|
Keno Fischer
Keno Fischer is a German computer scientist known for being a core member implementing the Julia programming language in Windows. He is an alumnus of Harvard for both his BA and MA. He works at Julia Computing, which he co-founded with Julia co-creators, Alan Edelman, Jeff Bezanson, Stefan Karpinski, Viral B. Shah and Deepak Vinchhi. He received a B.A. in mathematics and physics from Harvard in 2016, and he completed a Master of Arts in Physics also from Harvard in 2016. At the age of 25, Fischer was selected by Forbes for their 2019 ''30 Under 30 Enterprise Technology'' list for his work with Julia Computing company. Fischer, along with the rest of the Celeste team, was awarded the 2017 HPC Innovation Excellence Award for "the outstanding application of HPC for business and scientific achievements." The Celeste project, that ran on a top 6 supercomputer "created the first comprehensive catalog of visible objects in our universe by processing 178 terabytes of SDSS (Sloan Digit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any denomination, Harvard trained Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston elite. Following the American Civil War, under Harvard president Charles William Eliot's long tenure from 1869 to 1909, Harvard developed multiple professional schools, which transfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloan Digital Sky Survey
The Sloan Digital Sky Survey or SDSS is a major multi-spectral imaging and spectroscopic redshift survey using a dedicated 2.5-m wide-angle optical telescope at Apache Point Observatory in New Mexico, United States. The project began in 2000 and was named after the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, which contributed significant funding. A consortium of the University of Washington and Princeton University was established to conduct a redshift survey. The Astrophysical Research Consortium (ARC) was established in 1984 with the additional participation of New Mexico State University and Washington State University to manage activities at Apache Point. In 1991, the Sloan Foundation granted the ARC funding for survey efforts and the construction of equipment to carry out the work. Background At the time of its design, the SDSS was a pioneering combination of novel instrumentation as well as data reduction and storage techniques that drove major advances in astronomical observations, dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Programming Languages
This is a record of notable programming languages, by decade. 1790s 1800s 1830s 1840s 1870s 1940s 1950s 1960s 1970s 1980s 1990s 2000s 2010s 2020s See also * History of computing hardware * History of programming languages * Programming language A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Programming languages are described in terms of their Syntax (programming languages), syntax (form) and semantics (computer science), semantics (meaning), usually def ... * Timeline of computing * Timeline of programming language theory References External links Online Historical Encyclopaedia of Programming LanguagesEric Levenez's timeline diagram of computer languages history {{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Programming Languages Programming Lists of programming languages History of computer science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozilla
Mozilla is a free software community founded in 1998 by members of Netscape. The Mozilla community uses, develops, publishes and supports Mozilla products, thereby promoting free software and open standards. The community is supported institutionally by the Nonprofit organization, non-profit Mozilla Foundation and its tax-paying subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. List of Mozilla products, Mozilla's current products include the Firefox web browser, Mozilla Thunderbird, Thunderbird e-mail client (now through a subsidiary), the Bugzilla bug tracking system, the Gecko (software), Gecko layout engine, and the Pocket (service), Pocket "read-it-later-online" service. History On January 23, 1998, Netscape announced that its Netscape Communicator browser software would be free, and that its source code would also be free. One day later, Jamie Zawinski of Netscape registered . The project took its name, "Mozilla", from the original code name of the Netscape Navigator browser—a por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebAssembly
WebAssembly (Wasm) defines a portable binary-code format and a corresponding text format for executable programs as well as software interfaces for facilitating communication between such programs and their host environment. The main goal of WebAssembly is to facilitate high-performance applications on web pages, but it is also designed to be usable in non-web environments. It is an open standard intended to support any language on any operating system, and in practice many of the most popular languages already have at least some level of support. Announced in and first released in , WebAssembly became a World Wide Web Consortium recommendation on 5 December 2019 and it received the ''Programming Languages Software Award'' from ACM SIGPLAN in 2021. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) maintains the standard with contributions from Mozilla, Microsoft, Google, Apple, Fastly, Intel, and Red Hat. History The name WebAssembly is intended to suggest bringing assembly language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Summit Supercomputer
Summit or OLCF-4 was a supercomputer developed by IBM for use at Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility (OLCF), a facility at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, United States of America. It held the number 1 position on the TOP500 list from June 2018 to June 2020. As of June 2024, its LINPACK benchmark was clocked at 148.6 petaFLOPS. Summit was decommissioned on November 15, 2024. As of November 2019, the supercomputer had ranked as the 5th most energy efficient in the world with a measured power efficiency of 14.668 gigaFLOPS/watt. Summit was the first supercomputer to reach exaflop (a quintillion operations per second) speed, on a non-standard metric, achieving 1.88 exaflops during a genomic analysis and is expected to reach 3.3 exaflops using mixed-precision calculations. History The United States Department of Energy awarded a $325 million contract in November 2014 to IBM, Nvidia and Mellanox. The effort resulted in construction of Summit and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic Partial Differential Equation
Stochastic partial differential equations (SPDEs) generalize partial differential equations via random force terms and coefficients, in the same way ordinary stochastic differential equations generalize ordinary differential equations. They have relevance to quantum field theory, statistical mechanics, and spatial modeling. Examples One of the most studied SPDEs is the stochastic heat equation, which may formally be written as : \partial_t u = \Delta u + \xi\;, where \Delta is the Laplacian and \xi denotes space-time white noise. Other examples also include stochastic versions of famous linear equations, such as the wave equation and the Schrödinger equation. Discussion One difficulty is their lack of regularity. In one dimensional space, solutions to the stochastic heat equation are only almost 1/2-Hölder continuous in space and 1/4-Hölder continuous in time. For dimensions two and higher, solutions are not even function-valued, but can be made sense of as random d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Adversarial Network
A generative adversarial network (GAN) is a class of machine learning frameworks and a prominent framework for approaching generative artificial intelligence. The concept was initially developed by Ian Goodfellow and his colleagues in June 2014. In a GAN, two neural networks compete with each other in the form of a zero-sum game, where one agent's gain is another agent's loss. Given a training set, this technique learns to generate new data with the same statistics as the training set. For example, a GAN trained on photographs can generate new photographs that look at least superficially authentic to human observers, having many realistic characteristics. Though originally proposed as a form of generative model for unsupervised learning, GANs have also proved useful for semi-supervised learning, fully supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. The core idea of a GAN is based on the "indirect" training through the discriminator, another neural network that can tell ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program undertaken during World War II to produce the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States in collaboration with the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was directed by Major General Leslie Groves of the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist J. Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the bombs. The Army program was designated the Manhattan District, as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the name gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. The project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys, and subsumed the program from the American civilian Office of Scientific Research and Development. The Manhattan Project employed nearly 130,000 people at its peak and cost nearly US$2 billion (equivalent to about $ b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanford Site
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. It has also been known as SiteW and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation. Established in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project, the site was home to the Hanford Engineer Works and B Reactor, the first full-scale plutonium production reactor in the world. Plutonium manufactured at the site was used in the first atomic bomb, which was tested in the Trinity nuclear test, and in the Fat Man bomb used in the bombing of Nagasaki. During the Cold War, the project expanded to include nine nuclear reactors and five large plutonium processing complexes, which produced plutonium for most of the more than 60,000 weapons built for the U.S. nuclear arsenal. Nuclear technology developed rapidly during this period, and Hanford scientists produced major technological achievements. The town of Richland, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
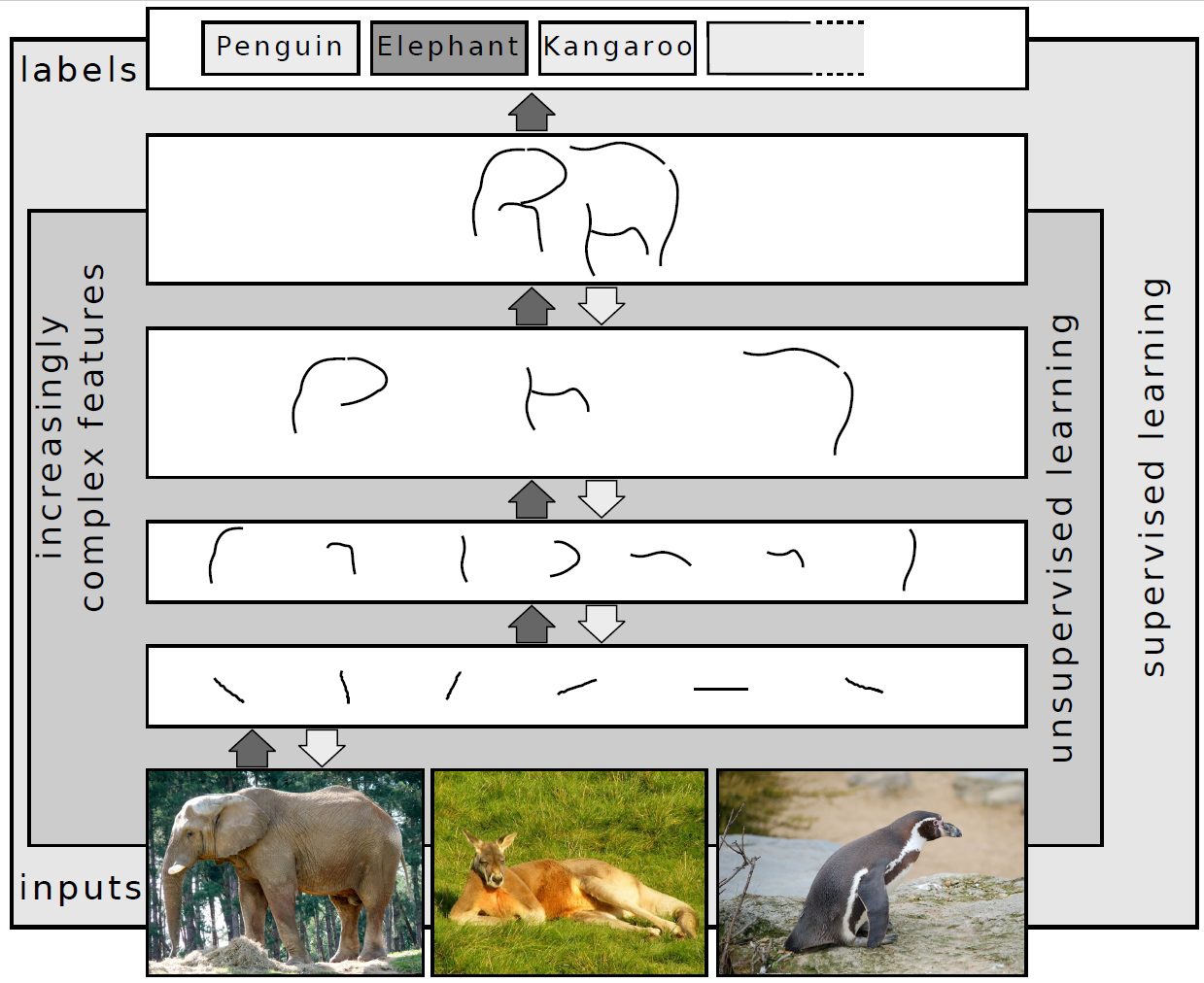
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |