|
Konstantina Bay
Konstantina Bay (Russian: ''Zaliv Konstantina'') is a small bay in the northwestern Sea of Okhotsk, just south of the Shantar Islands. It is a western branch of the larger Academy Bay to the east. The bay is about 9.6 km (6 mi) in diameter and its entrance is about 4.8 km (3 mi) wide. Spring tides rise 3.8 m (12.5 ft), while neaps rise 2.7 m (9 ft).United States. (1918). ''Asiatic Pilot, Volume 1: East coast of Siberia, Sakhalin Island and Chosen''. Washington: Hydrographic Office. Flora and fauna The bay's shores are covered with fir, larch, pine, birch, and various other species of trees. Waders use the southern part of Konstantina Bay as a stopover during their summer migration. The most abundant species is Terek sandpiper.Pronkevich, V. V. (1998). "Migration of waders in the Khabarovsk region of the Far East". ''International Wader Studies'' 10: 425-430. History It was frequented by American and Russian whaleships targeting bowhead whale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. It is the most spoken Slavic language, and the most spoken native language in Europe, as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird Migration
Bird migration is the regular seasonal movement, often north and south along a flyway, between breeding and wintering grounds. Many species of bird migrate. Migration carries high costs in predation and mortality, including from hunting by humans, and is driven primarily by the availability of food. It occurs mainly in the northern hemisphere, where birds are funneled onto specific routes by natural barriers such as the Mediterranean Sea or the Caribbean Sea. Migration of species such as storks, turtle doves, and swallows was recorded as many as 3,000 years ago by Ancient Greek authors, including Homer and Aristotle, and in the Book of Job. More recently, Johannes Leche began recording dates of arrivals of spring migrants in Finland in 1749, and modern scientific studies have used techniques including bird ringing and satellite tracking to trace migrants. Threats to migratory birds have grown with habitat destruction, especially of stopover and wintering sites, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Bedford, Massachusetts
New Bedford ( Massachusett: ) is a city in Bristol County, Massachusetts Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut [Massachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət],'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England .... It is located on the Acushnet River in what is known as the South Coast (Massachusetts), South Coast region. Up through the 17th century, the area was the territory of the Wampanoag Native American people. English colonists bought the land on which New Bedford would later be built from the Wampanoag in 1652, and the original colonial settlement that would later become the city was founded by English Quakers in the late 17th century. The town of New Bedford itself was officially incorporated in 1787. During the first half of the 19th century, New Bedford was one of the world's most important whaling ports. At its economic height during this period, New Bedfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
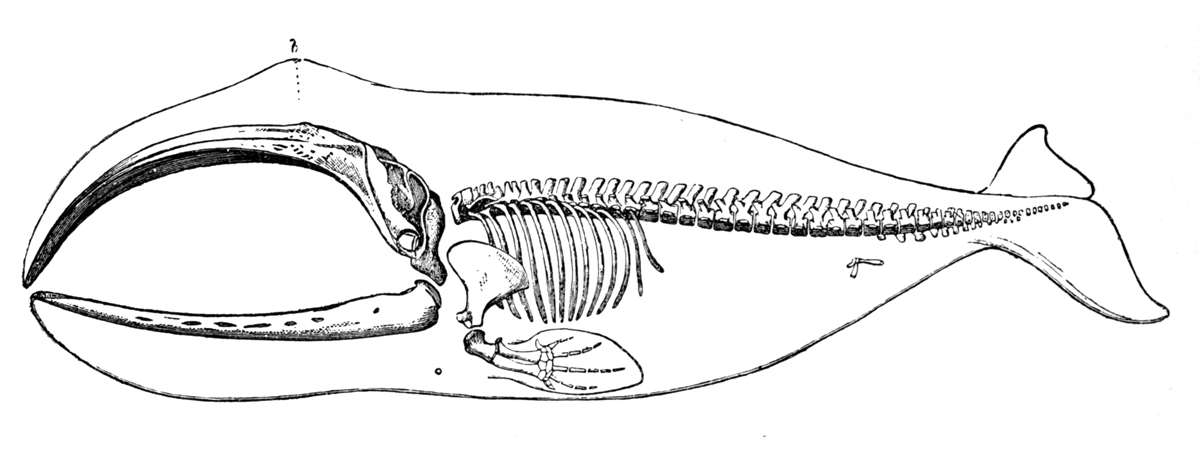
Bowhead Whales
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus'') is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. They are the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and are named after their characteristic massive triangular skull, which they use to break through Arctic ice. Other common names of the species are the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and Arviq in aboriginal languages (Inuktitut). American whalemen called them the steeple-top, polar whale, or Russian whale. Bowheads have the largest mouth of any animal representing almost one-third of the length of the body, the longest baleen plates with a maximum length of and may be the longest-lived mammals, with the ability to reach an age of more than 200 years. The bowhead was an early whaling target. Their population was severely reduced before a 1966 moratorium was passed to protect the species. Of the five stocks of bowhead populations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales. Terminology The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Japan, still dedicates a single factory ship for the industry. The vessels used by aboriginal whaling communities are much smaller and are used for various purposes over the course of the year. The ''whale catcher'' was developed during the age of steam, and then driven by diesel engines throughout much of the twentieth century. It was designed with a harpoon gun mounted at its bow and was fast enough to chase and catch rorquals such as the fin whale. At first, whale catchers either brought the whales they killed to a whaling station, a settlement ashore where the carcasses could be processed, or to its factory ship anchored in a sheltered bay or inlet. With the later development of the slipway at the ship's stern, whale catchers were abl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terek Sandpiper
The Terek sandpiper (''Xenus cinereus'') is a small migratory Palearctic wader species and is the only member of the genus ''Xenus''. It is named after the Terek River which flows into the west of the Caspian Sea, as it was first observed around this area. Taxonomy The Terek sandpiper was formally described and illustrated in 1775 by the German naturalist Johann Anton Güldenstädt under the binomial name ''Scolopax cinerea''. He reported that he had seen pairs breeding at the mouth of the Terek River where it flows into the Caspian Sea. It is now the only species placed in the genus ''Xenus'' that was introduced in 1829 by the German naturalist Johann Jakob Kaup. The genus name ''Xenus'' is from Ancient Greek ''xenos'' meaning "stranger"; the specific epithet ''cinereus'' is Latin for "ash-grey" from ''cinis, cineris'', "ashes". The species is considered to be monotypic, no subspecies are recognised. Among the Scolopacidae, ''Xenus'' is part of the shank- tattler- phalarope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wader
245px, A flock of Red_knot.html" ;"title="Dunlins and Red knot">Dunlins and Red knots Waders or shorebirds are birds of the order Charadriiformes commonly found wikt:wade#Etymology 1, wading along shorelines and mudflats in order to foraging, forage for food crawling or burrowing in the mud and sand, usually small arthropods such as aquatic insects or crustaceans. The term "wader" is used in Europe, while "shorebird" is used in North America, where "wader" may be used instead to refer to long-legged wading birds such as storks and herons. There are about 210 species of wader, most of which live in wetland or coastal environments. Many species of Arctic and temperate regions are strongly migratory, but tropical birds are often resident, or move only in response to rainfall patterns. Some of the Arctic species, such as the little stint, are amongst the longest distance migrants, spending the non- breeding season in the southern hemisphere. Many of the smaller species found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and north. The northeast corner is the Shelikhov Gulf. The sea is named after the Okhota river, which in turn named after the Even word () meaning "river". Geography The Sea of Okhotsk covers an area of , with a mean depth of and a maximum depth of . It is connected to the Sea of Japan on either side of Sakhalin: on the west through the Sakhalin Gulf and the Gulf of Tartary; on the south through the La Pérouse Strait. In winter, navigation on the Sea of Okhotsk is impeded by ice floes. Ice floes form due to the large amount of freshwater from the Amur River, lowering the sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains 30 to 60 known taxa of which 11 are on the IUCN 2011 Red List of Threatened Species. They are a typically rather short-lived pioneer species widespread in the Northern Hemisphere, particularly in northern areas of temperate climates and in boreal climates. Description Birch species are generally small to medium-sized trees or shrubs, mostly of northern temperate and boreal climates. The simple leaves are alternate, singly or doubly serrate, feather-veined, petiolate and stipulate. They often appear in pairs, but these pairs are really borne on spur-like, two-leaved, lateral branchlets. The fruit is a small samara, although the wings may be obscure in some species. They differ from the alders (''Alnus'', another genus in the family) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts 187 species names of pines as current, together with more synonyms. The American Conifer Society (ACS) and the Royal Horticultural Society accept 121 species. Pines are commonly found in the Northern Hemisphere. ''Pine'' may also refer to the lumber derived from pine trees; it is one of the more extensively used types of lumber. The pine family is the largest conifer family and there are currently 818 named cultivars (or Trinomial nomenclature, trinomials) recognized by the ACS. Description Pine trees are evergreen, coniferous resinous trees (or, rarely, shrubs) growing tall, with the majority of species reaching tall. The smallest are Siberian dwarf pine and Potosi pinyon, and the tallest is an tall ponderosa pine lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |