Wine (software) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wine is a free and open-source compatibility layer to allow
 There is the utility
There is the utility
 Some applications require more tweaking than simply installing the application in order to work properly, such as manually configuring Wine to use certain Windows DLLs. The Wine project does not integrate such workarounds into the Wine codebase, instead preferring to focus solely on improving Wine's implementation of the Windows API. While this approach focuses Wine development on long-term compatibility, it makes it difficult for users to run applications that require workarounds. Consequently, many third-party applications have been created to ease the use of those applications that do not work '' out of the box'' within Wine itself. The Wine wiki maintains a page of current and obsolete third-party applications.
* ''Winetricks'' is a script to install some basic components (typically Microsoft DLLs and fonts) and tweak settings required for some applications to run correctly under Wine. It can fully automate the install of a number of applications and games, including applying any needed workarounds. Winetricks has a GUI. The Wine project will accept bug reports for users of Winetricks, unlike most third-party applications. It is maintained by Wine developer Austin English.
* '' Q4Wine'' is an open GUI for advanced setup of Wine.
* '' Wine-Doors'' is an application management tool for the GNOME desktop which adds functionality to Wine. Wine-Doors is an alternative to WineTools which aims to improve upon WineTools' features and extend on the original idea with a more modern design approach.
* '' IEs4Linux'' is a utility to install all versions of Internet Explorer, including versions 4 to 6 and version 7 (in beta).
* ''Wineskin'' is a utility to manage Wine engine versions and create wrappers for
Some applications require more tweaking than simply installing the application in order to work properly, such as manually configuring Wine to use certain Windows DLLs. The Wine project does not integrate such workarounds into the Wine codebase, instead preferring to focus solely on improving Wine's implementation of the Windows API. While this approach focuses Wine development on long-term compatibility, it makes it difficult for users to run applications that require workarounds. Consequently, many third-party applications have been created to ease the use of those applications that do not work '' out of the box'' within Wine itself. The Wine wiki maintains a page of current and obsolete third-party applications.
* ''Winetricks'' is a script to install some basic components (typically Microsoft DLLs and fonts) and tweak settings required for some applications to run correctly under Wine. It can fully automate the install of a number of applications and games, including applying any needed workarounds. Winetricks has a GUI. The Wine project will accept bug reports for users of Winetricks, unlike most third-party applications. It is maintained by Wine developer Austin English.
* '' Q4Wine'' is an open GUI for advanced setup of Wine.
* '' Wine-Doors'' is an application management tool for the GNOME desktop which adds functionality to Wine. Wine-Doors is an alternative to WineTools which aims to improve upon WineTools' features and extend on the original idea with a more modern design approach.
* '' IEs4Linux'' is a utility to install all versions of Internet Explorer, including versions 4 to 6 and version 7 (in beta).
* ''Wineskin'' is a utility to manage Wine engine versions and create wrappers for

 The developers of the Direct3D portions of Wine have continued to implement new features such as pixel shaders to increase game support. Wine can also use native DLLs directly, thus increasing functionality, but then a license for Windows is needed unless the DLLs were distributed with the application itself.
Wine also includes its own open-source implementations of several Windows programs, such as '' Notepad'', '' WordPad'', '' Control Panel'', ''
The developers of the Direct3D portions of Wine have continued to implement new features such as pixel shaders to increase game support. Wine can also use native DLLs directly, thus increasing functionality, but then a license for Windows is needed unless the DLLs were distributed with the application itself.
Wine also includes its own open-source implementations of several Windows programs, such as '' Notepad'', '' WordPad'', '' Control Panel'', ''
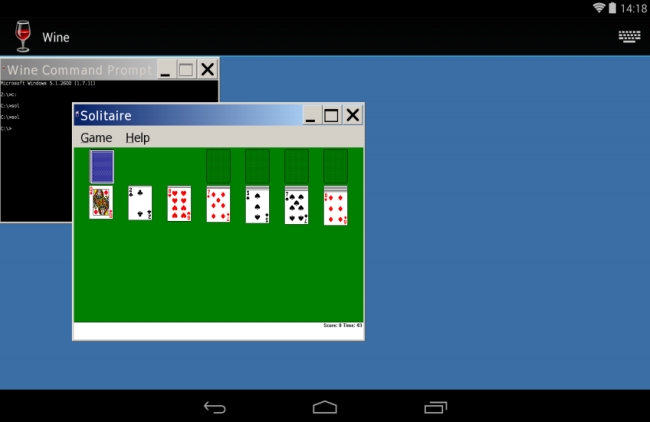 On 3 February 2013 at the FOSDEM talk in Brussels, Alexandre Julliard demonstrated an early demo of Wine running on Google's Android operating system.
Experimental builds of WINE for Android (x86 and ARM) were released in late 2017. It has been routinely updated by the official developers ever since. The default builds do not implement cross-architecture emulation via QEMU, and as a result ARM versions will only run ARM applications that use the Win32 API.
On 3 February 2013 at the FOSDEM talk in Brussels, Alexandre Julliard demonstrated an early demo of Wine running on Google's Android operating system.
Experimental builds of WINE for Android (x86 and ARM) were released in late 2017. It has been routinely updated by the official developers ever since. The default builds do not implement cross-architecture emulation via QEMU, and as a result ARM versions will only run ARM applications that use the Win32 API.
Jeremy White's Wine Answers
– Slashdot interview with Jeremy White of CodeWeavers * * Appointment of the Software Freedom Law Center as legal counsel to represent the Wine project
Wine: Where it came from, how to use it, where it's going
– a work by Dan Kegel
application software
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as ...
and computer games developed for Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
to run on Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s. Developers can compile Windows applications against WineLib to help port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manch ...
them to Unix-like systems. Wine is predominantly written using black-box testing reverse engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accompl ...
, to avoid copyright
A copyright is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the exclusive legal right to copy, distribute, adapt, display, and perform a creative work, usually for a limited time. The creative work may be in a literary, artistic, ...
issues. No code emulation or virtualization occurs, except on Apple Silicon Mac computers, where Rosetta 2 is used to translate x86 code to ARM code. Wine is primarily developed for Linux and macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
.
In a 2007 survey by desktoplinux.com of 38,500 Linux desktop users, 31.5% of respondents reported using Wine to run Windows applications. This plurality was larger than all x86 virtualization programs combined, and larger than the 27.9% who reported not running Windows applications.
History
Bob Amstadt, the initial project leader, and Eric Youngdale started the Wine project in 1993 as a way to run Windows applications onLinux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
. It was inspired by two Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc., often known as Sun for short, was an American technology company that existed from 1982 to 2010 which developed and sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services. Sun contributed sig ...
products, Wabi for the Solaris operating system, and the Public Windows Interface, which was an attempt to get the Windows API fully reimplemented in the public domain as an ISO
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
Me ...
standard but rejected due to pressure from Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
in 1996. Wine originally targeted 16-bit applications for Windows 3.x, but focuses on 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
and 64-bit versions which have become the standard on newer operating systems. The project originated in discussions on Usenet
Usenet (), a portmanteau of User's Network, is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose UUCP, Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Elli ...
in comp.os.linux in June 1993. Alexandre Julliard has led the project since 1994.
The project has proven time-consuming and difficult for the developers, mostly because of incomplete and incorrect documentation
Documentation is any communicable material that is used to describe, explain or instruct regarding some attributes of an object, system or procedure, such as its parts, assembly, installation, maintenance, and use. As a form of knowledge managem ...
of the Windows API. While Microsoft extensively documents most Win32 functions, some areas such as file format
A file format is a Computer standard, standard way that information is encoded for storage in a computer file. It specifies how bits are used to encode information in a digital storage medium. File formats may be either proprietary format, pr ...
s and protocols have no public, complete specification available from Microsoft. Windows also includes undocumented low-level functions, undocumented behavior and obscure bugs that Wine must duplicate precisely in order to allow some applications to work properly. Consequently, the Wine team has reverse-engineered many function calls and file formats in such areas as thunking.
The Wine project originally released Wine under the same MIT License
The MIT License is a permissive software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts very few restrictions on reuse and therefore has high license compatibility.
Unl ...
as the X Window System, but owing to concern about proprietary versions of Wine not contributing their changes back to the core project, work as of March 2002 has used the LGPL for its licensing.
Wine officially entered beta with version 0.9 on 25 October 2005. Version 1.0 was released on 17 June 2008, after 15 years of development. Version 1.2 was released on 16 July 2010, version 1.4 on 7 March 2012, version 1.6 on 18 July 2013, version 1.8 on 19 December 2015 and version 9.0 on 16 January 2024. Development versions are released roughly every two weeks.
Wine-staging is an independently maintained set of aggressive patches not deemed ready by WineHQ developers for merging into the Wine repository, but still considered useful by the wine-compholio fork. It mainly covers experimental functions and bug fixes. Since January 2017, patches in wine-staging begins to be actively merged into the WineHQ upstream as wine-compholio transferred the project to Alistair Leslie-Hughes, a key WineHQ developer. , WineHQ also provides pre-built versions of wine-staging.
Corporate sponsorship
The main corporate sponsor of Wine is CodeWeavers, which employs Julliard and many other Wine developers to work on Wine and on CrossOver, CodeWeavers' supported version of Wine. CrossOver includes some application-specific tweaks not considered suitable for the upstream version, as well as some additional proprietary components. Canadian software developer Corel for a time assisted the project, chiefly by employing Julliard and others to work on it. Corel had an interest in porting WordPerfect Office, itsoffice suite
Productivity software (also called personal productivity software or office productivity software) is application software used for producing information (such as documents, presentations, worksheets, databases, charts, graphs, digital paintin ...
, to Linux (especially Corel Linux). Corel later cancelled all Linux-related projects after Microsoft made major investments in Corel, stopping their Wine effort.
Other corporate sponsors include Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial ...
, which hired CodeWeavers to fix Wine so Picasa ran well enough to be ported directly to Linux using the same binary as on Windows; Google later paid for improvements to Wine's support for Adobe Photoshop CS2. Wine is also a regular beneficiary of Google's Summer of Code program.
Valve works with CodeWeavers to develop Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , Hydron (chemistry), H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' (elementary charge). Its mass is slightly less than the mass of a neutron and approximately times the mass of an e ...
, a Wine-based compatibility layer for Microsoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
games to run on Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
-based operating systems. Proton includes several patches that upstream Wine does not accept for various reasons, such as Linux-specific implementations of Win32 functions.
Design
The goal of Wine is to implement the Windows APIs fully or partially that are required by programs that the users of Wine wish to run on top of a Unix-like system.Basic architecture
The programming interface of Microsoft Windows consists largely of dynamic-link libraries (DLLs). These contain a huge number of wrapper sub-routines for the system calls of the kernel, the NTOS kernel-mode program (ntoskrnl.exe). A typical Windows program calls some Windows DLLs, which in turn calls user-mode gdi/user32 libraries, which in turn uses the kernel32.dll (win32 subsystem) responsible for dealing with the kernel through system calls. The system-call layer is considered private to Microsoft programmers as documentation is not publicly available, and published interfaces all rely on subsystems running on top of the kernel. Besides these, there are a number of programming interfaces implemented as services that run as separate processes. Applications communicate with user-mode services through RPCs. Wine implements the Windowsapplication binary interface
An application binary interface (ABI) is an interface exposed by software that is defined for in-process machine code access. Often, the exposing software is a library, and the consumer is a program.
An ABI is at a relatively low-level of a ...
(ABI) entirely in user space, rather than as a kernel module. Wine mostly mirrors the hierarchy, with services normally provided by the kernel in Windows instead provided by a daemon known as the wineserver, whose task is to implement basic Windows functionality, as well as integration with the X Window System
The X Window System (X11, or simply X) is a windowing system for bitmap displays, common on Unix-like operating systems.
X originated as part of Project Athena at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1984. The X protocol has been at ...
, and translation of signals into native Windows exceptions. Although wineserver implements some aspects of the Windows kernel, it is not possible to use native Windows drivers with it, due to Wine's underlying architecture.
Libraries and applications
Wine allows for loading both Windows DLLs and Unix shared objects for its Windows programs. Its built-in implementation of the most basic Windows DLLs, namely NTDLL, KERNEL32, GDI32, and USER32, uses the shared object method because they must use functions in the host operating system as well. Higher-level libraries, such as WineD3D, are free to use the DLL format. In many cases users can choose to load a DLL from Windows instead of the one implemented by Wine. Doing so can provide functionalities not yet implemented by Wine, but may also cause malfunctions if it relies on something else not present in Wine. Wine tracks its state of implementation through automatedunit testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
done at every git commit.
Graphics and gaming
While most office software does not make use of complex GPU-accelerated graphics APIs, computer games do. To run these games properly, Wine would have to forward the drawing instructions to the host OS, and even translate them to something the host can understand.DirectX
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct" ...
is a collection of Microsoft APIs for rendering, audio and input. As of 2019, Wine 4.0 contains a DirectX 12 implementation for Vulkan API, and DirectX 11.2 for OpenGL. Direct2D support has been updated to Direct2D 1.2. Wine 4.0 also allows Wine to run Vulkan applications by handing draw commands to the host OS, or in the case of macOS, by translating them into the Metal API by MoltenVK.
; XAudio
:, Wine 4.3 uses the FAudio library (and Wine 4.13 included a fix for it) to implement the XAudio2 audio API (and more).
; XInput and Raw Input
: Wine, since 4.0 (2019), supports game controller
A game controller, gaming controller, or simply controller, is an input device or Input/Output Device, input/output device used with video games or entertainment systems to provide input to a video game. Input devices that have been classified as ...
s through its builtin implementations of these libraries. They are built as Unix shared objects as they need to access the controller interfaces of the underlying OS, specifically through SDL.
Direct3D
Much of Wine's DirectX effort goes into building WineD3D, a translation layer from Direct3D and DirectDraw API calls intoOpenGL
OpenGL (Open Graphics Library) is a Language-independent specification, cross-language, cross-platform application programming interface (API) for rendering 2D computer graphics, 2D and 3D computer graphics, 3D vector graphics. The API is typic ...
. As of 2019, this component supports up to DirectX 11. As of 12 December 2016, Wine is good enough to run '' Overwatch'' with D3D11. Besides being used in Wine, WineD3D DLLs have also been used on Windows itself, allowing for older GPUs to run games using newer DirectX versions and for old DDraw-based games to render correctly.
Some work is ongoing to move the Direct3D backend to Vulkan API. Direct3D 12 support in 4.0 is provided by a "vkd3d" subproject, and WineD3D has in 2019 been experimentally ported to use the Vulkan API. Another implementation, DXVK, translates Direct3D 8, 9, 10, and 11 calls using Vulkan as well and is a separate project.
Wine, when patched, can alternatively run Direct3D 9 API commands directly via a free and open-source Gallium3D State Tracker (aka Gallium3D GPU driver) without translation into OpenGL API calls. In this case, the Gallium3D layer allows a direct pass-through of DX9 drawing commands which results in performance improvements of up to a factor of 2. As of 2020, the project is named Gallium.Nine. It is available now as a separate standalone package and no longer needs a patched Wine version.
User interface
Wine is usually invoked from the command-line interpreter:wine program.exe.
winecfg
 There is the utility
There is the utility winecfg that starts a graphical user interface with controls for adjusting basic options. It is a GUI configuration utility included with Wine. Winecfg makes configuring Wine easier by making it unnecessary to edit the registry directly, although, if needed, this can be done with the included registry editor (similar to Windows '' regedit'').
Third-party applications
 Some applications require more tweaking than simply installing the application in order to work properly, such as manually configuring Wine to use certain Windows DLLs. The Wine project does not integrate such workarounds into the Wine codebase, instead preferring to focus solely on improving Wine's implementation of the Windows API. While this approach focuses Wine development on long-term compatibility, it makes it difficult for users to run applications that require workarounds. Consequently, many third-party applications have been created to ease the use of those applications that do not work '' out of the box'' within Wine itself. The Wine wiki maintains a page of current and obsolete third-party applications.
* ''Winetricks'' is a script to install some basic components (typically Microsoft DLLs and fonts) and tweak settings required for some applications to run correctly under Wine. It can fully automate the install of a number of applications and games, including applying any needed workarounds. Winetricks has a GUI. The Wine project will accept bug reports for users of Winetricks, unlike most third-party applications. It is maintained by Wine developer Austin English.
* '' Q4Wine'' is an open GUI for advanced setup of Wine.
* '' Wine-Doors'' is an application management tool for the GNOME desktop which adds functionality to Wine. Wine-Doors is an alternative to WineTools which aims to improve upon WineTools' features and extend on the original idea with a more modern design approach.
* '' IEs4Linux'' is a utility to install all versions of Internet Explorer, including versions 4 to 6 and version 7 (in beta).
* ''Wineskin'' is a utility to manage Wine engine versions and create wrappers for
Some applications require more tweaking than simply installing the application in order to work properly, such as manually configuring Wine to use certain Windows DLLs. The Wine project does not integrate such workarounds into the Wine codebase, instead preferring to focus solely on improving Wine's implementation of the Windows API. While this approach focuses Wine development on long-term compatibility, it makes it difficult for users to run applications that require workarounds. Consequently, many third-party applications have been created to ease the use of those applications that do not work '' out of the box'' within Wine itself. The Wine wiki maintains a page of current and obsolete third-party applications.
* ''Winetricks'' is a script to install some basic components (typically Microsoft DLLs and fonts) and tweak settings required for some applications to run correctly under Wine. It can fully automate the install of a number of applications and games, including applying any needed workarounds. Winetricks has a GUI. The Wine project will accept bug reports for users of Winetricks, unlike most third-party applications. It is maintained by Wine developer Austin English.
* '' Q4Wine'' is an open GUI for advanced setup of Wine.
* '' Wine-Doors'' is an application management tool for the GNOME desktop which adds functionality to Wine. Wine-Doors is an alternative to WineTools which aims to improve upon WineTools' features and extend on the original idea with a more modern design approach.
* '' IEs4Linux'' is a utility to install all versions of Internet Explorer, including versions 4 to 6 and version 7 (in beta).
* ''Wineskin'' is a utility to manage Wine engine versions and create wrappers for macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
.
* '' PlayOnLinux'' is an application to ease the installation of Windows applications (primarily games). There is also a corresponding Macintosh version called '' PlayOnMac''.
* '' Lutris'' is an open-source application to install Windows games on Linux.
* ''Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( ; ; Gascon language, Gascon ; ) is a city on the river Garonne in the Gironde Departments of France, department, southwestern France. A port city, it is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the Prefectures in F ...
'' is a proprietary Wine GUI configuration manager that runs winelib applications. It also supports installation of third-party utilities, installation of applications and games, and the ability to use custom configurations. ''Bordeaux'' currently runs on Linux, FreeBSD, PC-BSD, Solaris, OpenSolaris, OpenIndiana, and macOS computers.
* ''Bottles'' is an open-source graphical Wine prefix and runners manager for Wine based on GTK4+ Libadwaita. It provides a repository-based dependency installation system and bottle versioning to restore a previous state.
* ''WineGUI'' is a free and open-source graphical interface to manage Wine. It allows a user to create Wine bottles and install Windows applications or games.
Functionality

Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated as IE or MSIE) is a deprecation, retired series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were u ...
'', and '' Windows Explorer''.
The Wine Application Database (AppDB) is a community-maintained on-line database about which Windows programs works with Wine and how well they work.
Backward compatibility
Wine ensures goodbackward compatibility
In telecommunications and computing, backward compatibility (or backwards compatibility) is a property of an operating system, software, real-world product, or technology that allows for interoperability with an older legacy system, or with Input ...
with legacy Windows applications, including those written for Windows 3.1x. Wine can mimic different Windows versions required for some programs, going as far back as Windows 2.0. However, Windows 1.x and Windows 2.x support was removed from Wine development version 1.3.12. If DOSBox is installed on the system (see below on MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
), Wine development version 1.3.12 and later nevertheless show the "Windows 2.0" option for the Windows version to mimic, but Wine still will not run most Windows 2.0 programs because MS-DOS and Windows functions are not currently integrated.
Backward compatibility in Wine is generally superior to that of Windows, as newer versions of Windows can force users to upgrade legacy Windows applications, and may break unsupported software forever as there is nobody adjusting the program for the changes in the operating system. In many cases, Wine can offer better legacy support than newer versions of Windows with "Compatibility Mode". Wine can run 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
Windows programs ( Win16) on a 64-bit operating system, which uses an x86-64 (64-bit) CPU, a functionality not found in 64-bit versions of Microsoft Windows. WineVDM allows 16-bit Windows applications to run on 64-bit versions of Windows.
Wine partially supports Windows console applications, and the user can choose which backend to use to manage the console (choices include raw streams, curses, and user32). When using the raw streams or curses backends, Windows applications will run in a Unix terminal.
64-bit applications
Preliminary support for 64-bit Windows applications was added to Wine 1.1.10, in December 2008. , the support is considered stable. The two versions of Wine are built separately, and as a result only building wine64 produces an environment only capable of running x86-64 applications. , Wine has stable support for a WoW64 build, which allows both 32-bit and 64-bit Windows applications to run inside the same Wine instance. To perform such a build, one must first build the 64-bit version, and then build the 32-bit version referencing the 64-bit version. Just like Microsoft's WoW64, the 32-bit build process will add parts necessary for handling 32-bit programs to the 64-bit build. This functionality is seen from at least 2010.MS-DOS
Early versions of Microsoft Windows run on top ofMS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few op ...
, and Windows programs may depend on MS-DOS programs to be usable. Wine does not have good support for MS-DOS, but starting with development version 1.3.12, Wine tries running MS-DOS programs in DOSBox if DOSBox is available on the system. However, due to a bug, current versions of Wine incorrectly identify Windows 1.x and Windows 2.x programs as MS-DOS programs, attempting to run them in DOSBox (which does not work).
Winelib
Wine provides Winelib, which allows its shared-object implementations of the Windows API to be used as actual libraries for a Unix program. This allows for Windows code to be built into native Unix executables. Since October 2010, Winelib also works on the ARM platform.Non-x86 architectures
Support for Solaris SPARC was dropped in version 1.5.26.ARM, Windows CE, and Windows RT
Wine provides some support for ARM (as well as ARM64/AArch64) processors and the Windows flavors that run on it. , Wine can run ARM/Win32 applications intended for unlocked Windows RT devices (but not Windows RT programs). Windows CE support (either x86 or ARM) is missing, but an unofficial, pre-alpha proof-of-concept version called WineCE allows for some support.Wine for Android
 On 3 February 2013 at the FOSDEM talk in Brussels, Alexandre Julliard demonstrated an early demo of Wine running on Google's Android operating system.
Experimental builds of WINE for Android (x86 and ARM) were released in late 2017. It has been routinely updated by the official developers ever since. The default builds do not implement cross-architecture emulation via QEMU, and as a result ARM versions will only run ARM applications that use the Win32 API.
On 3 February 2013 at the FOSDEM talk in Brussels, Alexandre Julliard demonstrated an early demo of Wine running on Google's Android operating system.
Experimental builds of WINE for Android (x86 and ARM) were released in late 2017. It has been routinely updated by the official developers ever since. The default builds do not implement cross-architecture emulation via QEMU, and as a result ARM versions will only run ARM applications that use the Win32 API.
Microsoft applications
Wine, by default, uses specialized Windows builds ofGecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates. They range from .
Geckos are unique among lizards ...
and Mono to substitute for Microsoft's Internet Explorer
Internet Explorer (formerly Microsoft Internet Explorer and Windows Internet Explorer, commonly abbreviated as IE or MSIE) is a deprecation, retired series of graphical user interface, graphical web browsers developed by Microsoft that were u ...
and .NET Framework. Wine has built-in implementations of JScript and VBScript. It is possible to download and run Microsoft's installers for those programs through winetricks or manually.
Wine is not known to have good support for most versions of Internet Explorer (IE). Of all the reasonably recent versions, Internet Explorer 8 for Windows XP is the only version that reports a usable rating on Wine's AppDB, out-of-the-box. However Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google. It was first released in 2008 for Microsoft Windows, built with free software components from Apple WebKit and Mozilla Firefox. Versions were later released for Linux, macOS, iOS, iPadOS, an ...
gets a gold rating (as of Wine 5.5-staging), and Microsoft's IE replacement web browser Edge, is known to be based on that browser (after switching from Microsoft's own rendering engine). Winetricks offer auto-installation for Internet Explorer 6 through 8, so these versions can be reasonably expected to work with its built-in workarounds.
An alternative for installing Internet Explorer directly is to use the now-defunct IEs4Linux. It is not compatible with the latest versions of Wine, and the development of IEs4Linux is inactive.
Other versions of Wine
The core Wine development aims at a correct implementation of the Windows API as a whole and has sometimes lagged in some areas of compatibility with certain applications. Direct3D, for example, remained unimplemented until 1998, although newer releases have had an increasingly complete implementation.CrossOver
CodeWeavers markets CrossOver specifically for running Microsoft Office and other major Windows applications, including some games. CodeWeavers employs Alexandre Julliard to work on Wine and contributes most of its code to the Wine project under the LGPL. CodeWeavers also released a new version called CrossOver Mac for Intel-based Apple Macintosh computers on 10 January 2007. Unlike upstream wine, CrossOver is notably able to run on the x64-only versions of macOS, using a technique known as "wine32on64". As of 2012, CrossOver includes the functionality of both the CrossOver Games and CrossOver Pro lines therefore CrossOver Games and CrossOver Pro are no longer available as single products. CrossOver Games was optimized for running Windowsvideo game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s. Unlike CrossOver, it didn't focus on providing the most stable version of Wine. Instead, experimental features are provided to support newer games.
Proton
On 21 August 2018, Valve announced a new variation of Wine, named Proton, designed to integrate with the Linux version of the company'sSteam
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is inv ...
software (including Steam installations built into their Linux-based SteamOS operating system and Steam Machine computers). Valve's goal for Proton is to enable Steam users on Linux to play games which lack a native Linux port (particularly back-catalog games), and ultimately, through integration with Steam as well as improvements to game support relative to mainline Wine, to give users "the same simple plug-and-play experience" that they would get if they were playing the game natively on Linux. Proton entered public beta immediately upon being announced.
Valve had already been collaborating with CodeWeavers since 2016 to develop improvements to Wine's gaming performance, some of which have been merged to the upstream Wine project. Some of the specific improvements incorporated into Proton include Vulkan-based Direct3D 9, 10, 11, and 12 implementations via vkd3d, DXVK, and D9VK multi-threaded performance improvements via esync, improved handling of fullscreen games, and better automatic game controller hardware support.
Proton is fully open-source and available via GitHub.
WINE@Etersoft
TheRussia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
n company Etersoft has been developing a proprietary version of Wine since 2006. WINE@Etersoft supports popular Russian applications (for example, 1C:Enterprise by 1C Company).
Other projects using Wine source code
Other projects using Wine source code include: * WineVDM, a.k.a. OTVDM, a 16-bit app compatibility layer for 64-bit Windows *ReactOS
ReactOS is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system for i586/amd64 personal computers that is intended to be binary-code compatibility, binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers developed for Wind ...
, a project to write an operating system compatible with Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Original ...
versions 5.x and up (which includes Windows 2000
Windows 2000 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft, targeting the server and business markets. It is the direct successor to Windows NT 4.0, and was Software release life cycle#Release to manufacturing (RT ...
and its successors) down to the device driver
In the context of an operating system, a device driver is a computer program that operates or controls a particular type of device that is attached to a computer or automaton. A driver provides a software interface to hardware devices, enabli ...
level. ReactOS uses Wine source code considerably. However, due to architectural differences, ReactOS cannot directly reuse Wine's NTDLL, USER32, KERNEL32, GDI32, and ADVAPI32 components. In July 2009, Aleksey Bragin, the ReactOS project lead, started a new ReactOS branch called Arwinss, and it was officially announced in January 2010. Arwinss is an alternative implementation of the core Win32 components, and uses mostly unchanged versions of Wine's user32.dll and gdi32.dll.
* WineBottler, a wrapper around Wine in the form of a normal Mac application. It manages multiple Wine configurations for different programs in the form of "bottles."
* ''Wineskin'', an open source Wine GUI configuration manager for macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
. Wineskin creates a wrapper around Wine in the form of a normal Mac Application. The wrapper can also be used to make a distributable "port" of software.
* Odin
Odin (; from ) is a widely revered god in Norse mythology and Germanic paganism. Most surviving information on Odin comes from Norse mythology, but he figures prominently in the recorded history of Northern Europe. This includes the Roman Em ...
, a project to run Win32 binaries on OS/2
OS/2 is a Proprietary software, proprietary computer operating system for x86 and PowerPC based personal computers. It was created and initially developed jointly by IBM and Microsoft, under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci, ...
or convert them to OS/2 native format. The project also provides the Odin32 API to compile Win32 programs for OS/2.
* Virtualization products such as Parallels Desktop for Mac and VirtualBox
Oracle VirtualBox (formerly Sun VirtualBox, Sun xVM VirtualBox and InnoTek VirtualBox) is a hosted hypervisor for x86 virtualization developed by Oracle Corporation. VirtualBox was originally created by InnoTek Systemberatung GmbH, which was ac ...
use WineD3D to make use of the GPU.
* WinOnX, a commercial package of Wine for macOS that includes a GUI for adding and managing applications and virtual machines.
* WineD3D for Windows, a compatibility wrapper which emulates old Direct3D versions and features that were removed by Microsoft in recent Windows releases, using OpenGL. This sometimes gets older games working again.
* Apple Game Porting Toolkit, a suite of software introduced at Apple's Worldwide Developer Conference in June 2023 to facilitate porting games from Windows to Mac.
Discontinued
* Cedega / WineX: TransGaming Inc. (now Findev Inc. since the sale of its software businesses) produced the proprietary Cedega software. Formerly known as WineX, Cedega represented a fork from the last MIT-licensed version of Wine in 2002. Much like CrossOver Games, TransGaming's Cedega was targeted towards running Windows video games. On 7 January 2011, TransGaming Inc. announced continued development of Cedega Technology under the GameTree Developer Program. TransGaming Inc. allowed members to keep using their Cedega ID and password until 28 February 2011. *Cider
Cider ( ) is an alcoholic beverage made from the Fermented drink, fermented Apple juice, juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom (particularly in the West Country) and Ireland. The United Kingdom has the world's highest ...
: TransGaming also produced Cider, a library for Apple–Intel architecture Macintoshes. Instead of being an end-user product, Cider (like Winelib) is a wrapper allowing developers to adapt their games to run natively on Intel Mac without any changes in source code.
* Darwine: a port of the Wine libraries to Darwin and Mac OS X for the PowerPC and Intel x86 (32-bit) architectures, created by the OpenDarwin team in 2004. Its PowerPC version relied on QEMU. Darwine was merged back into Wine in 2009.
* E/OS LX: a project attempting to allow any program designed for any operating system to be run without the need to actually install any other operating system.
* Pipelight: a custom version of Wine (wine-compholio) that acts as a wrapper for Windows NPAPI plugins within Linux browsers. This tool permits Linux users to run Microsoft Silverlight, the Microsoft equivalent of Adobe Flash, and the Unity web plugin, along with a variety of other NPAPI plugins. The project provides an extensive set of patches against the upstream Wine project, some of which were approved and added to upstream Wine. Pipelight is largely obsolete, as modern browsers no longer support NPAPI plugins and Silverlight has been deprecated by Microsoft.
Reception
The Wine project has received a number of technical and philosophical complaints and concerns over the years.Security
Because of Wine's ability to run Windows binary code, concerns have been raised over native Windows viruses and malware affecting Unix-like operating systems as Wine can run limited malware made for Windows. A 2018 security analysis found that 5 out of 30 malware samples were able to successfully run through Wine, a relatively low rate that nevertheless posed a security risk. For this reason the developers of Wine recommend never running it as thesuperuser
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of the ...
. Malware research software such as ZeroWine runs Wine on Linux in a virtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, to keep the malware completely isolated from the host system. An alternative to improve the security without the performance cost of using a virtual machine, is to run Wine in an LXC container, as Anbox software is doing by default with Android.
Another security concern is when the implemented specifications are ill-designed and allow for security compromise. Because Wine implements these specifications, it will likely also implement any security vulnerabilities they contain. One instance of this problem was the 2006 Windows Metafile vulnerability, which saw Wine implementing the vulnerable SETABORTPROC escape.
Wine vs. native Unix applications
A common concern about Wine is that its existence means that vendors are less likely to write native Linux, macOS, and BSD applications. As an example of this, it is worth considering IBM's 1994 operating system, OS/2 Warp. An article describes the weaknesses of OS/2 which killed it, the first one being: However, OS/2 had many problems with end user acceptance. Perhaps the most serious was that most computers sold already came with DOS and Windows, and many people didn't bother to evaluate OS/2 on its merits due to already having an operating system. "Bundling" of DOS and Windows and the chilling effect this had on the operating system market frequently came up in '' United States v. Microsoft Corporation''. The Wine project itself responds to the specific complaint of "encouraging" the continued development for the Windows API on one of its wiki pages: Also, the Wine Wiki page claims that Wine can help break the chicken-and-egg problem for Linux on the desktop: The use of Wine for gaming has proved specifically controversial in the Linux community, as some feel it is preventing, or at least hindering, the further growth of native Linux gaming on the platform. One quirk however is that Wine is now able to run16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two ...
and even certain 32-bit
In computer architecture, 32-bit computing refers to computer systems with a processor, memory, and other major system components that operate on data in a maximum of 32- bit units. Compared to smaller bit widths, 32-bit computers can perform la ...
applications and games that do not launch on current 64-bit Windows versions. This use-case has led to running Wine on Windows itself via Windows Subsystem for Linux or third-party virtual machines
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
, as well as encapsulated by means such as BoxedWine and otvdm.
Microsoft
Until 2020,Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company, technology conglomerate headquartered in Redmond, Washington. Founded in 1975, the company became influential in the History of personal computers#The ear ...
had not made any public statements about Wine. However, the Windows Update online service blocks updates to Microsoft applications running in Wine. On 16 February 2005, Ivan Leo Puoti discovered that Microsoft had started checking the Windows Registry
The Windows Registry is a hierarchical database that stores low-level settings for the Microsoft Windows operating system and for applications that opt to use the registry. The kernel, device drivers, services, Security Accounts Manager, a ...
for the Wine configuration key and would block the Windows Update for any component. As Puoti noted: "It's also the first time Microsoft acknowledges the existence of Wine."
In January 2020, Microsoft cited Wine as a positive consequence of being able to reimplement APIs, in its amicus curiae brief for '' Google LLC v. Oracle America, Inc.''
In August 2024, Microsoft donated the Mono Project, a reimplementation of the .NET Framework, to the developers of Wine.
See also
* Anbox * Columbia Cycada * Darling (software) * Executor (software) * Linux kernel API * List of free and open-source software packages *Mono (software)
Mono is a free and open-source software framework that aims to run software made for the .NET Framework on Linux and other OSes. Originally by Ximian which was acquired by Novell, it was later developed by Xamarin which was acquired by Microsoft. ...
* PlayOnLinux
* PlayOnMac
* ReactOS
ReactOS is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source operating system for i586/amd64 personal computers that is intended to be binary-code compatibility, binary-compatible with computer programs and device drivers developed for Wind ...
* Windows Interface Source Environment
* Windows Subsystem for Linux
Notes
References
Further reading
Jeremy White's Wine Answers
– Slashdot interview with Jeremy White of CodeWeavers * * Appointment of the Software Freedom Law Center as legal counsel to represent the Wine project
Wine: Where it came from, how to use it, where it's going
– a work by Dan Kegel
External links
* {{Unix–Windows interoperability 1993 software Compatibility layers Computing platforms Cross-platform software Free software programmed in C Free system software Linux APIs Linux emulation software Software using the GNU Lesser General Public License