|
Kazembe
Kazembe is a traditional kingdom in modern-day Zambia, and southeastern Congo. For more than 250 years, Kazembe has been an influential kingdom of the Kiluba-Chibemba, speaking the language of the Eastern Luba- Lunda people of south-central Africa (also known as the Luba, Luunda, Eastern Luba-Lunda, and Luba-Lunda-Kazembe). Its position on trade routes in a well-watered, relatively fertile and well-populated area of forestry, fishery and agricultural resources drew expeditions by traders and explorers (such as Scottish missionary David Livingstone David Livingstone and Horace Waller (ed.) (1874) ''The Last Journals of David Livingstone in Central Africa from 1865 to his Death''. Two volumes, John Murray.) who called it variously Kasembe, Cazembe and Casembe. Known by the title Mwata Yav now equivalent to 'Paramount Chief'or King, the monarchy with its annual Mutomboko festival stands out in the Luapula Valley and Lake Mweru in present-day Zambia, though its history in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazembe Kingdom 433x455
Kazembe is a traditional kingdom in modern-day Zambia, and southeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, Congo. For more than 250 years, Kazembe has been an influential kingdom of the Luba-Katanga language, Kiluba-Bemba language, Chibemba, speaking the language of the Eastern Luba people, Luba-Lunda people, Lunda people of south-central Africa (also known as the Luba, Luunda, Eastern Luba-Lunda, and Luba-Lunda-Kazembe). Its position on trade routes in a well-watered, relatively fertile and well-populated area of forestry, fishery and agricultural resources drew expeditions by traders and explorers (such as Scottish missionary David LivingstoneDavid Livingstone and Horace Waller (activist), Horace Waller (ed.) (1874) ''The Last Journals of David Livingstone in Central Africa from 1865 to his Death''. Two volumes, John Murray.) who called it variously Kasembe, Cazembe and Casembe. Known by the title Mwata Yav now equivalent to 'Paramount Chief'or King, the monarchy with its annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
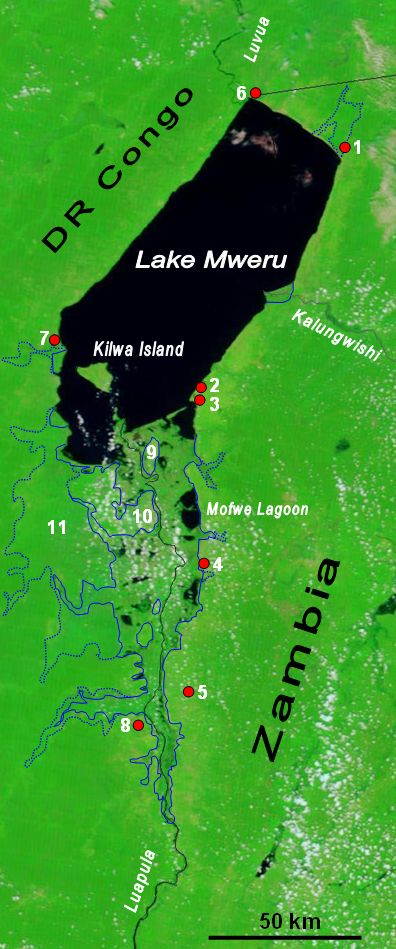
Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') (, ) is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length of the Congo, lying between its Luapula River (upstream) and Luvua River (downstream) segments.Google Earth accessed 29 March 2007. When in flood Lake Bangweulu and its swamps may temporarily have a larger area, but not a larger volume. Mweru means 'lake' in a number of Bantu languages, so it is often referred to as just 'Mweru'.The '' Northern Rhodesia Journal'' online at NZRAM.org: J B W Anderson: "Kilwa Island and the Luapula." Vol II, No. 3 pp87–88 (1954) Physical geography Mweru is mainly fed by the Luapula River, which comes in through swamps from the south, and the Kalungwishi River from the east. At its north end the lake is drained by the Luvua River, which flows in a northwesterly direction to join the Lualaba River and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bordered to the north by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania to the north-east, Malawi to the east, Mozambique to the southeast, Zimbabwe and Botswana to the south, Namibia to the southwest, and Angola to the west. The capital city of Zambia is Lusaka, located in the south-central part of Zambia. The population is concentrated mainly around Lusaka in the south and the Copperbelt Province to the north, the core economic hubs of the country. Originally inhabited by Khoisan peoples, the region was affected by the Bantu expansion of the thirteenth century. Following European colonization of Africa, European colonisers in the 18th century, the British colonised the region into the British protectorates of Barotziland–North-Western Rho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Lunda
The Lunda Empire or Kingdom of Lunda was a confederation of states in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo, north-eastern Angola, and north-western Zambia. Its central state was in Katanga Province, Katanga. Origin Initially, the core of what would become the Lunda confederation was a commune called a ''N'Gaange'' in the kiLunda (kiyaka-kipunu) language. It was ruled over by a monarch called the Mwane-a- n'Gaange. One of these rulers, Ilunga Tshibinda, came from the nation of Luba Kingdom, Luba where his brother ruled and married a royal woman from a nation to their south. Their son became the first paramount ruler of the Lunda, creating the title of Mwane-a-Yamvu (c. 1665). Other sources state the first well-attested historical ruler of Lunda was Nawej, who begin his rule about 1695. His father was said to have come from Kalundwe, a Luba language-speaking state. It is unclear, though, how much of the traditions of the kingdom before Nawej are historically accurate. Nawe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luapula
The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu (Zambia), which are fed by the Chambeshi River. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo before emptying into Lake Mweru. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province.Terracarta/International Travel Maps, Vancouver Canada: "Zambia, 2nd edition", 2000 Source and upper Luapula The Luapula drains Lake Bangweulu and its swamps into which flows the Chambeshi River, the source of the Congo. There is no single clear channel connecting the two rivers and the lake, but a mass of shifting channels, lagoons and swamps, as the explorer David Livingstone found to his cost. (He died exploring the area, and one of his last acts was to question Chief Chitambo about the course of the Luapula.)Blaikie, William Garden (1880): ''The Personal Life Of David Livingstone''Project Gutenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunda People
The Lunda (''Balunda'', ''Luunda'', ''Ruund'') are a Bantu peoples, Bantu ethnic group that originated in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo along the Kalanyi River and formed the Kingdom of Lunda in the 17th century under their ruler, Mwata Yamvo, Mwata Yamvo or Mwaant Yav, with their capital at Musumba.Pritchett, James Anthony: "Lunda". World Culture Encyclopedia. Retrieved 15 May 2007. From there they spread widely through Katanga (province), Katanga and into Eastern Angola, north-western Zambia (the Kanongesha-Lunda people, Kanongesha-Lunda and the Ishindi-Lunda people, Ishindi-Lunda, Gabon, Republic of Congo) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pombeiros
''Pombeiros'' were African and sometimes mulatto agents who purchased slaves in the African interior on behalf of the Portuguese crown or private Portuguese traders for the Atlantic slave trade. The term ''pombeiro'' comes from Pumbe, a market located by the Malebo Pool.Roland Oliver and Anthony Atmore, ''Africa since 1800'', 5th edn (Cambridge University Press, 2005), p. 27. In general, the Portuguese government did not want Portuguese slave traders going into the interior. It preferred them to stay at its colonies of Benguela and Luanda on the coast, while the native ''pombeiros'' led caravans into the interior to buy slaves. During their trips into the interior, the ''pombeiros'' resided at fortified marketplaces called ''feiras'', to which Africans from beyond the frontier would come to sell produce, wares and slaves.Oliver and Atmore 2005, pp. 78–81. According to one account from 1700, the ''pombeiros'' would set out with their own slaves, who in turn had slaves under them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mofwe Lagoon
The Mofwe Lagoon is the largest of several lagoons in the Luapula River swamps south of Lake Mweru, in the Luapula Province of Zambia. Geography Its size and shape depends on the season and amount of water flowing into the swamps, especially from the Mbereshi River to the southeast, its main supplier. Generally its north–south axis is about 14 km and its east–west axis is about 6 km. Floating islands of sedge are usually found in an east–west line across its middle, which may effectively cut it in two, and at times vegetation has covered much of the southern half. The importance of the Mofwe lies in its fishery, which attracted Mwata Kazembe to settle in the town of Kanyembo on its eastern edge in the 19th century.Macola, Giacomo (2003)''The kingdom of Kazembe: history and politics in North-Eastern Zambia and Katanga to 1950 (Studies on African History)'' Lit Verlag, p. 50. The Mofwe does not have a definite shore and is not easily accessed, being lined by a den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livingstone, from the prominent 18th-century Moffat missionary family. Livingstone came to have a mythic status as a Protestant missionary martyr, working-class " rags-to-riches" inspirational story, scientific investigator and explorer, imperial reformer, anti-slavery crusader, and advocate of British commercial and colonial expansion. As a result, he became one of the most popular British heroes of the late 19th-century Victorian era. Livingstone's fame as an explorer and his obsession with learning the sources of the Nile was founded on the belief that if he could solve that age-old mystery, his fame would give him the influence to end the East African Arab–Swahili slave trade. "The Nile sources", he told a friend, "are valuable only as a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mwata Yamvo
Mwata Yamvo was a 16th-century founding ruler of the Lunda Kingdom including Suku, mbumba, yaka, Lozi, impangala, and the title given to all subsequent rulers or paramount chiefs of the Lunda (or Luunda or Ruund) people to the present day. The name has variety of spellings: ''Mwaante Yah-mvu, Mwaant Yaav, Muata Jamvo, Mwata Yamfwa''. See also * List of Mwata Yamvo rulers * Mwata Kazembe References Year of death unknown Year of birth unknown 16th-century monarchs in Africa {{DRCongo-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luba People
The Luba people or Baluba are a Bantu ethno-linguistic group indigenous to the south-central region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The majority of them live in this country, residing mainly in Katanga Province, Katanga, Kasai Province, Kasaï, Kasaï-Oriental, Kasaï-Central, Lomami Province, Lomami and Maniema. The Baluba consist of many sub-groups or clans. The Baluba developed a society and culture by about the 400s CE, later developing a well-organised community in the Upemba Depression known as the Baluba in Katanga confederation. Luba society consisted of miners, smiths, woodworkers, potters, crafters, and people of various other professions. Kingdoms of the Savanna: The Luba and Lunda Empires Alexander Ives Bortolot (2003), Department of Art History and Archaeology, Columbia Univ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Luba
The Luba Empire or Kingdom of Luba was a pre-colonial Central African state that arose in the marshy grasslands of the Upemba Depression in what is now southern Democratic Republic of Congo. Origins and foundation Archaeological research shows that the Upemba Depression had been occupied continuously since at least the 4th century AD. In the 4th century, the region was occupied by iron-working farmers. Over the centuries, the people of the region learned to use nets, harpoons, make dugout canoes, and clear canals through swamps. They had also learned techniques for drying fish, which were an important source of protein; they began trading the dried fish with the inhabitants of the protein-starved savanna. By the 6th century, fishing people lived on lakeshores, worked iron, and traded palm oil. By the 10th century, the people of Upemba had diversified their economy, combining fishing, farming and metal-working. Metal-workers relied on traders to bring them the copper and charc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |