|
Karnan (1964 Film)
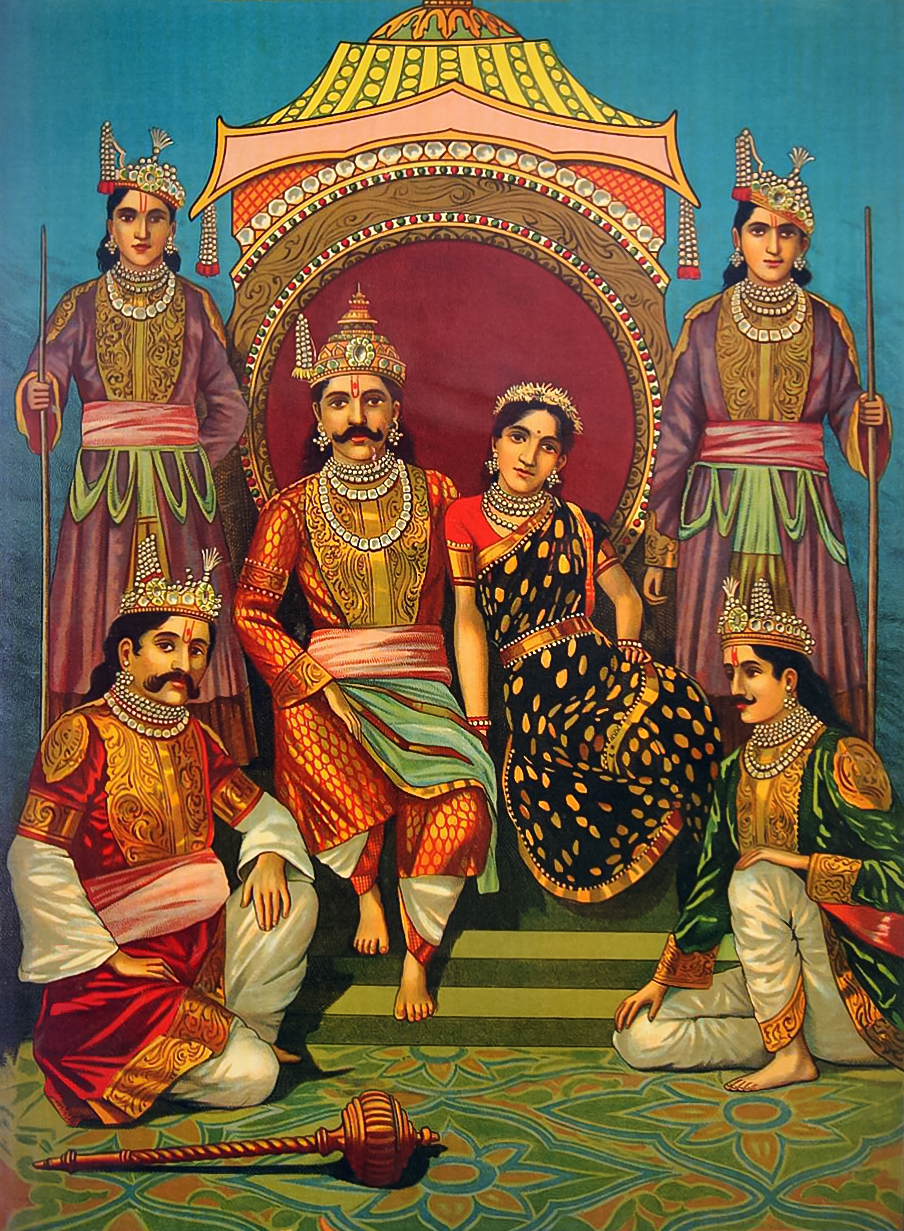
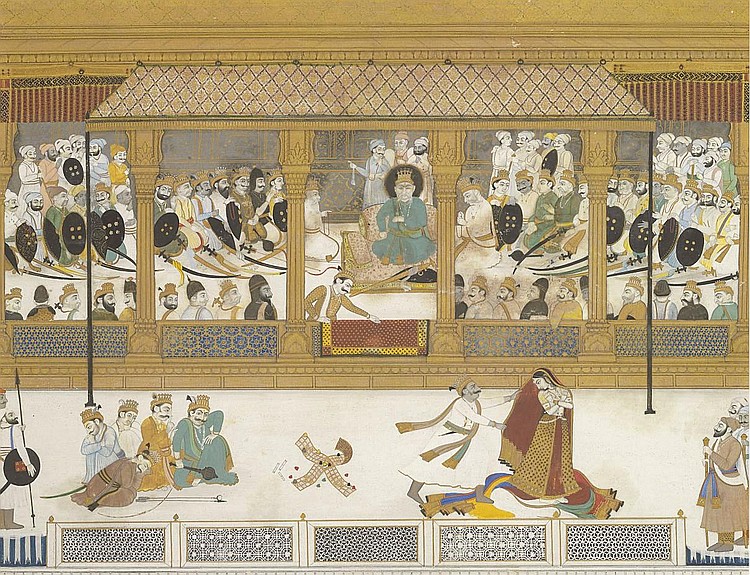
''Karnan'' () is a 1964 Indian Tamil-language Hindu mythological film produced and directed by B. R. Panthulu. It stars Sivaji Ganesan leading an ensemble cast consisting of N. T. Rama Rao, S. A. Ashokan, R. Muthuraman, Savitri, Devika and M. V. Rajamma. The film is based on the story of Karna, a character from the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. ''Karnan'', which was officially launched in 1963, was shot in palaces at Jaipur and the war sequences were filmed in Kurukshetra, which featured several soldiers from the Indian Army. The film's original soundtrack was composed by the duo Viswanathan–Ramamoorthy, while the lyrics were written by Kannadasan. The screenplay was written by A. S. Nagarajan and the dialogues by Sakthi T. K. Krishnasamy. The film was the first in Tamil to be entirely shot and released in Eastmancolor. ''Karnan'' was released on 14 January 1964, during the festival occasion of Pongal. The film ran for over 100 days in theatres, and later won the Cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakthi T
Sakthi may refer to: * ''Sakthi'' (1972 film), a Malayalam film by Crossbelt Mani * ''Sakthi'' (1980 film), a Malayalam film by Vijay Anand * ''Sakthi'' (1997 film), a Tamil film * ''Sakthi'' (2011 film), a Telugu film * ''Sakthi'' (TV series), an Indian Tamil soap opera * Sakthi Group, an Indian conglomerate company * R. C. Sakthi (1940-2015), Indian filmmaker and actor See also * Shakti (other) {{disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastmancolor
Eastmancolor is a trade name used by Eastman Kodak for a number of related film and processing technologies associated with color motion picture production and referring to George Eastman, founder of Kodak. Eastmancolor, introduced in 1950, was one of the first widely successful "single-strip colour" processes, and eventually displaced the more cumbersome Technicolor. Eastmancolor was known by a variety of names, such as DeLuxe Color, Warnercolor, Metrocolor, Pathécolor, Columbiacolor, and others. For more information on Eastmancolor, see * Color motion picture film, for background on Eastmancolor and other motion picture processes in general * Eastman Kodak Fine Grain color negative films (1950 onwards), within the "List of motion picture film stocks" article Eastman Color Negative Eastman Color Negative (ECN) is a photographic processing system created by Kodak in the 1950s for the development of monopack color negative motion picture film stock. It is part of the Eastmanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arjuna
Arjuna (, , Help:IPA/Sanskrit, [ɐɾd͡ʒun̪ə]) is one of the central characters of the ancient Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. He is the third of the five Pandava brothers, and is widely regarded as the most important and renowned among them. He is the son of Indra, the king of the Deva (Hinduism), gods, and Kunti, wife of King Pandu of Kuru kingdom, Kuru dynasty—making him a Demigod, divine-born hero. Arjuna is famed for his extraordinary prowess in archery and mastery over Astra (weapon), celestial weapons. Throughout the epic, Arjuna sustains a close friendship with his maternal cousin, Krishna, who serves as his spiritual guide. Arjuna is celebrated for numerous heroic exploits throughout the epic. From childhood, he emerges as an excellent pupil, studying under the warrior-sage Drona. In his youth, Arjuna wins the hand of Draupadi, the princess of the Pañcāla, Panchalas, by excelling in a formidable archery competition. Soon after, he goes on a journey during a period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pandava
The Pandavas (Sanskrit: पाण्डव, aɳɖɐʋᵊ IAST: Pāṇḍava) is a group name referring to the five legendary brothers, Yudhishtira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva, who are central figures of the Hindu epic ''Mahabharata''. They are acknowledged as the sons of Pandu, the King of Kuru, but were fathered by different '' Devas'' (gods) due to Pandu's cursed inability to naturally sire children. In the epic, the Pandavas married Draupadi, the princess of Panchala, and founded the city of Indraprastha after the Kuru Kingdom was split to avoid succession disputes. After the split, the other part of the kingdom was ruled by their cousins, the Kauravas. However, the Pandavas lost their kingdom to Duryodhana (eldest and king of the Kauravas) when Yudhishthira gambled it away during a game of dice. The bet Yudhishtira agreed to was that the Pandavas would hand the kingdom over to the Kauravas and go into exile for 12 followed by an year in hiding. After this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drona
Droṇa (, ), also referred to as Dronacharya (, ), is a major character of the Hindu epic Mahabharata. In the epic, he serves as the royal preceptor of the Kauravas and the Pandavas. He is one of the primary counsellors and warriors featured in the epic. Drona is the son of the sage Bharadvaja, and a descendant of the sage Angirasa. Despite being master of advanced military arts and the divine weapons known as astras, Drona initially chooses a life of poverty until he is humiliated by his friend Drupada, the king of Panchala. With the help of his students, he captures Drupada and takes away half of the kingdom. Drona serves as the second commander-in-chief of the Kaurava army, from the 11th day to the 15th day. The acharya fails four times in capturing Yudhishthira (the 11th day, 12th day, 14th day, and the 14th night). He was beheaded by Dhrishtadyumna—his student and son of Drupada—when he meditates to release his soul on the battlefield. Etymology Drona's name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adhiratha
The ''Mahabharata'' is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India composed by Veda Vyasa. At its heart lies the epic struggle between the Pandavas and the Kauravas. The central characters include the five Pandava brothers—Yudhishthira, Bhima, Arjuna, Nakula, and Sahadeva—along with their wife Draupadi. On the opposing side, the hundred Kaurava brothers are led by the elder brother, Duryodhana. However, the ''Mahabharata'' is richly populated with other notable figures including Krishna, Bhishma, Drona, Karna, Kunti, Dushasana, Kripa, Dhritrashtra, Gandhari (Mahabharata), Gandhari, Shakuni, Ashwatthama, Balarama, Subhadra, Vyasa, Abhimanyu, Pandu, Satyavati and Amba (Mahabharata), Amba. The ''Mahabharata'' manuscripts exist in numerous versions, wherein the specifics and details of major characters and episodes vary, often significantly. Except for the sections containing the ''Bhagavad Gita'' which is remarkably consistent between the numerous manuscripts, the rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surya
Surya ( ; , ) is the Sun#Dalal, Dalal, p. 399 as well as the solar deity in Hinduism. He is traditionally one of the major five deities in the Smarta tradition, Smarta tradition, all of whom are considered as equivalent deities in the Panchayatana puja and a means to realise Brahman. Other names of Surya in ancient Indian literature include Āditya, Arka, Bhānu, Savitṛ, Pūṣan, Ravi, Mārtāṇḍa, Mitra, Bhāskara, Prabhākara, Kathiravan, and Vivasvat.#Dalal, Dalal, pp. 5, 311 The iconography of Surya is often depicted riding a chariot harnessed by horses, often seven in number which represent the seven colours of visible light, and the seven days of the week. During the medieval period, Surya was worshipped in tandem with Brahma during the day, Shiva at noon, and Vishnu in the evening. In some ancient texts and art, Surya is presented syncretically with Indra, Ganesha, and others. Surya as a deity is also found in the arts and literature of Buddhism and Jainism. Surya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantra
A mantra ( ; Pali: ''mantra'') or mantram (Devanagari: मन्त्रम्) is a sacred utterance, a numinous sound, a syllable, word or phonemes, or group of words (most often in an Indo-Iranian language like Sanskrit or Avestan) believed by practitioners to have religious, magical or spiritual powers. Feuerstein, Georg (2003), ''The Deeper Dimension of Yoga''. Shambala Publications, Boston, MA Some mantras have a syntactic structure and a literal meaning, while others do not. ꣽ, ॐ (Aum, Om) serves as an important mantra in various Indian religions. Specifically, it is an example of a seed syllable mantra ( bijamantra). It is believed to be the first sound in Hinduism and as the sonic essence of the absolute divine reality. Longer mantras are phrases with several syllables, names and words. These phrases may have spiritual interpretations such as a name of a deity, a longing for truth, reality, light, immortality, peace, love, knowledge, and action. Examples of lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durvasa
In Hindu scriptures, Durvasa (, ), also known as Durvasas (), is a legendary rishi (sage). He is the son of Anasuya and Atri. According to some Puranas, Durvasa is a partial avatar of Shiva, known for his short temper. Wherever he goes, he is received with great reverence by humans and devas alike. Curses and boons The rishi Durvasa, being short-tempered, is said to have both cursed and gifted boons to several notable deities and people in the Hindu scriptures. Some of them include: Curses # Indra, whom he cursed to lose all his powers, after Indra's elephant Airavata threw down a rather fragrant garland given by Durvasa to Indra. # Saraswati, whom he cursed to be born as a human because she laughed at his incorrect recitation of the Vedas. Ubhay Bharati was the human incarnation of the Goddess Saraswati on the earth during 8th Century CE. # Rukmini, whom he cursed to be separated from her husband, Krishna, because she drank water without seeking Durvasa's permission. # Sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunti
Kunti (, un̪t̪iː ), also known as Pritha (, ">r̩t̪ʰaː/nowiki>, ), is a prominent female character in the ancient Hindu epic '' Mahabharata''. She is chiefly recognised as the mother of the central characters—the five Pandavas—having given birth to the three eldest, Yudhishthira, Bhima, and Arjuna, while also raising their younger stepbrothers, the twins Nakula and Sahadeva, as her own. She is portrayed as possessing intelligence, beauty and shrewdness. Born to the Yadava chief Shurasena, Pritha was adopted by her childless uncle, Kuntibhoja, and subsequently bestowed with the name Kunti. During her adolescence, she garnered the favour of the sage Durvasa, receiving a divine '' mantra'' which she could use to invoke any god and bear his child. Intrigued and wanting to test its efficiency, she employed this mantra to invoke the sun god Surya, resulting in the birth of her first born son, Karna. Faced with the societal stigma associated with bearing a chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinema Of South India
Cinema of South India, refers to the cinema of the four major film industries in South India; primarily engaged in making feature films in the four major Dravidian languages of the region, namely Telugu, Tamil, Malayalam and Kannada. They are often colloquially referred to as Tollywood, Kollywood, Mollywood and Sandalwood, respectively. Although the four industries developed independently for a long period of time, gross exchange of artists and technicians, as well as globalisation helped to shape this new identity. By 2010, South India became the home for 6320, or about 62% of the 10,167 cinema theatres in India. In 2021, Telugu film industry emerged as the largest film industry of India in terms of box office revenue. In 2022, Telugu cinema represented 20% of Indian box office revenue, followed by Tamil representing 14%, Malayalam representing 8%, and Kannada representing 5%. As of 2022, the combined revenue of South Indian film industries has surpassed that of the Mumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |