet Republic, which was formed in 1919 as one of the first communist states created after the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR). It was designated a "people's democracy (Marxism–Leninism), people's democratic republic" by the Soviet Union in the 1940s. Geographically, it bordered Socialist Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Steering
Power steering is a system for reducing a driver's effort to turn a steering wheel of a motor vehicle, by using a power source to assist steering. Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver can provide less effort to turn the steered wheels when driving at typical speeds, and considerably reduce the physical effort necessary to turn the wheels when a vehicle is stopped or moving slowly. Power steering can also be engineered to provide some artificial feedback of forces acting on the steered wheels. Hydraulic power steering systems for cars augment steering effort via an actuator, a hydraulic cylinder that is part of a servo system. These systems have a direct mechanical connection between the steering wheel and the steering linkage that steers the wheels. This means that power-steering system failure (to augment effort) still permits the vehicle to be steered using manual effort alone. Electric power steering systems use elec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MAZ-500
MAZ-500 is a Soviet truck manufactured at the Minsk Automobile Plant. The first prototype MAZ-500 ran as early as 1955 and they were shown to the public in 1958. Delays in engine development pushed full production back to 1965, although limited production started in 1963. The MAZ-500 is a cab over truck instead of the MAZ-200's conventional layout. This was done to increase payload and reduce weight as well as reduce fuel consumption. The engine itself was quite modern, a direct injection diesel V6 built by the Yaroslavl Motor Plant (who had also originally developed the preceding MAZ-200 truck) with at 2100 rpm. The truck's design was also innovative, with a tilting cabin, which was still rare in the West as well. It also had a number of features designed to make the truck operable under the arduous conditions found in Siberia. The MAZ-500/500A was in production from 1963 (with full production commencing in 1965) until 1977 with modernizations taking place in 1970 and 1977 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Škoda 9Tr
Škoda means "pity" in the Czech and Slovak languages. It may also refer to: Czech brands and enterprises * Škoda Auto, automobile and previously bicycle manufacturer in Mladá Boleslav ** Škoda Motorsport, the division of Škoda Auto responsible for motorsport activities * Škoda Transportation, engineering company that manufactures rail vehicles, based in Plzeň * Škoda Works, engineering company, predecessor of Škoda Transportation * Škoda-Kauba, aircraft manufacturing subsidiary of the Škoda Works in occupied Czechoslovakia in World War II * Doosan Škoda Power, subsidiary of the Doosan Group, based in Plzeň People * Škoda (surname) * Skoda (Portuguese footballer) (born 1960) Art * ''Škoda lásky'', the original Czech title of the "Beer Barrel Polka" Other * British Rail Class 90, an electric locomotive nicknamed Skoda * ''Skoda'' (barquentine), sailing vessel built in Kingsport, Nova Scotia, in 1893 * Skoda Xanthi F.C., former name of the Greek football club Xan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZiU-5
The ZiU-5 (in Russian ''ЗиУ-5'') is a Soviet Union, Soviet trolleybus model that was built by the Uritsky (company), Uritsky factory. The ZiU acronym stands for ''Zavod imeni Uritskogo'' (in Russian ''Завод имени Урицкого'', ''ЗиУ''), which translates as ''Plant named after Uritskiy'' (Moisei Uritsky, a Russian revolutionary). This model of city trolleybus was in mass production from 1959 to 1972. The total number of ZiU-5s produced exceeded 14,500 vehicles. This allowed the ZiU-5 to become dominant model of trolleybus in Soviet towns and cities of that time. The last vehicles were withdrawn from active service in the mid-1980s (the exact date varies from city to city). The small number of surviving vehicles are kept now for museum purposes. History of development The first decade after the Second World War was a period of huge expansion of trolleybus systems in the Soviet Union. They were considered as an innovative decision in comparison with "semi-obso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharkiv
Kharkiv, also known as Kharkov, is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city in Ukraine.Kharkiv "never had eastern-western conflicts" , ''Euronews'' (23 October 2014) Located in the northeast of the country, it is the largest city of the historic region of Sloboda Ukraine. Kharkiv is the administrative centre of Kharkiv Oblast and Kharkiv Raion. Prior to the Russian invasion of Ukraine in early 2022, it had an estimated population of 1,421,125. Founded in 1654 as a Cossacks, Cossack fortress, by late 19th century Kharkiv had developed within the Russian Empire as a major commercial and industrial centre. From December 1919 to January 1934, Kharkiv was the capital of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |