|
Kleptography
Kleptography is the study of stealing information securely and subliminally. The term was introduced by Adam Young and Moti Yung in the Proceedings of Advances in Cryptology – Crypto '96. Kleptography is a subfield of cryptovirology and is a natural extension of the theory of subliminal channels that was pioneered by Gustavus Simmons, Gus Simmons while at Sandia National Laboratory. A kleptographic backdoor is synonymously referred to as an asymmetric backdoor. Kleptography encompasses secure and covert communications through cryptosystems and cryptographic protocols. This is reminiscent of, but not the same as steganography that studies covert communications through graphics, video, digital audio data, and so forth. Kleptographic attack Meaning A kleptographic attack is an attack which uses asymmetric cryptography to implement a cryptographic backdoor (computing), backdoor. For example, one such attack could be to subtly modify how the public-key cryptography, public and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual EC DRBG
Dual_EC_DRBG (Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic Random Bit Generator) is an algorithm that was presented as a cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) using methods in elliptic curve cryptography. Despite wide public criticism, including the public identification of the possibility that the National Security Agency put a backdoor (cryptography), backdoor into a recommended implementation, it was, for seven years, one of four CSPRNGs standardized in NIST SP 800-90A as originally published circa June 2006, until it was withdrawn in 2014. Weakness: a potential backdoor Weaknesses in the cryptographic security of the algorithm were known and publicly criticised well before the algorithm became part of a formal standard endorsed by the American National Standards Institute, ANSI, International Organization for Standardization, ISO, and formerly by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). One of the weaknesses publicly identified was the pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptographic Attack
Kleptography is the study of stealing information securely and subliminally. The term was introduced by Adam Young and Moti Yung in the Proceedings of Advances in Cryptology – Crypto '96. Kleptography is a subfield of cryptovirology and is a natural extension of the theory of subliminal channels that was pioneered by Gus Simmons while at Sandia National Laboratory. A kleptographic backdoor is synonymously referred to as an asymmetric backdoor. Kleptography encompasses secure and covert communications through cryptosystems and cryptographic protocols. This is reminiscent of, but not the same as steganography that studies covert communications through graphics, video, digital audio data, and so forth. Kleptographic attack Meaning A kleptographic attack is an attack which uses asymmetric cryptography to implement a cryptographic backdoor. For example, one such attack could be to subtly modify how the public and private key pairs are generated by the cryptosystem so that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moti Yung
Mordechai M. "Moti" Yung is a cryptographer and computer scientist known for his work on cryptovirology and kleptography. Career Yung earned his PhD from Columbia University in 1988 under the supervision of Zvi Galil. In the past, he worked at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, CertCo, RSA Laboratories, and Google. In 2016, Yung moved from Google to Snap Inc. Yung is currently a research scientist at Google. Yung is an adjunct senior research faculty member at Columbia University, and has co-advised PhD students including Gödel Prize winner Matthew K. Franklin, Jonathan Katz, and Aggelos Kiayias. Research Yung research covers primarily the area of cryptography and its applications to information security and data privacy. He has worked on defining and implementing malicious (offensive) cryptography: cryptovirology and kleptography, and on various other foundational and applied fields of cryptographic research, including: user and entity electronic authent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptographic Pseudo-random Number Generator
A cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) or cryptographic pseudorandom number generator (CPRNG) is a pseudorandom number generator (PRNG) with properties that make it suitable for use in cryptography. It is also referred to as a cryptographic random number generator (CRNG). Background Most cryptographic applications require random numbers, for example: * key generation * initialization vectors * nonces * salts in certain signature schemes, including ECDSA and RSASSA-PSS * token generation The "quality" of the randomness required for these applications varies. For example, creating a nonce in some protocols needs only uniqueness. On the other hand, the generation of a master key requires a higher quality, such as more entropy. And in the case of one-time pads, the information-theoretic guarantee of perfect secrecy only holds if the key material comes from a true random source with high entropy, and thus just any kind of pseudorandom number genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backdoor (computing)
A backdoor is a typically covert method of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer, product, embedded device (e.g. a home router), or its embodiment (e.g. part of a cryptosystem, algorithm, chipset, or even a "homunculus computer"—a tiny computer-within-a-computer such as that found in Intel's AMT technology). Backdoors are most often used for securing remote access to a computer, or obtaining access to plaintext in cryptosystems. From there it may be used to gain access to privileged information like passwords, corrupt or delete data on hard drives, or transfer information within autoschediastic networks. In the United States, the 1994 Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act forces internet providers to provide backdoors for government authorities. In 2024, the U.S. government realized that China had been tapping communications in the U.S. using that infrastructure for months, or perhaps longer; China recorded presidential candidate campaign offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptovirology
Cryptovirology refers to the study of cryptography use in malware, such as ransomware and asymmetric backdoors. Traditionally, cryptography and its applications are defensive in nature, and provide privacy, authentication, and security to users. Cryptovirology employs a twist on cryptography, showing that it can also be used offensively. It can be used to mount extortion based attacks that cause loss of access to information, loss of confidentiality, and information leakage, tasks which cryptography typically prevents. The field was born with the observation that public-key cryptography can be used to break the symmetry between what an antivirus analyst sees regarding malware and what the attacker sees. The antivirus analyst sees a public key contained in the malware, whereas the attacker sees the public key contained in the malware as well as the corresponding private key (outside the malware) since the attacker created the key pair for the attack. The public key allows the malw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NIST SP 800-90A
NIST SP 800-90A ("SP" stands for "''special publication''") is a publication by the National Institute of Standards and Technology with the title ''Recommendation for Random Number Generation Using Deterministic Random Bit Generators''. The publication contains the specification for three allegedly cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generators for use in cryptography: Hash DRBG (based on hash functions), HMAC DRBG (based on HMAC), and CTR DRBG (based on block ciphers in counter mode). Earlier versions included a fourth generator, Dual_EC_DRBG (based on elliptic curve cryptography). Dual_EC_DRBG was later reported to probably contain a kleptographic backdoor inserted by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). History NIST SP 800-90A was published by the National Institute of Standards and Technology in June 2006 as NIST SP 800-90 with the title ''Recommendation for Random Number Generation Using Deterministic Random Bit Generators''. The publication contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
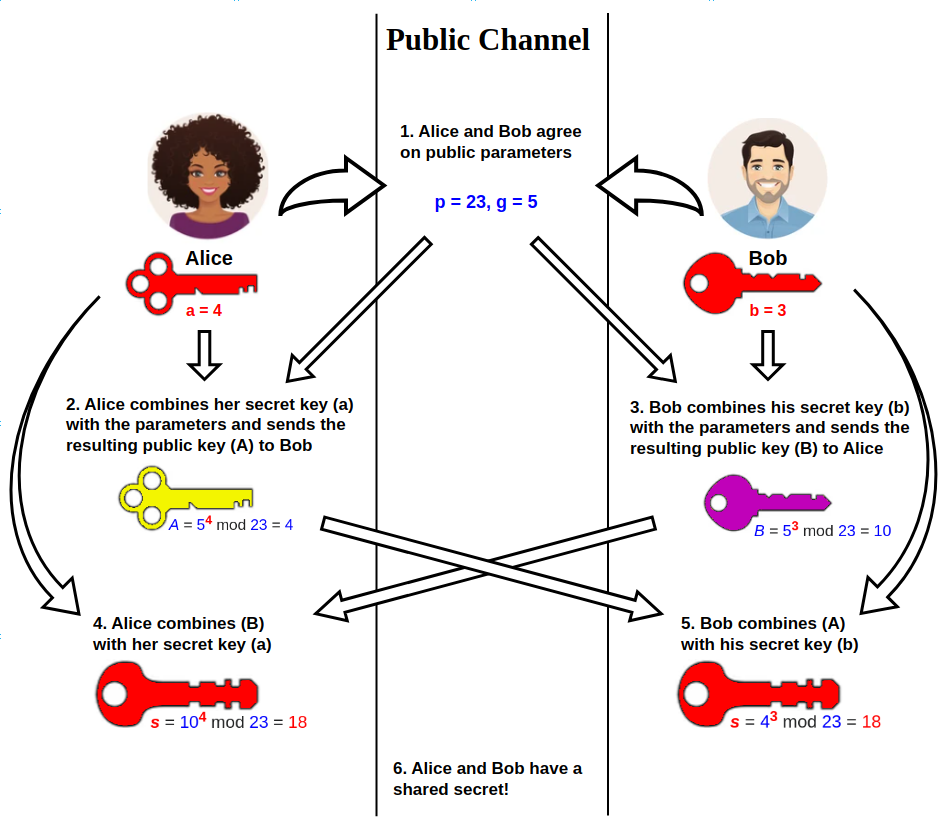
Diffie–Hellman Key Exchange
Diffie–Hellman (DH) key exchangeSynonyms of Diffie–Hellman key exchange include: * Diffie–Hellman–Merkle key exchange * Diffie–Hellman key agreement * Diffie–Hellman key establishment * Diffie–Hellman key negotiation * Exponential key exchange * Diffie–Hellman protocol * Diffie–Hellman handshake is a mathematical method of securely generating a symmetric cryptographic key over a public channel and was one of the first public-key protocols as conceived by Ralph Merkle and named after Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman. DH is one of the earliest practical examples of public key exchange implemented within the field of cryptography. Published in 1976 by Diffie and Hellman, this is the earliest publicly known work that proposed the idea of a private key and a corresponding public key. Traditionally, secure encrypted communication between two parties required that they first exchange keys by some secure physical means, such as paper key lists transported by a tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CrypTool
CrypTool is an open-source project that is a free e-learning software for illustrating cryptographic and cryptanalytic concepts. History The development of CrypTool started in 1998. Originally developed by German companies and universities, it is an open-source project since 2001. Currently 4 versions of CrypTool are maintained and developed: The CrypTool 1 (CT1) software is available in 6 languages (English, German, Polish, Spanish, Serbian, and French). CrypTool 2 (CT2), JCrypTool (JCT), and CrypTool-Online (CTO) are available in English and German. CrypTool 2 builds upon its predecessor, CrypTool 1 by introducing more cryptographic types and analysis tools. The goal of the CrypTool project is to make users aware of how cryptography can help against network security threats and to explain the underlying concepts of cryptology. CrypTool 1 (CT1) is written in C++ and designed for the Microsoft Windows operating system. In 2007, development began on two additional projec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The term can be used to refer to many inner workings, such as those of a transistor, an engine, an algorithm, the human brain, or an institution or government. To analyze an open system with a typical "black box approach", only the behavior of the stimulus/response will be accounted for, to infer the (unknown) ''box''. The usual representation of this "black box system" is a data flow diagram centered in the box. The opposite of a black box is a system where the inner components or logic are available for inspection, which is most commonly referred to as a white box (sometimes also known as a "clear box" or a "glass box"). History The modern meaning of the term "black box" seems to have entered the English language around 1945. In electroni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |