|
Kai Siegbahn
Kai Manne Börje Siegbahn (20 April 1918 – 20 July 2007) was a Swedish physicist who shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics. Biography Siegbahn was born in Lund, Sweden, son of Manne Siegbahn the 1924 physics Nobel Prize winner. Siegbahn earned his doctorate at the Stockholm University in 1944. He was professor at the Royal Institute of Technology 1951–1954, and then professor of experimental physics at Uppsala University 1954–1984, which was the same chair his father had held. He shared the 1981 Nobel Prize in Physics with Nicolaas Bloembergen and Arthur Schawlow. Siegbahn received half the prize "for his contribution to the development of high-resolution electron spectroscopy" while Bloembergen and Schawlow received one quarter each "for their contribution to the development of laser spectroscopy". Siegbahn referred to his technique as Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA); it is now usually known as X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). In 1967 he publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lund
Lund (, ;"Lund" (US) and ) is a city in the provinces of Sweden, province of Scania, southern Sweden. The town had 94,393 inhabitants out of a municipal total of 130,288 . It is the seat of Lund Municipality, Scania County. The Öresund Region, which includes ''Lund'', is home to more than 4.2 million people. Archeologists date the founding of Lund to around 990, when Scania was part of Denmark. From 1103 it was the seat of the Catholic Metropolitan Archdiocese of Lund, and the towering Lund Cathedral, built –1145, still stands at the centre of the town. Denmark ceded the city to Sweden in the Treaty of Roskilde in 1658. Lund University, established in 1666, is one of Scandinavia's oldest and largest institutions for education and research. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
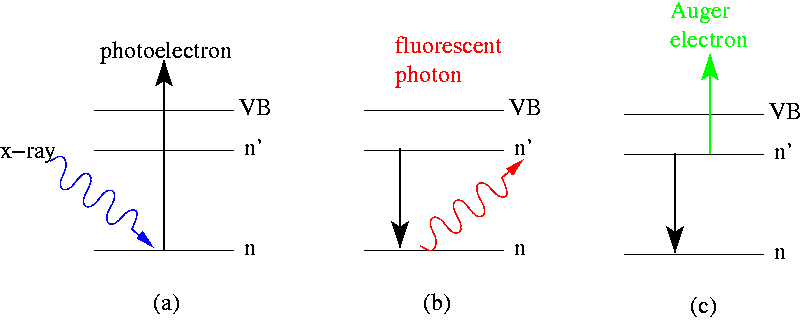
Electron Spectroscopy
Electron spectroscopy refers to a group formed by techniques based on the analysis of the energies of emitted electrons such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectrons and Auger electrons. This group includes X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), which also known as Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA), Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS), Ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS), and Auger electron spectroscopy (AES). These analytical techniques are used to identify and determine the elements and their electronic structures from the surface of a test sample. Samples can be solids, gases or liquids.Yang Leng; ''Materials Characterization: Introduction to Microscopic and Spectroscopic Methods (Second Edition)''; Publisher John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated 2013; p: 191-192, 221-224.Daintith, J.; ''Dictionary of Chemistry (6th Edition)''; Oxford University Press, 2008; p: 191, 416, 541 Chemical information is obtained only from the uppermost atomic layers of the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Pontifical Academy Of Sciences
Member may refer to: * Military jury, referred to as "Members" in military jargon * Element (mathematics), an object that belongs to a mathematical set * In object-oriented programming, a member of a class ** Field (computer science), entries in a database ** Member variable, a variable that is associated with a specific object * Limb (anatomy), an appendage of the human or animal body ** Euphemism for penis * Structural component of a truss, connected by nodes * User (computing), a person making use of a computing service, especially on the Internet * Member (geology), a component of a geological formation * Member of parliament * The Members, a British punk rock band * Meronymy, a semantic relationship in linguistics * Church membership, belonging to a local Christian congregation, a Christian denomination and the universal Church * Member, a participant in a club or learned society A learned society ( ; also scholarly, intellectual, or academic society) is an organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Lund
The term "the people" refers to the public or common mass of people of a polity. As such it is a concept of human rights law, international law as well as constitutional law, particularly used for claims of popular sovereignty. In contrast, a people is any plurality of persons considered as a whole. Used in politics and law, the term "a people" refers to the collective or community of an ethnic group or nation. Concepts Legal Chapter One, Article One of the Charter of the United Nations states that "peoples" have the right to self-determination. Though the mere status as peoples and the right to self-determination, as for example in the case of Indigenous peoples (''peoples'', as in all groups of indigenous people, not merely all indigenous persons as in ''indigenous people''), does not automatically provide for independent sovereignty and therefore secession. Indeed, judge Ivor Jennings identified the inherent problems in the right of "peoples" to self-determination, as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The KTH Royal Institute Of Technology
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockholm University Alumni
Stockholm (; ) is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, most populous city of Sweden, as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in the Nordic countries. Approximately 1 million people live in the Stockholm Municipality, municipality, with 1.6 million in the Stockholm urban area, urban area, and 2.5 million in the Metropolitan Stockholm, metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Mälaren, Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Outside the city to the east, and along the coast, is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. The city serves as the county seat of Stockholm County. Stockholm is the cultural, media, political, and economic centre of Sweden. The Stockholm region alone accounts for over a third of the country's Gros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Physicists
Swedish or ' may refer to: Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically: * Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland ** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by the Swedish language * Swedish people or Swedes, persons with a Swedish ancestral or ethnic identity ** A national or citizen of Sweden, see demographics of Sweden ** Culture of Sweden * Swedish cuisine See also * * Swedish Church (other) * Swedish Institute (other) * Swedish invasion (other) * Swedish Open (other) Swedish Open is a tennis tournament. Swedish Open may also refer to: * Swedish Open (badminton) * Swedish Open (table tennis) * Swedish Open (squash) * Swedish Open (darts) {{disambiguation ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Laureates In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is awarded annually by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to scientists in the various fields of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the 1895 will and testament, will of Alfred Nobel (who died in 1896), awarded for outstanding contributions in physics. As dictated by Nobel's will, the award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The award is presented in Stockholm at an annual ceremony on 10 December, the anniversary of Nobel's death. Each recipient receives a medal, a diploma and a monetary award prize that has varied throughout the years. Statistics The Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to 226 individuals as of 2024. The first prize in physics was awarded in 1901 to Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, of Germany, who received 150,782 Swedish krona, SEK. John Bardeen is the only laureate to win the prize twice—in 1956 and 1972. Lawrence Bragg, Willi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Experimental Physicists
An experiment is a procedure carried out to support or refute a hypothesis, or determine the efficacy or likelihood of something previously untried. Experiments provide insight into cause-and-effect by demonstrating what outcome occurs when a particular factor is manipulated. Experiments vary greatly in goal and scale but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results. There also exist natural experimental studies. A child may carry out basic experiments to understand how things fall to the ground, while teams of scientists may take years of systematic investigation to advance their understanding of a phenomenon. Experiments and other types of hands-on activities are very important to student learning in the science classroom. Experiments can raise test scores and help a student become more engaged and interested in the material they are learning, especially when used over time. Experiments can vary from personal and informal natural comparisons ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2007 Deaths
This is a list of lists of deaths of notable people, organized by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked below. 2025 2024 2023 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 1986 Earlier years ''Deaths in years earlier than this can usually be found in the main articles of the years.'' See also * Lists of deaths by day * Deaths by year (category) {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1918 Births
The ceasefire that effectively ended the First World War took place on the eleventh hour of the eleventh day of the eleventh month of this year. Also in this year, the Spanish flu pandemic killed 50–100 million people worldwide. In Russia, this year runs with only 352 days. As the result of Julian to Gregorian calendar switch, 13 days needed to be skipped. Wednesday, January 31 ''(Julian Calendar)'' was immediately followed by Thursday, February 14 ''(Gregorian Calendar)''. Events World War I will be abbreviated as "WWI" January * January – 1918 flu pandemic: The "Spanish flu" ( influenza) is first observed in Haskell County, Kansas. * January 4 – The Finnish Declaration of Independence is recognized by Soviet Russia, Sweden, Germany and France. * January 8 – American president Woodrow Wilson presents the Fourteen Points as a basis for peace negotiations to end the war. * January 9 – Battle of Bear Valley: U.S. troops engage Yaqui Native Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Physics
The International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP; ) is an international non-governmental organization whose mission is to assist in the worldwide development of physics, to foster international cooperation in physics, and to help in the application of physics toward solving problems of concern to humanity. It was established in 1922 and the first General Assembly was held in 1923 in Paris. The Union is domiciled in Geneva, Switzerland. IUPAP carries out this mission by: sponsoring international meetings; fostering communications and publications; encouraging research and education; fostering the free circulation of scientists; promoting international agreements on the use of symbols, units, nomenclature and standards; and cooperating with other organizations on disciplinary and interdisciplinary problems.Therefore it is very important . IUPAP is a member of the International Science Council. IUPAP is the lead organization promoting the adoption of the International Yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |