|
K. C. Kesava Pillai
Kanakku Chembakaraman Kesava Pillai (1868–1914) was an Indian composer of Carnatic music and a poet of Malayalam literature. He was the Poet Laureate of Travancore and was known for ''Kesaveeyam'', a mahakavya in Malayalam, two attakathas and several bhajans and kirtans. He also translated the Sanskrit text, Narayaniyam, into Malayalam under the title, ''Bhashanarayaniyam''. Biography K. C. Kesava Pillai was born on February 4, 1868, in Travancore kingdom to Valiyavelichathu Veettil Raman Pillai and Desathu Lakshmy Amma. His early schooling was at Paravur Malayalam School where he studied up to 5th standard and followed it up with Sanskrit studies under the tutelage of Paravur Kesavan Asan and grammar studies under Enakkattu Rajaraja Varma. As a boy, Pillai regularly watched Kathakali and learnt the basics of Kathakali literature, costumes and mudras, besides gaining proficiency in music. Aged 15, he wrote his first attakadha, ''Prahladacharitham''. Simultaneously, he stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travancore
The kingdom of Travancore (), also known as the kingdom of Thiruvithamkoor () or later as Travancore State, was a kingdom that lasted from until 1949. It was ruled by the Travancore Royal Family from Padmanabhapuram, and later Thiruvananthapuram. At its zenith, the kingdom covered most of the south of modern-day Kerala ( Idukki, Kottayam, Alappuzha, Pathanamthitta, Kollam, and Thiruvananthapuram districts, major portions of Ernakulam district, Puthenchira village of Thrissur district) and the southernmost part of modern-day Tamil Nadu ( Kanyakumari district and some parts of Tenkasi district) with the Thachudaya Kaimal's enclave of Irinjalakuda Koodalmanikyam temple in the neighbouring kingdom of Cochin. However Tangasseri area of Kollam city and Anchuthengu near Attingal in Thiruvananthapuram were parts of British India. Malabar District of Madras Presidency was to the north, the Madurai and Tirunelveli districts of Pandya Nadu region in Madras Presidency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sree Moolam Thirunal
Sir Sri Moolam Thirunal Rama Varma VI (1857–1924) was Maharajah of the princely state of Travancore between 1885 and 1924, succeeding his uncle Maharajah Visakham Thirunal (1880–1885). Moolam Thirunal is considered as the first in India to implement the concept of public participation in governance through the formation of Travancore Legislative Council. Early life and education Mulam Thirunal Rama Varma was born on 25September 1857 to Prince Raja Raja Varma of the Changanassery Royal Family and Maharani Lakshmi Bayi of Travancore, niece of Maharajah Swathi Thirunal. His mother died when he was only a few days old. The Maharajah had an elder brother, Hastham Thirunal. After the usual vernacular Malayalam studies, the two princes were placed under the tutorship of Annaji Rao B.A. and later under Raghunath Rao B.A. at a country house built specially for the purpose. Hastham Thirunal soon had to stop his studies owing to ill health and so Rama Varma remained the only p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kumaran Asan
Mahakavi Kumaran Asan (12 April 1871 – 16 January 1924) was a poet of Malayalam literature, Indian social reformer and a philosopher. He is known to have initiated a revolution in Malayalam poetry during the first quarter of the 20th century, transforming it from the metaphysical to the lyrical and his poetry is characterised by its moral and spiritual content, poetic concentration and dramatic contextualisation. He is one of the Triumvirate poets of modern Malayalam, triumvirate poets of Kerala and a disciple of Narayana Guru, Sree Narayana Guru. He was awarded the prefix "Mahakavi" in 1922 by the Madras university which means "great poet". Biography Asan was born on 12 April 1873, in a merchant family belonging to Ezhava community in Kayikkara village, Chirayinkeezhu taluk, Anchuthengu, Anchuthengu Grama Panchaayath in Travancore to Narayanan Perungudi, a polyglot well versed in Malayalam language, Malayalam and Tamil languages, and Kochupennu as the second of their nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kadaksham
''Kadaksham'' is a 2010 Malayalam film by Sasi Paravoor starring Suresh Gopi, Shwetha Menon and Shwetha Vijay. Plot Kadaksham is a women-oriented movie which states the story of how women have to survive against all odds, even in a society which still has a contemporary outlook. Cast * Shwetha Vijay * Suresh Gopi * Shweta Menon * Vijaya Raghavan * Jagathy Sreekumar * Indrans * Manasa Radhakrishnan Malu(child artist) * Jijoy Rajagopal * Sreedhanya as Nirmala * Madhupal as Padmanabhan Thampi Soundtrack *"Prananathan" - K. S. Chithra Krishnan Nair Shantakumari Chithra (born 27 July 1963) is an Indian playback singer and Carnatic musician. In a career spanning around five decades, she has recorded over 25,000 Songs in various Indian languages languages such as Tamil, Kann ... *"Omanapennallayo" - Sharreth *"Parayathevayya" - M. Jayachandra *"Khalchowdvi" - Fiaz Khan References External links * Nowrunning.com Cinecurry.com 2010 films 2010s Malayalam-language fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantuvarali
Kamavardhani (pronounced kāmavardhini – కామవర్ధిని/ ಕಾಮವರ್ಧಿನಿ/ காமவர்தினி / कामवर्धिनि) is a ragam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is the 51st ''Melakarta'' rāgam in the 72 ''melakarta'' rāgam system of Carnatic music. It is also referred by the name ''Pantuvarāḷi.''''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications This rāgam is very popular with musicians who typically sing it in the beginning of a concert. It is called Kāshirāmakriya in the Muthuswami Dikshitar school. The Hindustani music equivalent of ''Kamavardhini'' is the '' Poorvi thaat''/ Puriya Dhanashree.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras Structure and Lakshana It is the 3rd rāgam in the 9th ''chakra Brahma''. The mnemonic name is ''Brahma-Go''. The mnemonic phrase is ''sa ra gu mi pa dha nu''. Its ' structure (ascendin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
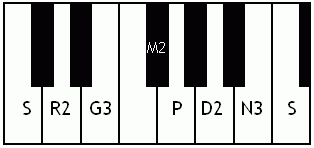
Kalyani (raga)
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It is the prati madhyama equivalent of the raga Sankarabharanam. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapi (raga)
Kāpi is a popular rāga in Carnatic music, the classical music of South India. ''Kāpi'' is a janya rāgam of '' Kharaharapriya'' with a meandering vakra scale. Typically performed at slow and medium speeds, it is capable of inducing moods of devotion, pathos and sadness in the listeners. ''Kāpi'' is different from the Hindustani raag and thaat '' Kafi.'' The equivalent raag in Hindustani is Pilu. Structure and Lakshana Kāpi is an audava-vakra sampoorna rāgam with an ascending pentatonic scale and a descending scale with seven notes, but not in a descending order. Use of Kakali Nishadam and Anthara Gandharam make it a Bhashanga Raagam. * : * : The presence of different ''nishāda'' swarās (N2 and N3) lends a distinctive quality to Kāpi, along with the fact that it uses a set of vakra swarās (N2 D2 N2). There is also a mild presence of shuddha daivatham (D1) that renders an invaluable feeling of devotion to the raagam. This, and the presence of Anthara Gan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohanam
Mohanam is a raga in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāga (or ''owdava'' rāga, meaning pentatonic scale). It is usually described as a ''janya'' rāga of Harikamboji (28th Melakartha Raga). However, alternate opinions suggest that ''Mechakalyani'' or even ''Sankarabharanam (raga), Shankarabharanam'' may be a more appropriate classification based on the lakshana of the raga. The equivalent of ''Mohanam'' in Hindustani music is ''Raga Bhopali, Bhoop''''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications (or ''Bhopali''''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras). It is one of the most common pentatonic scales across the world and is very popular in East Asian and Southeast Asian music, including China and Japan. Structure and Lakshana ''Mohanam'' is a symmetric rāga that does not contain ''madhyamam'' and ''nishādham''. It is a symmetric pentatonic scale (''audava-au ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sankarabharanam (ragam)
Dhīraśankarābharaṇaṃ, commonly known as ''Śankarābharaṇaṃ'', is a rāga in Carnatic music. It is the 29th ''Melakarta'' rāga in the 72 ''Melakarta'' rāga system of Carnatic music. Since this raga has many Gamakās (ornamentations), it is glorified as ''"Sarva Gamaka Māṇika Rakti Rāgaṃ".'' By scale wise, the Śankarābharaṇaṃ scale corresponds to ''Bilaval'' in the Hindustani music system. The Western equivalent is the major scale, or the ''Ionian mode''.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras Hence this rāga is one of the most popular scales across the world, known with different names in different musical styles. Its nature is mellifluous and smooth. This rāga offers a large scope for compositions. It is ideal for a melodious, but still laid back majestic presentation. Structure and Lakshana It is the 5th Rāga in the 5th ''Chakra Bāṇ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Todi (raga)
Miyan ki Todi, often simply referred to as Todi or Darbari Todi (), is a Hindustani classical raga which gave its name to the Todi thaat, one of the ten types of classical music according to the musicologist Bhatkhande. Ragas from the Todi raganga (class of ragas) include Todi (a.k.a. Miyan ki Todi) itself, Bilaskhani Todi, Gujari Todi (also called Gurjari Todi), Desi Todi, Hussaini Todi, Asavari Todi (more commonly known as Komal Rishabh Asavari), and Bahaduri Todi. The equivalent raga in Carnatic music is Shubhapantuvarali. But in Todi, the pancham is omitted in the Arohana, whereas Shubhapanthuvarali uses the panchamam in both the arohana and avarohana. The Carnatic Melakarta Hanumatodi is the equivalent of Bhairavi thaat, but the Hindustani Bhairavi raga is the equivalent of Carnatic Sindhu Bhairavi. Carnatic Todi does not have any similarity with Hindustani Todi (Miyan ki Todi) raga. Though the Swarasthana orders of Carnatic Thodi are similar to Hindustani Bhairavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyme
A rhyme is a repetition of similar sounds (usually the exact same phonemes) in the final Stress (linguistics), stressed syllables and any following syllables of two or more words. Most often, this kind of rhyming (''perfect rhyming'') is consciously used for a musical or aesthetic effect in the final position of Line (poetry), lines within poems or songs. More broadly, a rhyme may also variously refer to other types of similar sounds near the ends of two or more words. Furthermore, the word ''rhyme'' has come to be sometimes used as a pars pro toto, shorthand term for any brief poem, such as a nursery rhyme or Balliol rhyme. Etymology The word derives from or , which might be derived from , a Germanic term meaning "series", or "sequence" attested in Old English (Old English: meaning "enumeration", series", or "numeral") and , ultimately cognate to , ( "number"). Alternatively, the Old French words may derive from , from (, rhythm). The spelling ''rhyme'' (from the original r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanta Kavyam
Khanta is a village in the Harishchandrapur II CD block in the Chanchal subdivision of Malda district in the state of West Bengal, India. Geography Location Khanta is located at . The map of Harishchandrapur II CD block on page 153 of District Census Handbook 2011 specifies Khanta (Barduari). Area overview The area shown in the adjacent map covers two physiographic regions – the ''Barind'' in the east and the ''tal'' in the west. The eastern part is comparatively high (up to 40 metres above mean sea level at places) and uneven. The soils of the eastern region are “hard salty clays of a reddish hue and the ground is baked hard as iron.” It lies to the east of the Mahananda River. The area lying to the west of the Mahananda River, the ''tal'', is a flat low land and “is strewn with innumerable marshes, bils and oxbow lakes.” The ''tal'' area is prone to flooding by local rivers. The total area is overwhelmingly rural. There are two important historical/ archaeologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |