|
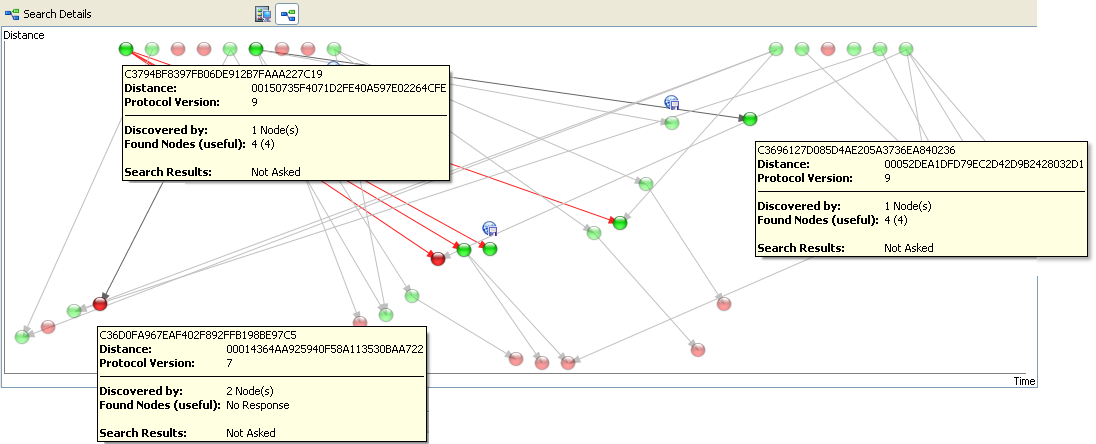
Kad Network
The Kad network is a peer-to-peer (P2P) network which implements the Kademlia P2P overlay protocol. The majority of users on the Kad Network are also connected to servers on the eDonkey network, and Kad Network clients typically query known nodes on the eDonkey network in order to find an initial node on the Kad network. Usage The Kad network uses a UDP-based protocol to: * Find sources for eD2k hashes. * Search for eD2k hashes based on keywords in the file name. * Find comments and ratings for files (hashes). * Provide buddy services for firewalled ( Low ID) nodes. * Store locations, comments and (keywords out of) filenames. Note that the Kad network is not used to actually transfer files across the P2P network. Instead, when a file transfer is initiated, clients connect directly to each other (using the standard public IP network). This traffic is susceptible to blocking/shaping/tracking by an ISP or any other opportunistic middle-man. As with all decentralized networ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peer-to-peer
Peer-to-peer (P2P) computing or networking is a distributed application architecture that partitions tasks or workloads between peers. Peers are equally privileged, equipotent participants in the network, forming a peer-to-peer network of Node (networking), nodes. In addition, a personal area network (PAN) is also in nature a type of Decentralized computing, decentralized peer-to-peer network typically between two devices. Peers make a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants, without the need for central coordination by servers or stable hosts. Peers are both suppliers and consumers of resources, in contrast to the traditional client–server model in which the consumption and supply of resources are divided. While P2P systems had previously been used in many application domains, the architecture was popularized by the Internet file sharing system Napster, originally released in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine (software)
Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer to allow application software and computer games developed for Microsoft Windows to run on Unix-like operating systems. Developers can compile Windows applications against WineLib to help port them to Unix-like systems. Wine is predominantly written using black-box testing reverse engineering, to avoid copyright issues. No code emulation or virtualization occurs, except on Apple Silicon Mac computers, where Rosetta 2 is used to translate x86 code to ARM code. Wine is primarily developed for Linux and macOS. In a 2007 survey by desktoplinux.com of 38,500 Linux desktop users, 31.5% of respondents reported using Wine to run Windows applications. This plurality was larger than all x86 virtualization programs combined, and larger than the 27.9% who reported not running Windows applications. History Bob Amstadt, the initial project leader, and Eric Youngdale started the Wine project in 1993 as a way to run Windows applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key-based Routing
Key-based routing (KBR) is a lookup method used in conjunction with distributed hash tables (DHTs) and certain other overlay networks. While DHTs provide a method to find a host responsible for a certain piece of data, KBR provides a method to find the ''closest'' host for that data, according to some defined Metric (unit), metric. This may not necessarily be defined as physical distance, but rather the number of network hops. Key-based routing networks * Freenet * GNUnet * Kademlia * Onion routing * Garlic routing See also * Public-key cryptography * Distributed hash table#Overlay network, Distributed Hash Table - Overlay Network * Anonymous P2P References Anonymity networks Routing File sharing networks Distributed data storage Network architecture Cryptographic protocols Key-based routing {{Compu-network-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Hash Table
A distributed hash table (DHT) is a Distributed computing, distributed system that provides a lookup service similar to a hash table. Key–value pairs are stored in a DHT, and any participating node (networking), node can efficiently retrieve the value associated with a given key. The main advantage of a DHT is that nodes can be added or removed with minimum work around re-distributing keys. ''Keys'' are unique identifiers which map to particular ''values'', which in turn can be anything from addresses, to Electronic document, documents, to arbitrary Data (computing), data. Responsibility for maintaining the mapping from keys to values is distributed among the nodes, in such a way that a change in the set of participants causes a minimal amount of disruption. This allows a DHT to scale (computing), scale to extremely large numbers of nodes and to handle continual node arrivals, departures, and failures. DHTs form an infrastructure that can be used to build more complex services, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botnet
A botnet is a group of Internet-connected devices, each of which runs one or more Internet bot, bots. Botnets can be used to perform distributed denial-of-service attack, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, steal data, send Spamming, spam, and allow the attacker to access the device and its connection. The owner can control the botnet using command and control (C&C) software. The word "botnet" is a portmanteau of the words "robot" and "Computer network, network". The term is usually used with a negative or malicious connotation. Overview A botnet is a logical collection of Internet-connected devices, such as computers, smartphones or Internet of things (IoT) devices whose Computer security, security have been breached and control ceded to a third party. Each compromised device, known as a "bot," is created when a device is penetrated by software from a ''malware'' (malicious software) distribution. The controller of a botnet is able to direct the activities of these comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alureon
Alureon (also known as TDSS or TDL-4) is a trojan and rootkit created to steal data by intercepting a system's network traffic and searching for banking usernames and passwords, credit card data, PayPal information, social security numbers, and other sensitive user data. Following a series of customer complaints, Microsoft determined that Alureon caused a wave of BSoDs on some 32-bit Microsoft Windows systems. The update, MS10-015, triggered these crashes by breaking assumptions made by the malware author(s). According to research conducted by Microsoft, Alureon was the second most active botnet in the second quarter of 2010. Description The Alureon bootkit was first identified around 2007. Personal computers are usually infected when users manually download and install Trojan software. Alureon is known to have been bundled with the rogue security software, "Security Essentials 2010". When the dropper is executed, it first hijacks the print spooler service (spoolsv.exe) to updat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BitTorrent Protocol
BitTorrent is a communication protocol for peer-to-peer file sharing (P2P), which enables users to distribute data and electronic files over the Internet in a decentralized manner. The protocol is developed and maintained by Rainberry, Inc., and was first released in 2001. To send or receive files, users use a BitTorrent client on their Internet-connected computer, which are available for a variety of computing platforms and operating systems, including an official client. BitTorrent trackers provide a list of files available for transfer and allow the client to find peer users, known as "seeds", who may transfer the files. BitTorrent downloading is considered to be faster than HTTP ("direct downloading") and FTP due to the lack of a central server that could limit bandwidth. BitTorrent is one of the most common protocols for transferring large files, such as digital video files containing TV shows and video clips, or digital audio files. BitTorrent accounted for a third of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lphant
Lphant was a peer-to-peer file sharing client for the Microsoft Windows, Linux and Mac OS operating systems, which supports the eDonkey Network and the BitTorrent protocol. It was available in 19 languages. The name and logo of the original Lphant application has been replicated in a program called "Lphant 6.0" (see Domain Name Acquisition). Features Lphant is a multi-network client, capable of searching for files by connecting to ed2k servers or through the emule source exchange and the kad network. Files can be downloaded simultaneously using the ed2k and BitTorrent protocols. Lphant supports various experimental ed2k features such as Protocol obfuscation, endgame althorithm and webcache, some of which are only found in eMule mods. However, some emule modders consider Lphant a leeching application and have therefore created algorithms which emulate their mods to Lphant when connecting to an Lphant client. Domain Name Acquisition On March 9, 2009, Discordia Ltd, a Cyprus-ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MLDonkey
MLDonkey is an open-source, multi-protocol, peer-to-peer file sharing application that runs as a back-end server application on many platforms. It can be controlled through a user interface provided by one of many separate front-ends, including a Web interface, telnet interface and over a dozen native client programs. Originally a Linux client for the eDonkey protocol, it now runs on many flavors of Unix-like, OS X, Microsoft Windows and MorphOS and supports numerous peer-to-peer protocols. It is written in OCaml, with some C and some assembly. History Development of the software began in late 2001. The original developer of MLDonkey is Fabrice Le Fessant from INRIA. It was originally conceived as an effort to spread the use of OCaml in the open source community. In January 2003, Slyck.com reported brief friction between MLDonkey developers and the official Overnet MetaMachine developers, which denounced MLDonkey as a "rogue client", allegedly for incorrect behavior on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and library (computing), libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license. List of Linux distributions, Thousands of Linux distributions exist, many based directly or indirectly on other distributions; popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, Linux Mint, Arch Linux, and Ubuntu, while commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise, and ChromeOS. Linux distributions are frequently used in server platforms. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMule Plus
eMule is a free peer-to-peer file sharing application for Microsoft Windows. Started in May 2002 as an alternative to eDonkey2000, eMule connects to both the eDonkey network and the Kad network. The distinguishing features of eMule are the direct exchange of sources between client nodes, recovery of corrupted downloads, and the use of a credit system to reward frequent uploaders. eMule transmits data in zlib-compressed form to save bandwidth. eMule is written in C++ using the Microsoft Foundation Classes. Since July 2002 eMule has been free software, released under the GNU General Public License; which has led to eMule's codebase being used as the basis of cross-platform clients aMule, JMule, xMule, along with the release of eMule modifications of the original eMule. it is the fifth most downloaded project on SourceForge, with over 693 million downloads. Development was later restarted by the community as eMule Community. History The eMule project was started on May 13, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |