|
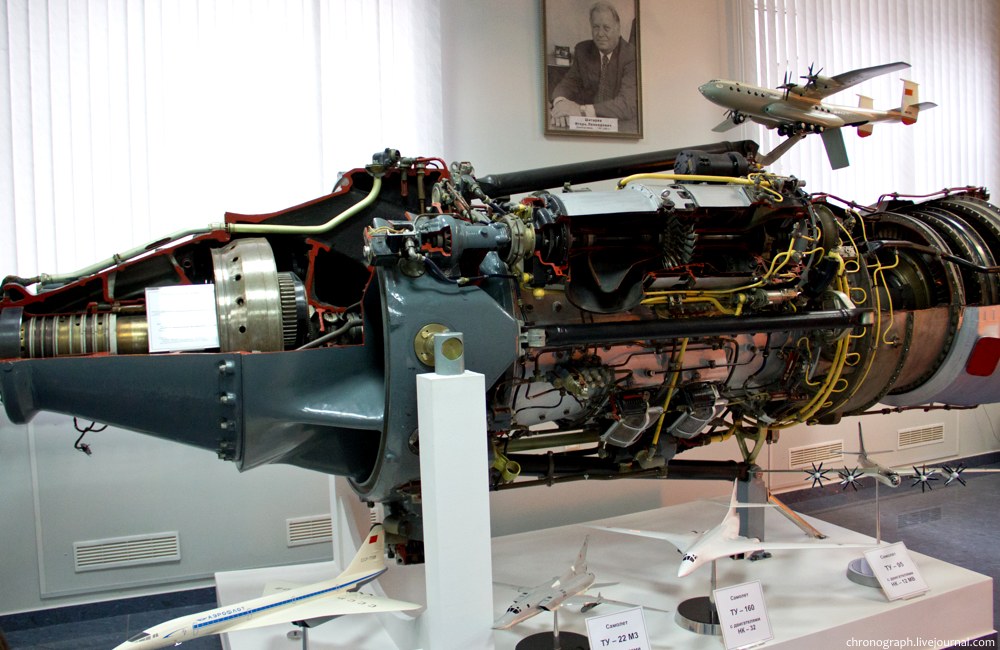
Kuznetsov TV-022
The Kuznetsov TV-022 was the first Soviet turboprop engine, designed by the Kuybyshev Engine Design Bureau. Development Development of the TV-022 began in 1947 at the State Union Experimental Plant No. 2 near Kuybyshev. A team of both Soviet and deported German engineers worked on the project. The TV-022 was based on the uncompleted Junkers Jumo 022 turboprop designed by Junkers during the later stages of World War II. Factory tests of the TV-022 took place in June 1949 and state tests where passed in October 1950. The TV-022 featured a reduction gearbox (i=0.145) for two coaxial contra-rotating AB-41 propellers. The engine was started with a 50 kW "Rut" air starter. Modifications to the TV-022 resulted in the TV-2, which had more power (6,250 hp). The TV-2 was then further modified into the NK-12 The Kuznetsov NK-12 is a Soviet turboprop engine of the 1950s, designed by the Kuznetsov design bureau. The NK-12 drives two large four-bladed contra-rotating propeller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough energy to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtained by extracting additional power (beyond that necessary to drive the compressor) from turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a Federation, federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, fifteen national republics; in practice, both Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, its economy were highly Soviet-type economic planning, centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Saint Petersburg, Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kyiv, Kiev (Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic, Ukrainian SSR), Minsk (Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic, Byelorussian SSR), Tas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuznetsov Design Bureau
The Kuznetsov Design Bureau (russian: СНТК им. Н. Д. Кузнецова, also known as OKB-276) was a Russian design bureau for aircraft engines, administrated in Soviet times by Nikolai Dmitriyevich Kuznetsov. It was also known as (G)NPO Trud (or NPO Kuznetsov) and Kuybyshev Engine Design Bureau (KKBM). NPO Trud was replaced in 1994 by a Joint Stock Company (JSC), Kuznetsov R & E C. By the early 2000s the lack of funding caused by the poor economic situation in Russia had brought Kuznetsov on the verge of bankruptcy. In 2009 the Russian government decided to consolidate a number of engine-making companies in the Samara region under a new legal entity. This was named JSC Kuznetsov, after the design bureau. Products The Kuznetzov Bureau first became notable for producing the monstrous Kuznetsov NK-12 turboprop engine that powered the Tupolev Tu-95 bomber beginning in 1952 as a development of the Junkers 0022 engine. The new engine eventually generated about 15,000 ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers Jumo 022
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded there in Dessau, Germany, in 1895 by Hugo Junkers, initially manufacturing boilers and radiators. During World War I and following the war, the company became famous for its pioneering all-metal aircraft. During World War II the company produced the German army's Luftwaffe planes, as well as piston and jet aircraft engines, albeit in the absence of its founder, who had been removed by the Nazis in 1934. History Early inter-war period In the immediate post-war era, Junkers used their J8 layout as the basis for the F-13, first flown on 25 June 1919 and certified airworthy in July of the same year. This four passenger monoplane was the world's first all-metal airliner. Of note, in addition to significant European sales, some twenty-five of these airplanes w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuznetsov TV-2
The Kuznetsov TV-2 was an early Soviet turboprop engine, designed by the Kuybyshev Engine Design Bureau. Applications ;TV-2F: Antonov An-8 (proposed) Tupolev '101' (project)Tupolev '102' (project)Tupolev Tu-118 (project) ;TV-2M: Tupolev Tu-91 The Tupolev Tu-91 (NATO reporting name Boot) was a Soviet carrier-borne attack aircraft. It was built only in prototype form, and was converted into a land-based aircraft after Joseph Stalin's death in 1953 cancelled the aircraft carriers being ... (prototype only) ;TV-2T: Antonov An-8 (proposed) Specifications (TV-2F) See also References {{Aeroengine-specs 1950s turboprop engines Kuznetsov aircraft engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turboprop
A turboprop is a turbine engine that drives an aircraft propeller. A turboprop consists of an intake, reduction gearbox, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air enters the intake and is compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine stages, generating power at the point of exhaust. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor and electric generator. The gases are then exhausted from the turbine. In contrast to a turbojet or turbofan, the engine's exhaust gases do not provide enough energy to create significant thrust, since almost all of the engine's power is used to drive the propeller. Technological aspects Exhaust thrust in a turboprop is sacrificed in favor of shaft power, which is obtained by extracting additional power (beyond that necessary to drive the compressor) from turb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samara
Samara ( rus, Сама́ра, p=sɐˈmarə), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara rivers, with a population of over 1.14 million residents, up to 1.22 million residents in the urban agglomeration, not including Novokuybyshevsk, which is not conurbated. The city covers an area of , and is the eighth-largest city in Russia and tenth agglomeration, the third-most populous city on the Volga, as well as the Volga Federal District. Formerly a closed city, Samara is now a large and important social, political, economic, industrial, and cultural centre in Russia and hosted the European Union—Russia Summit in May 2007. It has a continental climate characterised by hot summers and cold winters. The life of Samara's citizens has always been intrinsically linked to the Volga River, which has not only served as the main commercial thoroughfare of Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers
Junkers Flugzeug- und Motorenwerke AG (JFM, earlier JCO or JKO in World War I, English: Junkers Aircraft and Motor Works) more commonly Junkers , was a major German aircraft and aircraft engine manufacturer. It was founded there in Dessau, Germany, in 1895 by Hugo Junkers, initially manufacturing boilers and radiators. During World War I and following the war, the company became famous for its pioneering all-metal aircraft. During World War II the company produced the German army's Luftwaffe planes, as well as piston and jet aircraft engines, albeit in the absence of its founder, who had been removed by the Nazis in 1934. History Early inter-war period In the immediate post-war era, Junkers used their J8 layout as the basis for the F-13, first flown on 25 June 1919 and certified airworthy in July of the same year. This four passenger monoplane was the world's first all-metal airliner. Of note, in addition to significant European sales, some twenty-five of these air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million Military personnel, personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Air warfare of World War II, Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contra-rotating
Contra-rotating, also referred to as coaxial contra-rotating, is a technique whereby parts of a mechanism rotate in opposite directions about a common axis, usually to minimise the effect of torque. Examples include some aircraft propellers, resulting in the maximum power of a single piston or turboprop engine to drive two propellers in opposite rotation. Contra-rotating propellers are also common in some marine transmission systems, in particular for large speed boats with planing hulls. Two propellers are arranged one behind the other, and power is transferred from the engine via planetary gear transmission. The configuration can also be used in helicopter designs termed coaxial rotors, where similar issues and principles of torque apply. Contra-rotating propellers should not be confused with counter-rotating propellers, a term which describes non-coaxial propellers on separate shafts; one turning clockwise and the other counter-clockwise. Tandem-rotor helicopters such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuznetsov NK-12
The Kuznetsov NK-12 is a Soviet turboprop engine of the 1950s, designed by the Kuznetsov design bureau. The NK-12 drives two large four-bladed contra-rotating propellers, diameter (NK-12MA), and diameter (NK-12MV). It is the most powerful turboprop engine to enter service. Design and development The design that eventually became the NK-12 turboprop was developed after World War II by a team of Soviet scientists and deported German engineers under Ferdinand Brandner, who had worked for Junkers previously; the design bureau was headed by chief engineer Nikolai D. Kuznetsov. Thus, the NK-12 design evolved from late-war German turboprop studies. This started with the postwar development of the wartime Jumo 022 turboprop design that was designed to develop , weighing . The effort continued with a , weighing , completed by 1947. Evolution to the TV-12 engine required extensive use of new Soviet-developed alloys and was completed in 1951. The NK-12 is the most powerful turboprop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |