|
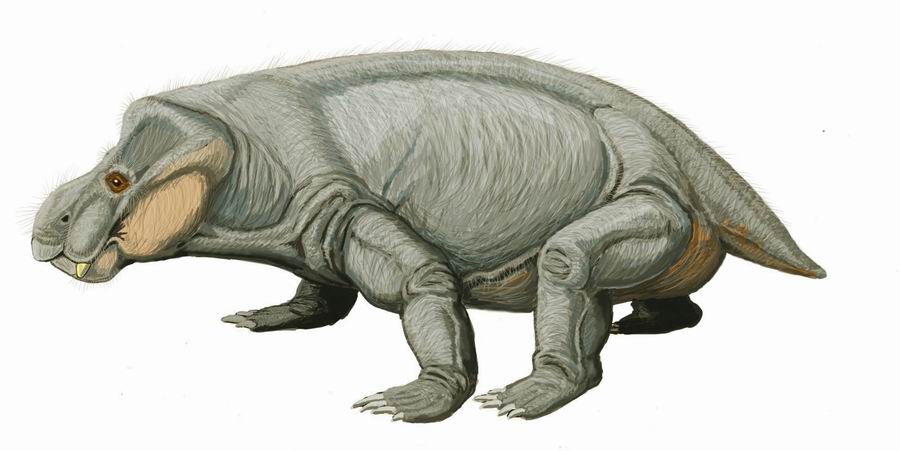
Kannemeyeria
''Kannemeyeria'' is a genus of dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Africa and South America. The generic name is given in honor of Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer, the South African fossil collector who discovered the original specimen. It is one of the first representatives of the family, and hence one of the first large herbivores of the Triassic. Description ''Kannemeyeria'' was about in length, about the size of an ox. Although it had a large head, it was lightweight due to the size of the eye sockets and nasal cavity. It also had limb girdles which formed massive plates of bone that helped support its heavily built body. ''Kannemeyeria'' was well-adapted to living as a herbivore; it had a powerful beak and strong jaw muscles built for shearing plant material. ''Kannemeyeria'' had a massive head with unusually large openings for the eyes, nostrils and jaw muscles. It evidently tore up roots, stripped leaves from the vegetation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynognathus Assemblage Zone
The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is a tetrapod biozone utilized in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. It is equivalent to the Burgersdorp Formation, the youngest Lithostratigraphy, lithostratigraphic Geological formation, formation in the Beaufort Group, which is part of the fossiliferous and geologically important Karoo Supergroup. The ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone is the youngest of the eight biozones found in the Beaufort Group, and is considered to be late Early Triassic (Olenekian) to early Middle Triassic (Anisian) in age (around 247 Ma). The name of the biozone refers to ''Cynognathus, Cynognathus crateronotus'', a large and carnivorous cynodont therapsid which occurs throughout the entire biozone. History The first fossils to be found in the Beaufort Group rocks that encompass the current eight biozones were discovered by Andrew Geddes Bain in 1856. However, it was not until 1892 that it was observed that the geological strata of the Beaufort Group could be different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannemeyeria DB
''Kannemeyeria'' is a genus of dicynodont that lived during the Anisian age of Middle Triassic period in what is now Africa and South America. The generic name is given in honor of Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer, the South African fossil collector who discovered the original specimen. It is one of the first representatives of the family, and hence one of the first large herbivores of the Triassic. Description ''Kannemeyeria'' was about in length, about the size of an ox. Although it had a large head, it was lightweight due to the size of the eye sockets and nasal cavity. It also had limb girdles which formed massive plates of bone that helped support its heavily built body. ''Kannemeyeria'' was well-adapted to living as a herbivore; it had a powerful beak and strong jaw muscles built for shearing plant material. ''Kannemeyeria'' had a massive head with unusually large openings for the eyes, nostrils and jaw muscles. It evidently tore up roots, stripped leaves from the vegetation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omingonde Formation
The Omingonde Formation is an Early Triassic, Early to Middle Triassic (Anisian to Ladinian) geologic Formation (geology), formation, part of the Karoo Supergroup, in the western Otjozondjupa Region and northeastern Erongo Region of north-central Namibia. The formation has a maximum thickness of about and comprises sandstones, shales, siltstones and conglomerate (geology), conglomerates, was deposited in a fluvial depositional environment, environment, alternating between a meandering river, meandering and braided river setting. The Omingonde Formation is correlated with a series of formations in northwestern Argentina and the Paraná Basin in southeastern Brazil, deposited in a larger basinal area, 120 million years before the break-up of Pangea. The formation has provided fossils of several therapsids, amphibians and ichnofossils and belongs to the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone, ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone. The Omingonde Formation preserves the most diverse fauna of Middle Tria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ntawere Formation
The Ntawere Formation is a Middle Triassic (Anisian) geological formation in Zambia, preserving fossils of synapsids, archosaurs, and temnospondyls. Geology Several different facies are present in the Ntawere Formation, reconstructing a floodplain environment. The coarsest facies are trough cross-bedded conglomeratic sandstone full of mineral concretions. These coarse deposits formed in ancient channels such as riverbeds. Another type of facies involves thick beds of mudstone interbedding with thinner layers of fine-grained sandstone, indicating alternating low- and high-energy water flow within the channels. Graded sandstone to mudstone overbank deposits (complete with ripple marks) occur near channel deposits. Extensive successions of laminated or massive mudstone are common, often containing slickensides, calcareous nodules or layers ( marls), and/or hematite nodules. These types of thick mud/marl layers likely formed in more quiet parts of the floodplain isolated from tur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manda Formation
The Manda Formation (also known as the Manda Beds) is a Middle Triassic (Anisian?) or possibly Late Triassic (Carnian?) Formation (stratigraphy), geologic formation in Tanzania. It preserves fossils of many terrestrial vertebrates from the Triassic, including some of the earliest Dinosauromorpha, dinosauromorph archosaurs. The formation is often considered to be Anisian in age according to general tetrapod biochronology hypotheses and correlations to the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone, ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone of South Africa. However, some recent studies cast doubt to this age, suggesting that parts deposits may actually be younger (Carnian) in age. History of study One of the first to study rocks of the Manda Formation was British geologist G. M. Stockley. In 1932, Stockley explored the geology of the Ruhuhu Basin in Tanzania. He called a series of layers dating from the Late Carboniferous to the Middle Triassic the Songea Series and divided it into eight units labelled K1- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer
Daniel Rossouw Kannemeyer (26 December 1843 Cape Town – 1 January 1925 Bloemfontein) was a South African medical practitioner, naturalist, archaeologist and palaeontologist, the son of Daniel Gerhardus Kannemeyer and Johanna Susanna Rossouw He is best remembered for his contributions to palaeontology and archaeology although his collections of zoological specimens are greatly valued by the museums which acquired them. Kannemeyer's family settled in Burgersdorp in the Eastern Cape around 1848. Daniel was a pupil at the South African College in Cape Town between 1859 and 1863. Next he qualified in 1871 as Bachelor of Medicine (MB) and was later licensed to practice by the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh. During that same period he married Helen Hill of Edinburgh in November 1871. The couple returned to Burgersdorp and Kannemeyer practised there, in Aliwal North and Smithfield for the next forty years. His wife was locally acclaimed for her soprano voice, while he served ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivores that typically bore a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typically toothless beak, unique amongst all synapsids. Dicynodonts first appeared in Southern Pangaea during the mid-Permian, ca. 270–260 million years ago, and became globally distributed and the dominant herbivorous animals in the Late Permian, ca. 260–252 Mya. They were devastated by the end-Permian Extinction that wiped out most other therapsids ca. 252 Mya. They rebounded during the Triassic but died out towards the end of that period. They were the most successful and diverse of the non-mammalian therapsids, with over 80-90 genera known, varying from rat-sized burrowers to elephant-sized browsers. Characteristics The dicynodont skull is highly specialised, light but strong, with the synapsid temporal openings at the rear o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaanbeikannemeyeria
''Shaanbeikannemeyeria'' is an extinct genus of dicynodont known from the Early Triassic of China. It contains a single species, ''S. xilougoensis'', which was described in 1980 by Zheng-Wu Cheng from a skull catalogued as IGCAGS V315. The specimen was lost, and a neotype skull IVPP V 11674 was later designated. A second species, ''S. buergondia'', was named by Jin-Lin Li in 1980 from a partial skeleton, but it has since been regarded as a synonym of ''S. xilougoensis''. Paleobiology ''Shaanbeikannemeyeria'' hails from the Ermaying Formation, which also yields the genera ''Fenhosuchus'', ''Eumetabolodon'', ''Halazhaisuchus'', '' Guchengosuchus'', '' Neoprocolophon'', '' Ordosiodon'', ''Wangisuchus ''Wangisuchus'' is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile from the Middle Triassic of China that is known from fragmentary fossil jaw bones. These bones were found at the Hsishihwa locality in the upper Ermaying Formation, which dates to the ...'' and ''Shansisuchus''. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1908 In Paleontology
Arthropoda Newly named insects Archosauromorphs Newly named basal archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaur
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics, cladistic sense of the term includes all living and extinct relatives of birds and crocodilians such as non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, phytosaurs, aetosaurs and rauisuchians as well as many marine reptile#Extinct groups, Mesozoic marine reptiles. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives; and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphology (biology), morphological ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country on the west coast of Southern Africa. Its borders include the Atlantic Ocean to the west, Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south; in the northeast, approximating a quadripoint, Zimbabwe lies less than 200 metres (660 feet) away along the Zambezi, Zambezi River near Kazungula, Zambia. Namibia's capital and largest city is Windhoek. Namibia is the driest country in sub-Saharan Africa, and has been inhabited since prehistoric times by the Khoekhoe, Khoi, San people, San, Damara people, Damara and Nama people. Around the 14th century, immigration, immigrating Bantu peoples arrived as part of the Bantu expansion. From 1600 the Ovambo people#History, Ovambo formed kingdoms, such as Ondonga and Oukwanyama. In 1884, the German Empire established rule over most of the territory, forming a colony known as German South West Africa. Between 1904 and 1908, German troops waged a punitive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |