|
Khandbari Municipality
Khandbari is the district headquarters of Sankhuwasabha District in Koshi Province of north-eastern Nepal. Demographics At the time of the 2011 Nepal census, Khandbari Municipality had a population of 31,534. Of these, 68.7% spoke Nepali, 5.5% Lohorung, 4.1% Tamang, 3.5% Sherpa, 3.1% Rai, 2.9% Kulung, 2.8% Magar, 2.1% Newar, 1.7% Gurung, 0.8% Yamphu, 0.4% Thulung, 0.3% Khaling, 0.3% Koi, 0.3% Limbu, 0.3% Maithili, 0.2% Bantawa, 0.2% Bhujel, 0.2% Chamling, 0.2% Dumi, 0.2% Kulung, 0.2% Majhi, 0.2% Mewahang, 0.2% Nachhiring, 0.2% Yakkha, 0.1% Bahing, 0.1% Bote, 0.1% Lhomi, 0.1% Sampang, 0.1% Tharu and 0.8% other languages as their first language. In terms of ethnicity/caste, 19.4% were Chhetri, 18.2% Rai, 9.1% Newar, 7.9% Hill Brahmin, 7.5% Gurung, 7.2% Kami, 6.9% Tamang, 5.3% Magar, 3.1% Sherpa, 2.9% Damai/Dholi, 2.8% Kumal, 1.9% Sarki, 1.3% Kulung, 0.8% Limbu, 0.7% Bhote, 0.7% Sanyasi/Dasnami, 0.6% Gharti/Bhujel, 0.5% Lohorung, 0.5% Majhi, 0.3% Yakkha, 0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the governing body of a given municipality. A municipality is a general-purpose administrative subdivision, as opposed to a special district (United States), special-purpose district. The English language, English word is derived from French language, French , which in turn derives from the Latin language, Latin , based on the word for social contract (), referring originally to the Latin communities that supplied Rome with troops in exchange for their own incorporation into the Roman state (granting Roman citizenship to the inhabitants) while permitting the communities to retain their own local governments (a limited autonomy). A municipality can be any political jurisdiction (area), jurisdiction, from a sovereign state s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiranti Languages
The Kiranti languages are a major family of Sino-Tibetan languages spoken in Nepal and India (notably Sikkim, Darjeeling, Kalimpong, and Bhutan) by the Kirati people. External relationships George van Driem had formerly proposed that the Kiranti languages were part of a Mahakiranti family, although specialists are not completely certain of either the existence of a Kiranti subgroup or its precise membership. LaPolla (2003), though, proposes that Kiranti may be part of a larger " Rung" group. Classification There are about two dozen Kiranti languages. Among the better known are Limbu, Sunuwar, Bantawa, Chamling, Khaling, Bahing, Yakkha, Wayu, Dungmali, Lohorung, and Kulung. Kiranti verbs are not easily segmentable, due in large part to the presence of portmanteau morphemes, crowded affix strings, and extensive (and often nonintuitive) allomorphy. Thus their relationship to each other has been a subject of debate. Overall, Kiranti languages are classified: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chamling Language
Chamling is one of the Kirati languages spoken by the Chamling people, a subgroup of the Kirat (Horsungchha, Dikhalichha, Mulihachha, Ditumachha, Mansungcha, Lipuhochha, Malekungchha, Maidhung, Kherasung, Rakhomi, Bhijaichha, Hodorichha, Yayochha, Pitruchha etc) of Nepal, India and Bhutan. Alternate renderings and names include ''Chamling'', ''Chamlinge'' and ''Rodong''. It is closely related to the Bantawa (some Bantawa-speaking communities call their language "Camling") and Puma languages of the Kiranti language family in eastern Nepal, and it belongs to the broader Sino-Tibetan language family. Chamling has SOV word order. History The Chamling language is one of the languages of the ancient Kiranti culture, which existed well before vedic period 3500–5000 in South Asia. Important versions of the '' Mundum'' — the main religious text forming the religious foundation of the Kirant Mundum religion and the cultural heritage of the various Kirati people — are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhujel Language
Bhujel, also called Bujhyal, is a Chepangic language of Greater Magaric Branch spoken in central Nepal. It is a semi-tonal language, employing a complex array of affixes. Bhujel are from Tibetan burman family. Bhujel people normally are with Mongoloid features rather than with Caucasoid features. Due to the social structure & social development, this term has been the identity of many other ethnic people too. Geographical distribution Bhujel is spoken in the following villages of Nepal (''Ethnologue''). *Tanahun District, Gandaki Zone: Kulmun, Arthumpka, Andimul, and Baniyatar *Gorkha District, Gandaki Zone: Beltar *Nawalparasi District, Lumbini Zone: Dhodeni *Chitwan District, Narayani Zone: Chanaute Dialects ''Ethnologue ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantawa Language
The Bantawa Language (also referred to as An Yüng, Bantaba, Bantawa Dum, Bantawa Yong, Bantawa Yüng, Bontawa, Kirawa Yüng), is a Kiranti language spoken in the eastern Himalayan hills of eastern Nepal by Kirati Bantawa ethnic groups. They use a syllabic alphabet system known as Kirat Rai. Among the Khambu or Rai people of Koshi Province in Nepal, Sikkim, Darjeeling and Kalimpong in India, Bantawa is the most extensively spoken language. According to the 2001 National Census, at least 1.63% of the Nepal's total population speaks Bantawa. About 370,000 speak Bantawa language mostly in eastern hilly regions of Nepal (2001). Although Bantawa is among the more widely used variety of the Bantawa language, it falls in the below-100,000 category of endangered languages. It is experiencing language shift to Nepali, especially in the northern region. Bantawa is spoken in subject-object-verb order, and has no noun classes or genders. Dialects Most of the Bantawa clan are now settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maithili Language
Maithili ( , ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of India and Nepal. It is native to the Mithila region, which encompasses parts of the eastern Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand as well as Nepal's Koshi Province, Koshi and Madhesh Provinces. It is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. It is the second most commonly spoken native languages of Nepal, Nepalese language constitutionally registered as one of the fourteen provincial official languages of Nepal. It is spoken by 21.7 million people. Of those, 3.2 million are Nepalis, Nepalese speakers. The language is predominantly written in Devanagari, but the historical Tirhuta script, Tirhuta and Kaithi scripts retained some use until today. Official status In 2003, Maithili was included in the 8th Schedule, Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution as a recognised language of India, Indian language, which allows it to be used in education, government, and other official contexts in India. The Maithili language i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
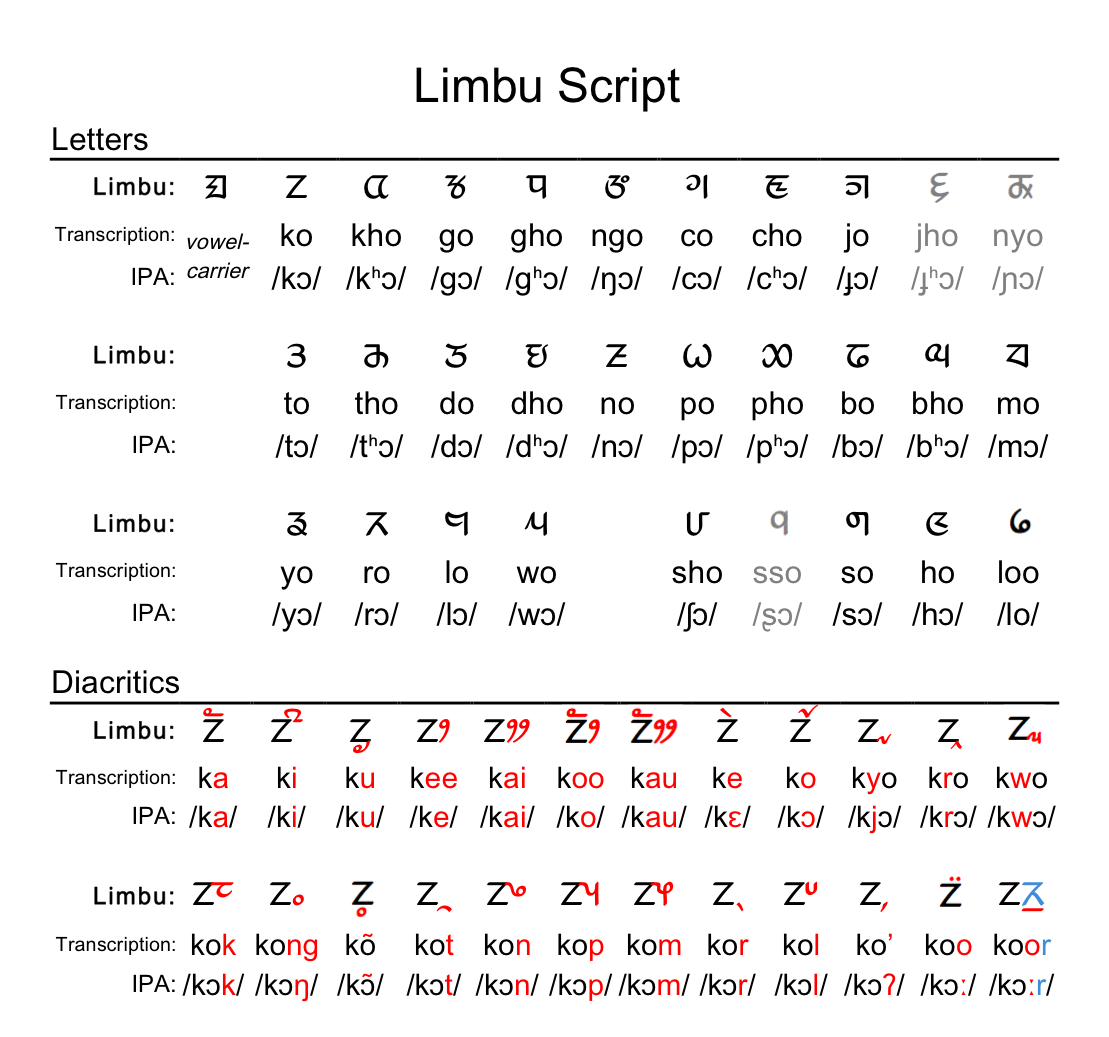
Limbu Language
Limbu (Limbu: , ''yakthuṅ pan'') is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Limbu people of Nepal and Northeastern India (particularly West Bengal, Sikkim, Assam and Nagaland) as well as expatriate communities in Bhutan. The Limbu refer to themselves as ''Yakthung'' and their language as ''Yakthungpan.'' Yakthungpan has four main dialects: Phedape, Chhathare, Tambarkhole and Panthare dialects.A Grammar of Limbu By George van Driem 1987 Among four dialects, the Phedape dialect is widely spoken and well understood by most Yakthungpan speakers. However, as there are some dominant Panthare scholars who have role to create knowledge and control knowledge in the Limbu communities, Panthare dialect is being popularised as a "standard" Limbu language. As Panthare Yakthungs are much more engaged in central political position and administrative positions, they are trying to introduce Panthare dialect as a Standard Yakthungpan. Yakthungpan (Limbu language) is one of the major languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koi Language
Koyee (कोयी) is a Sino-Tibetan language belonging to the Kiranti languages spoken in the Khotang district of Nepal. Like other Kiranti languages, it displays a fairly complex system of person-marking and stem alternations. The term "Koyee" has dual significance, describing both a language and a tribe. Its origins trace back to various sources. According to records from 2015 BS, the term could have been derived from "kuyama" (IPA- kujämä), words in the Koyee language that mean "dark." This might be connected to the location of Sungdel on the hill 'Lourya,' which seems to be dark. The people residing in this shadowy area came to be known as the Koyee tribe, and the language they spoke became known as Koyee language. Over time, phonological changes, such as the shift from "u" to "o(backness)" have contributed to the evolution of the term. Koyee people who settle down in easter side of Nepal are known as Koyu (कोयू). Alternate spellings and names are Kohi, Koi B.� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaling Language
Khaling (kʰɛ̂l brâː ख्या:ल् ब्रा:) is a Kiranti language spoken in Solukhumbu district, Nepal and Sikkim, Darjeeling, and Kalimpong in India. It is one of the few Kiranti languages with tonal contrasts, which are of secondary origin. Khaling has approximately 15,000 speakers and is therefore considered a vulnerable language. Khaling has a complex system of stem alternations: as many as 10 distinct stems have to be posited for a word (Jacques et al. 2012). Khaling is very unusual in having an auditory demonstrative (see Jacques and Lahaussois 2014). Khaling is also known as Rai, Khalinge Rai, Khael Bra, and Khael Baat. General information Khaling is still being acquired by children who live in Khaling-speaking areas, as well as non-Khaling children who happen to live in that area. Geographical distribution Khaling is spoken in the following VDC's of Nepal (''Ethnologue''). *Solukhumbu District, Province No. 1: Kanku, Basa, Waku, Buksa, Jubing, Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thulung Language
Thulung or Thulung lwa () is a Sino-Tibetan Kirati languages or Thulung language spoken in parts of Nepal and Sikkim Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the .... References Sources * * External links *Allen, N.JSketch of Thulung Grammar: with three texts and a glossary Cornell East Asia Series. Ithaca, New York, 1975. (Full text.) Languages of Sikkim Languages of Nepal Kiranti languages Languages of Koshi Province Languages written in Devanagari {{st-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamphu Language
Yamphu language is a Kirati language spoken by the Kirat Yamphu people, a Kirati people of the Himalayas of Nepal. Tomyang (Chongka) is a recently discovered dialect spoken by only 20 people. Both it and Yamphe are distinct. Southern Yamphu is also considered to be Southern Kirat Lorung language. These varieties are all closely related. Geographical distribution Yamphu is spoken in the following locations of Nepal: * Sankhuwasabha District, Kosi Zone: Hedangna, Num, Seduwa, Peppuwa, Mangsimma, Karmarang, Tungkhaling, Uwa, Ala, Uling, and Walung villages *Matsya Pokhari VDC, located in the upper Arun River valley in the Eastern hills; extreme north Lorung area, directly southwest of the Jaljale Mountains * Bhojpur District, Kosi Zone *Ilam district, Fikkal, Kolbung, Panchakanya, Jitpur, Danabari, Mahamai (VDCs). *Jhapa district Jhapa District (; ) is a district of Koshi Province in eastern Nepal named after a Rajbanshi Surjapuri language word "Jhapa", meaning "to cover" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gurung Language
Gurung (Devanagari: ), also known as Tamu Kyi (, ; Tibetan: ) or Tamu Bhāṣā (, ), is a Sino-Tibetan language spoken by the Gurung people of Nepal. The total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal was 227,918 in 1991 and 325,622 in 2011. The official language of Nepal, Nepali, is an Indo-European language, whereas Gurung is a Sino-Tibetan language. Gurung is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, Bhutan, and by diaspora communities in places such as Singapore and Hong Kong. Geographical distribution Gurung is spoken in the following districts of Nepal and India (''Ethnologue''): * Gandaki Province: Kaski District, Syangja District, Lamjung District, Tanahu District, Gorkha District, Manang District and Mustang District * Dhawalagiri Zone: Parbat district *Sikkim: South Sikkim, West Sikkim, East Sikkim Classification At higher levels, Gurung is a member of the Tibeto-Burman (or Trans-Himalayan) family. Robert Shafer classified Guru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |