|
Cryptovirology
Cryptovirology refers to the study of cryptography use in malware, such as ransomware and asymmetric backdoors. Traditionally, cryptography and its applications are defensive in nature, and provide privacy, authentication, and security to users. Cryptovirology employs a twist on cryptography, showing that it can also be used offensively. It can be used to mount extortion based attacks that cause loss of access to information, loss of confidentiality, and information leakage, tasks which cryptography typically prevents. The field was born with the observation that public-key cryptography can be used to break the symmetry between what an antivirus analyst sees regarding malware and what the attacker sees. The antivirus analyst sees a public key contained in the malware, whereas the attacker sees the public key contained in the malware as well as the corresponding private key (outside the malware) since the attacker created the key pair for the attack. The public key allows the malw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moti Yung
Mordechai M. "Moti" Yung is a cryptographer and computer scientist known for his work on cryptovirology and kleptography. Career Yung earned his PhD from Columbia University in 1988 under the supervision of Zvi Galil. In the past, he worked at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center, CertCo, RSA Laboratories, and Google. In 2016, Yung moved from Google to Snap Inc. Yung is currently a research scientist at Google. Yung is an adjunct senior research faculty member at Columbia University, and has co-advised PhD students including Gödel Prize winner Matthew K. Franklin, Jonathan Katz, and Aggelos Kiayias. Research Yung research covers primarily the area of cryptography and its applications to information security and data privacy. He has worked on defining and implementing malicious (offensive) cryptography: cryptovirology and kleptography, and on various other foundational and applied fields of cryptographic research, including: user and entity electronic authent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleptography
Kleptography is the study of stealing information securely and subliminally. The term was introduced by Adam Young and Moti Yung in the Proceedings of Advances in Cryptology – Crypto '96. Kleptography is a subfield of cryptovirology and is a natural extension of the theory of subliminal channels that was pioneered by Gustavus Simmons, Gus Simmons while at Sandia National Laboratory. A kleptographic backdoor is synonymously referred to as an asymmetric backdoor. Kleptography encompasses secure and covert communications through cryptosystems and cryptographic protocols. This is reminiscent of, but not the same as steganography that studies covert communications through graphics, video, digital audio data, and so forth. Kleptographic attack Meaning A kleptographic attack is an attack which uses asymmetric cryptography to implement a cryptographic backdoor (computing), backdoor. For example, one such attack could be to subtly modify how the public-key cryptography, public and pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
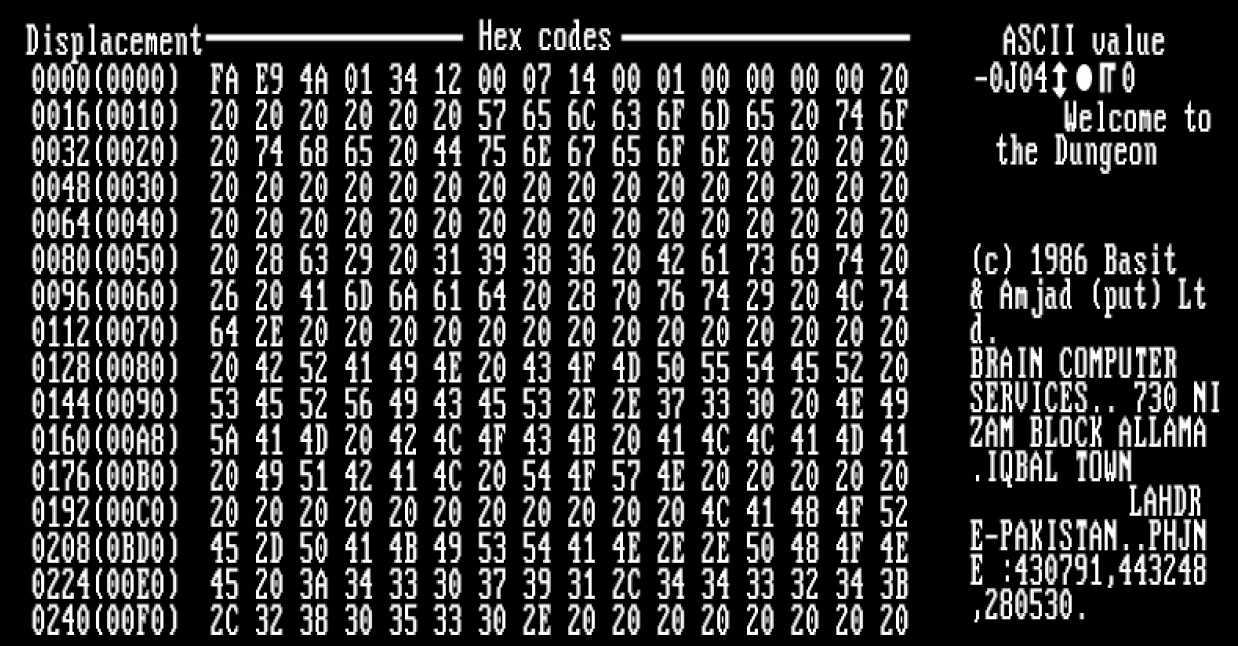
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that Encryption, encrypts the victim's personal data until a ransom is paid. Difficult-to-trace Digital currency, digital currencies such as paysafecard or Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency, cryptocurrencies are commonly used for the ransoms, making tracing and prosecuting the perpetrators difficult. Sometimes the original files can be retrieved without paying the ransom due to implementation mistakes, leaked cryptographic keys or a complete lack of encryption in the ransomware. Ransomware attacks are typically carried out using a Trojan horse (computing), Trojan disguised as a legitimate file that the user is tricked into downloading or opening when it arrives as an email attachment. However, one high-profile example, the WannaCry worm, traveled automatically between computers without user interaction. Starting as early as 1989 with the first documented ransomware known as the AIDS (Trojan horse), AIDS trojan, the use of ransomware scams grew inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backdoor (computing)
A backdoor is a typically covert method of bypassing normal authentication or encryption in a computer, product, embedded device (e.g. a home router), or its embodiment (e.g. part of a cryptosystem, algorithm, chipset, or even a "homunculus computer"—a tiny computer-within-a-computer such as that found in Intel's AMT technology). Backdoors are most often used for securing remote access to a computer, or obtaining access to plaintext in cryptosystems. From there it may be used to gain access to privileged information like passwords, corrupt or delete data on hard drives, or transfer information within autoschediastic networks. In the United States, the 1994 Communications Assistance for Law Enforcement Act forces internet providers to provide backdoors for government authorities. In 2024, the U.S. government realized that China had been tapping communications in the U.S. using that infrastructure for months, or perhaps longer; China recorded presidential candidate campaign offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual EC DRBG
Dual_EC_DRBG (Dual Elliptic Curve Deterministic Random Bit Generator) is an algorithm that was presented as a cryptographically secure pseudorandom number generator (CSPRNG) using methods in elliptic curve cryptography. Despite wide public criticism, including the public identification of the possibility that the National Security Agency put a backdoor (cryptography), backdoor into a recommended implementation, it was, for seven years, one of four CSPRNGs standardized in NIST SP 800-90A as originally published circa June 2006, until it was withdrawn in 2014. Weakness: a potential backdoor Weaknesses in the cryptographic security of the algorithm were known and publicly criticised well before the algorithm became part of a formal standard endorsed by the American National Standards Institute, ANSI, International Organization for Standardization, ISO, and formerly by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). One of the weaknesses publicly identified was the pote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goat File
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server (computing), server, Client (computing), client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. Researchers tend to classify malware into one or more sub-types (i.e. computer viruses, Computer worm, worms, Trojan horse (computing), Trojan horses, logic bombs, ransomware, spyware, adware, rogue software, Wiper (malware), wipers and keyloggers). Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to NortonLifeLock, Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gpcode
PGPCoder or GPCode is a trojan that encrypts files on the infected computer and then asks for a ransom in order to release these files, a type of behavior dubbed ransomware or cryptovirology. Trojan Once installed on a computer, the trojan creates two registry keys: one to ensure it is run on every system startup, and the second to monitor the progress of the trojan in the infected computer, counting the number of files that have been analyzed by the malicious code. Once it has been run, the trojan embarks on its mission, which is to encrypt, using a digital encryption key, all the files it finds on computer drives with extensions corresponding to those listed in its code. These extensions include .doc, .html, .jpg, .xls, .zip, and .rar. The blackmail is completed with the trojan dropping a text file in each directory, with instructions to the victim of what to do. An email address is supplied through which users are supposed to request for their files to be released after payi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malware
Malware (a portmanteau of ''malicious software'')Tahir, R. (2018)A study on malware and malware detection techniques . ''International Journal of Education and Management Engineering'', ''8''(2), 20. is any software intentionally designed to cause disruption to a computer, server (computing), server, Client (computing), client, or computer network, leak private information, gain unauthorized access to information or systems, deprive access to information, or which unknowingly interferes with the user's computer security and privacy. Researchers tend to classify malware into one or more sub-types (i.e. computer viruses, Computer worm, worms, Trojan horse (computing), Trojan horses, logic bombs, ransomware, spyware, adware, rogue software, Wiper (malware), wipers and keyloggers). Malware poses serious problems to individuals and businesses on the Internet. According to NortonLifeLock, Symantec's 2018 Internet Security Threat Report (ISTR), malware variants number has increased to 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Viruses
A computer virus is a type of malware that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code into those programs. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. By contrast, a computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptosystem
In cryptography, a cryptosystem is a suite of cryptographic algorithms needed to implement a particular security service, such as confidentiality (encryption). Typically, a cryptosystem consists of three algorithms: one for key generation, one for encryption, and one for decryption. The term ''cipher'' (sometimes ''cypher'') is often used to refer to a pair of algorithms, one for encryption and one for decryption. Therefore, the term ''cryptosystem'' is most often used when the key generation algorithm is important. For this reason, the term ''cryptosystem'' is commonly used to refer to public key techniques; however both "cipher" and "cryptosystem" are used for symmetric key techniques. Formal definition Mathematically, a cryptosystem or encryption scheme can be defined as a tuple (\mathcal,\mathcal,\mathcal,\mathcal,\mathcal) with the following properties. # \mathcal is a set called the "plaintext space". Its elements are called plaintexts. # \mathcal is a set called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Department Of Health And Human Services
The United States Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) is a cabinet-level executive branch department of the US federal government created to protect the health of the US people and providing essential human services. Its motto is "Improving the health, safety, and well-being of America". Before the separate federal Department of Education was created in 1979, it was called the Department of Health, Education, and Welfare (HEW). HHS is administered by the secretary of health and human services, who is appointed by the president with the advice and consent of the United States Senate. The United States Public Health Service Commissioned Corps, the uniformed service of the PHS, is led by the surgeon general who is responsible for addressing matters concerning public health as authorized by the secretary or by the assistant secretary for health in addition to his or her primary mission of administering the Commissioned Corps. History Federal Security Agency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an Logical assertion, assertion, such as the Digital identity, identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicating a person or thing's identity, authentication is the process of verifying that identity. Authentication is relevant to multiple fields. In art, antiques, and anthropology, a common problem is verifying that a given artifact was produced by a certain person, or in a certain place (i.e. to assert that it is not counterfeit), or in a given period of history (e.g. by determining the age via carbon dating). In computer science, verifying a user's identity is often required to allow access to confidential data or systems. It might involve validating personal identity documents. In art, antiques and anthropology Authentication can be considered to be of three types: The ''first'' type of authentication is accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |