Luapula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the
The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the
Project Gutenberg Ebook #13262
release date: August 23, 2004.
accessed 2007. Below the Bangweulu swamps and floodplain, the Luapula flows steadily in an arc south-west turning north-west then north, with some rapids and well-known set of cataracts, Mambilima Falls near the main road. A far less well-known site is Tangwa, about south where the river has eroded a gap through rocky hills carving huge caves, arches, and potholes, and leaving giant boulders, including two balancing rocks called 'God's Corn Bin'.William Lammond
"The Luapula Valley"
''The
''64th Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting'.' (2001). Accessed 30 March 2007. The Luizi structure can be seen on Google Earth at decimal latitude/longitude 10.16 S, 28.00 E.
 The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the
The Luapula River is a north-flowing river of central Africa, within the Congo River
The Congo River, formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second-longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the third-largest river in the world list of rivers by discharge, by discharge volume, following the Amazon Ri ...
watershed. It rises in the wetlands of Lake Bangweulu
Lake Bangweulu ('where the water sky meets the sky') is a Fresh water, freshwater lake in northern Zambia. Bangweulu is one of the world's great Wetland, wetland systems, comprising Lake Bangweulu, the Bangweulu Wetlands and the Bangweulu flats or ...
(Zambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
), which are fed by the Chambeshi River
The Chambeshi (or Chambezi) River of northeastern Zambia is the most remote headstream of the Congo River (in length) and therefore it is considered the source of the Congo River. (However, by volume of water, the Lualaba River provides a greater ...
. The Luapula flows west then north, marking the border between Zambia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
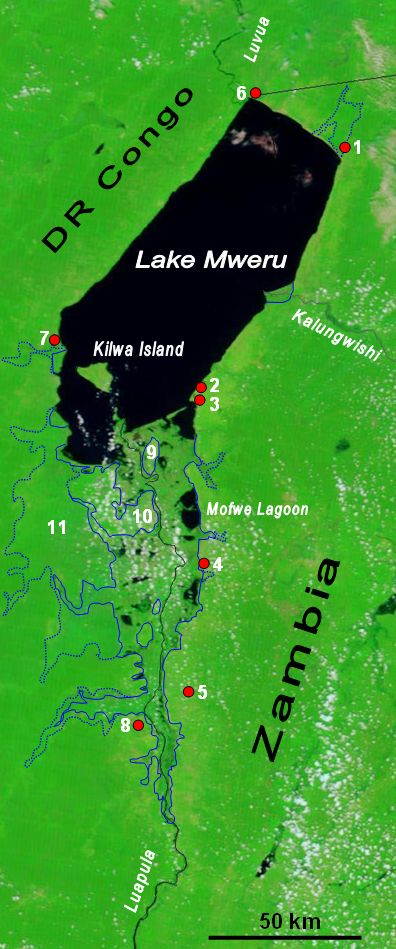
before emptying into Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') (, ) is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length ...
. The river gives its name to Zambia's Luapula Province
Luapula Province is one of Zambia's ten Provinces of Zambia, provinces located in the northern part of the country. Luapula Province is named after the Luapula River and its capital is Mansa, Zambia, Mansa. As per the 2022 Zambian census, the ...
.Terracarta/International Travel Maps, Vancouver Canada: "Zambia, 2nd edition", 2000
Source and upper Luapula
The Luapula drainsLake Bangweulu
Lake Bangweulu ('where the water sky meets the sky') is a Fresh water, freshwater lake in northern Zambia. Bangweulu is one of the world's great Wetland, wetland systems, comprising Lake Bangweulu, the Bangweulu Wetlands and the Bangweulu flats or ...
and its swamps into which flows the Chambeshi River
The Chambeshi (or Chambezi) River of northeastern Zambia is the most remote headstream of the Congo River (in length) and therefore it is considered the source of the Congo River. (However, by volume of water, the Lualaba River provides a greater ...
, the source of the Congo. There is no single clear channel connecting the two rivers and the lake, but a mass of shifting channels, lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') an ...
s and swamps, as the explorer David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livings ...
found to his cost. (He died exploring the area, and one of his last acts was to question Chief Chitambo about the course of the Luapula.)Blaikie, William Garden (1880): ''The Personal Life Of David Livingstone''Project Gutenberg Ebook #13262
release date: August 23, 2004.
David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livings ...
and Horace Waller (ed.): ''The Last Journals of David Livingstone in Central Africa from 1865 to his Death''. Two volumes, John Murray, 1874. The channel boldly marked as the 'Luapula' and confidently shown on many maps flowing south out of Lake Bangweulu at 11°25'S 29°49'E can be seen on satellite images such as Google Earth
Google Earth is a web mapping, web and computer program created by Google that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satelli ...
to actually peter out into green vegetation around 11°46'S 29°48'E.Google Earthaccessed 2007. Below the Bangweulu swamps and floodplain, the Luapula flows steadily in an arc south-west turning north-west then north, with some rapids and well-known set of cataracts, Mambilima Falls near the main road. A far less well-known site is Tangwa, about south where the river has eroded a gap through rocky hills carving huge caves, arches, and potholes, and leaving giant boulders, including two balancing rocks called 'God's Corn Bin'.William Lammond
"The Luapula Valley"
''The
Northern Rhodesia Journal
The ''Northern Rhodesia Journal'', often referred to simply as "NRJ", was produced between 1950 and 1965, by the Northern Rhodesian Government Printer, to record some of the early history of Northern Rhodesia. It is one of the most important sour ...
'', Vol 2 No 5 (1954), pp50−55. Accessed 16 December 2017.
Valley
From the Chembe Bridge to Lake Mweru, the long Luapula Valley has a higher rural population than the plateau through which it cuts to a depth of up to . The river is known for this valley and for its long thindelta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), the fourth letter of the Greek alphabet
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta"), the fourth letter in the Latin alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* Delta Air Lines, a major US carrier ...
entering Lake Mweru, usually referred to as the Luapula Swamps. The well-populated part of the valley starts north from Mambilima Falls, and along the rest of its length is nicknamed 'Mwapoleni Road', after the Chibemba
Bemba (natively known as ''Chibemba, Ichibemba'' and ''Chiwemba''), is a Bantu language spoken primarily in north-eastern Zambia by the Bemba people.
History
Bemba is spoken in rural and urban areas of the region, and is one of Zambia's sev ...
greeting called out as people pass each other.
For many practical study purposes, the lower Luapula and Mweru can be considered as one entity. They lie in a rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges produced by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear ...
or graben
In geology, a graben () is a depression (geology), depressed block of the Crust (geology), crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German language, German, meaning 'ditch' or 't ...
once considered separate from the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
but now seen as a branch of it. Mweru, however, drains not into Lake Tanganyika
Lake Tanganyika ( ; ) is an African Great Lakes, African Great Lake. It is the world's List of lakes by volume, second-largest freshwater lake by volume and the List of lakes by depth, second deepest, in both cases after Lake Baikal in Siberia. ...
in the Albertine Rift
The Albertine Rift is the western branch of the East African Rift, covering parts of Uganda, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Rwanda, Burundi and Tanzania.
It extends from the northern end of Lake Albert to the southern end of Lake Tan ...
but via the Luvua River
The Luvua River (or ''Lowa River'') () is a river in the Katanga Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It flows from the northern end of Lake Mweru on the Zambia-Congo border in a northwesterly direction for to its confluence ...
, which has cut a deep, narrow zigzag valley to join the Lualaba River
The Lualaba River (, , ) flows entirely within the eastern part of Democratic Republic of the Congo. It provides the greatest streamflow to the Congo River, while the River source, source of the Congo is recognized as the Chambeshi River, Chambeshi ...
, as the upper Congo is named. The Luapula is part of the longest tributary of the Congo, and hence, by convention, is part of its source, even though the upper Lualaba carries more water.
Overlying the edge of the rift valley west of the Luapula Swamps is the Luizi structure, a wide series of concentric rings. It has been recently confirmed as a meteoritic impact crater (an astrobleme) formed less than 600 million years ago.P Master, P. Dumont and H. Ladmirant: "Age Constraints On The Luizi Structure"''64th Annual Meteoritical Society Meeting'.' (2001). Accessed 30 March 2007. The Luizi structure can be seen on Google Earth at decimal latitude/longitude 10.16 S, 28.00 E.
Swamps
The swamps stretch along the last of the river before it reaches the lake, and for much of that, they are wide, covering an area of about . There are four inhabited islands in the DR Congo part of the delta, including the largest in the system which is connected to dry land in the dry season. Zambia has three inhabited islands in the delta including Chisenga Island. There are also many lagoons, the largest of which isMofwe Lagoon
The Mofwe Lagoon is the largest of several lagoons in the Luapula River swamps south of Lake Mweru, in the Luapula Province of Zambia.
Geography
Its size and shape depends on the season and amount of water flowing into the swamps, especially from ...
on the Zambian side.
As in the Bangweulu Swamps, floating beds of papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
are a feature of the swamps, which often block channels and change the shape of lagoons. However, the main river channel does not get blocked and stays consistently about wide. It has not developed the branching channels typical of river deltas.
Very tall reeds grow at the edge of the swamps in most places, making it difficult to see over the lagoons from land or to find the way to the maze of narrow channels used by dugout canoes. Guides are needed to navigate through them, and they are a haven for smuggling between the two countries sharing the swamps.
Crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include ...
and hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Sahar ...
are common and a hazard for fishermen and travellers. However, the Shila people used to hunt hippopotamus using nothing more than harpoons thrown from canoes.
On the western side of the delta in DR Congo is a broad grassy floodplain covering about 1600 km2. At the end of the rainy season, the combined Luapula wetlands exceed . The floodplain was home to herds of lechwe
The lechwe, red lechwe, or southern lechwe (''Kobus leche'') is an antelope found in wetlands of south-central Africa.
Range
The lechwe is native to Botswana, Zambia, southeastern Democratic Republic of the Congo, northeastern Namibia, and easte ...
and the shy sitatunga
The sitatunga (''Tragelaphus spekii'') or marshbuck is a swamp-dwelling medium-sized antelope found throughout central Africa, centering on the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, parts of South Sudan, Southern ...
, the famous semi-aquatic antelopes of the region, but both are believed extinct in the lower Luapula due to hunting and the lack of wildlife management.
Human settlement
The upper and middle reaches of the Luapula are quite sparsely populated. The natural resources of the lower valley, which include fisheries in the river, lagoons and wetlands with fertile farmland at the margins, attracted the Lunda invaders of Mwata Kazembe to settle there around 1750. Their present capital is at Mwansabombwe on the edge of the delta.Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
traders and slavers from Zanzibar
Zanzibar is a Tanzanian archipelago off the coast of East Africa. It is located in the Indian Ocean, and consists of many small Island, islands and two large ones: Unguja (the main island, referred to informally as Zanzibar) and Pemba Island. ...
and Portuguese traders from Mozambique
Mozambique, officially the Republic of Mozambique, is a country located in Southeast Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi and Zambia to the northwest, Zimbabwe to the west, and Eswatini and South Afr ...
were attracted to the area in the 18th and 19th Centuries. David Livingstone
David Livingstone (; 19 March 1813 – 1 May 1873) was a Scottish physician, Congregationalist, pioneer Christian missionary with the London Missionary Society, and an explorer in Africa. Livingstone was married to Mary Moffat Livings ...
was the first Briton
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs modern British citizenship and nationality, w ...
to visit in 1867. He did not explore the river but in his hunt for the origin of the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
, Mwata Kazembe was the first to tell him that the Luapula connects the Chambeshi/Bangweulu and Mweru/Luvua/Lualaba systems. Livingstone wrongly believed the Lualaba then flowed to the Nile rather than to the River Congo.
Some of the first missionaries in Central Africa were also attracted to the valley. The first was the Garanganze Mission of the Plymouth Brethren
The Plymouth Brethren or Assemblies of Brethren are a low church and Nonconformist (Protestantism), Nonconformist Christian movement whose history can be traced back to Dublin, Ireland, in the mid to late 1820s, where it originated from Anglica ...
at Mambilima around 1892, followed by the London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed tradition, Reformed in outlook, with ...
at Mbereshi
Mbereshi (also spelled and pronounced Mbeleshi) is a village in the Luapula Province of Zambia, named after the Mbereshi River on its north side. It is the site of a large mission founded in 1900 by the London Missionary Society. In 1915 the missi ...
in 1900.
The first large town of the colonial era Colonial period (a period in a country's history where it was subject to management by a colonial power) may refer to:
Continents
*European colonization of the Americas
* Colonisation of Africa
* Western imperialism in Asia
Countries
* Col ...
was the river port, Kasenga, in DR Congo, which grew prosperous in the 1930s from supplying fish to Elizabethville and other towns of the Katanga Copperbelt
The Copperbelt () is a natural region in Central Africa which sits on the border region between northern Zambia and the south eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. It is known for copper mining and is the second largest global reserve of copper, ...
via the first motor road to reach the valley. Most of the fish was caught in Lake Mweru and brought by boat up the Luapula to Kasenga, where it was packed in ice produced in several plants. Although the fish catch has declined and most now travels on the better roads of Zambia, Kasenga remains the only port on the river. For more on the fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farm ...
of the area, see ''Lake Mweru
Lake Mweru (also spelled ''Mwelu'', ''Mwero'') (, ) is a freshwater lake on the longest arm of Africa's second-longest river, the Congo. Located on the border between Zambia and Democratic Republic of the Congo, it makes up of the total length ...
''.
On the Zambian side of the Luapula, an outbreak of sleeping sickness
African trypanosomiasis is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals.
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is caused by the species '' Trypanosoma b ...
made the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
colonial authorities move their Fort Rosebery boma out of the valley onto the plateau at Mansa, while fears of malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
in the Luapula Swamps made them establish the next on the plateau at Kawambwa
Kawambwa is a town in the Zambian province of Luapula located on the edge of the northern Zambian plateau above the Luapula valley at an altitude of 1300 m. It was chosen as an administrative district of the same name by the British colonial au ...
. Consequently, the towns and villages in the valley, such as the largest, Mwansabombwe, do not have the same ex-colonial character as the administrative towns. However, following the lead of missionary builders and Mwata Kazembe, from the early 1900s, most housing in the valley was of solid brick construction, sun-dried brick
Mudbrick or mud-brick, also known as unfired brick, is an air-dried brick, made of a mixture of mud (containing loam, clay, sand and water) mixed with a binding material such as rice husks or straw. Mudbricks are known from 9000 BCE.
From ...
mainly, but with some burnt brick.
Water transport
Before the advent of road transport, people travelled by canoe along the river between lakes Bangweulu and Mweru. The lower river between Kasenga and Kilwa on Mweru is now the only stretch of the river carrying much boat transport and most of that is now for DR Congo, where roads are frequently impassable. Up to the late 1940s, the upper Luapula from Kapalala to Lake Bangweulu and the Chambeshi River was one of the most important stretches for river transport in the thenNorthern Rhodesia
Northern Rhodesia was a British protectorate in Southern Africa, now the independent country of Zambia. It was formed in 1911 by Amalgamation (politics), amalgamating the two earlier protectorates of Barotziland-North-Western Rhodesia and North ...
. Goods travelled by road from the railhead
{{Short pages monitor