|
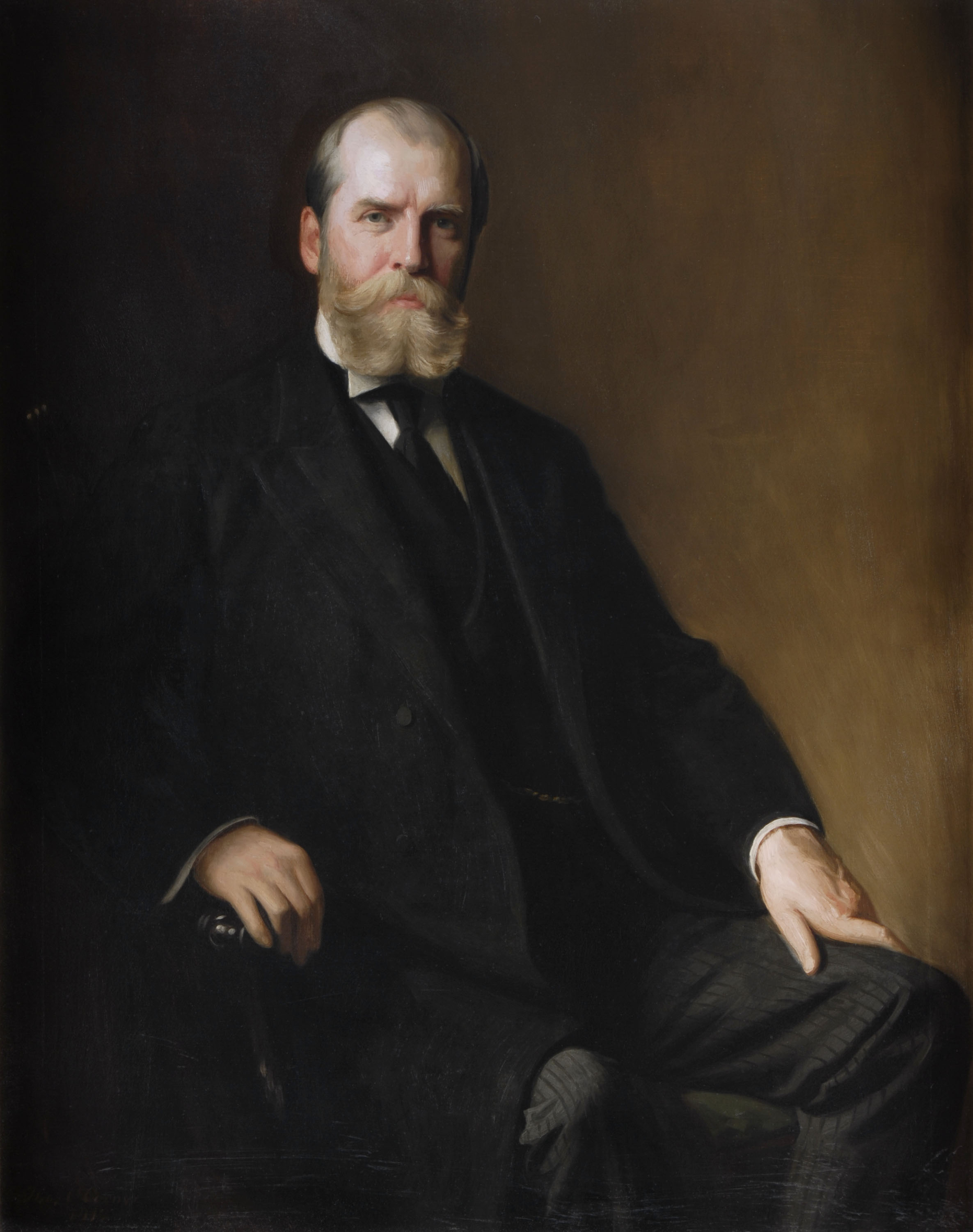
José Miguel Gómez
José Miguel Gómez y Gómez (; 6 July 1858 – 13 June 1921) was a Cuban politician and revolutionary who was one of the leaders of the rebel forces in the Cuban War of Independence. He later served as President of Cuba from 1909 to 1913. Early career At the Constitutional Convention, Gómez was one of those who voted in favor of adopting the Platt Amendment. Born in Sancti Spíritus, in the former Las Villas Province, Gómez went on to govern Santa Clara and became quite popular in Cuba. In 1905, Gómez planned to run for the presidency with Alfredo Zayas on behalf of the Liberals. Violence prevented the Liberals from winning much in the election so Gómez dropped out of the running. Gómez and Zayas began to split the Liberal party. A strong showing by the Conservatives against the divided Liberals convinced them to rejoin. Term in office Gómez and Zayas won the 1908 election as the candidates for the Liberal Party. He was very well liked among the people and Góme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
President Of Cuba
The president of Cuba (), officially the president of the Republic of Cuba (), is the head of state of Cuba. The office in its current form was established under the Constitution of 2019. The President is the second-highest office in Cuba and the highest state office. Miguel Díaz-Canel became President of the Council of State on 19 April 2018, taking over from Raúl Castro, and has been President of Cuba since 10 October 2019. The First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba continues to be the highest-ranking political position in Cuba. Fidel Castro held the position from 1976 to 2011, and Raúl Castro from 2011 until the 8th Congress of the Communist Party of Cuba, held 16–19 April 2021, when he retired from office. History Under the 1901 constitution, Cuba had a presidential system based on that of the United States. In 1940, a new constitution reformed the government into a semi-presidential system. On 2 December 1976, the executive was reformed again by a new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negro Rebellion
The War of 1912 (), also known as the Little Race War, the Negro Rebellion, or The Twelve, was a series of protests and uprisings in 1912 in Cuba, which saw conflict between Afro-Cuban rebels and the armed forces of Cuba. It took place mainly in the eastern region of the island, where most Afro-Cubans were employed. After weeks of fighting, which involved massacres of Afro-Cubans by the Cuban National Army led by General and a U.S. military intervention to protect American companies, the rebellion was put down. The leaders of the Afro-Cuban rebels, and Pedro Ivonnet, were killed during the rebellion and their political movement, The Independent Party of Color, was dissolved. Between 3,000 and 6,000 people were killed in the rebellion. Background Social conditions Conditions in Cuba were poor for the black inhabitants, most of whom worked in the sugarcane industry. Evaristo Estenoz began a movement in 1895 to better these conditions, during the war for independence from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1858 Births
Events January–March * January 9 ** Revolt of Rajab Ali: British forces finally defeat Rajab Ali Khan of Chittagong. ** Anson Jones, the last president of the Republic of Texas, commits suicide. * January 14 – Orsini affair: Piedmontese revolutionary Felice Orsini and his accomplices fail to assassinate Napoleon III in Paris, but their bombs kill eight and wound 142 people. Because of the involvement of French émigrés living in Britain, there is a brief anti-British feeling in France, but the emperor refuses to support it. * January 25 – The '' Wedding March'' by Felix Mendelssohn becomes a popular wedding recessional, after it is played on this day at the marriage of Queen Victoria's daughter Victoria, Princess Royal, to Prince Friedrich of Prussia in St James's Palace, London. * January ** Benito Juárez becomes the Liberal President of Mexico and its first indigenous president. At the same time, the conservatives installed Félix María Zuloaga as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Lady Of Cuba
First Lady of Cuba () is ''de facto'' title of the wife of the President of Cuba, President of the Republic of Cuba. The current first lady of Cuba is Lis Cuesta Peraza, the second wife of President Miguel Díaz-Canel, who is also the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, the most senior position in the Cuban government. She is the first presidential wife to be referred to as "first lady" by Cuban state media since the 1960s. History The term "First Lady of Cuba" was first used as far back as 1913 to refer to the wife of the Cuban president. The role of first lady is purely ceremonial, and the first ladies since the Cuban Revolution hold little official influence on the politics of Cuba. Although the wife of the president of Cuba is referred to unofficially as the "first lady", it is used in state ceremonies, Protocol (diplomacy), protocol events, and international tours. However, no official government position currently exists, particularly since the Cuban Revolution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerardo Machado Y Morales
Gerardo Machado y Morales (28 September 1869 – 29 March 1939) was a general of the Cuban War of Independence and President of Cuba from 1925 to 1933. Machado was elected president in 1924 as the leader of the Liberal Party, a moderate reform-oriented party. He entered the presidency with widespread popularity and support from the major political parties. However, his support declined over time and Machado took dictatorial powers. Despite promising to govern only for one term, he ran for re-election in 1928 and won a non-democratic election where the opposition was repressed. As protests and rebellions became more strident, his administration curtailed free speech and imprisoned, exiled, and murdered Machado's opponents. Ultimately, in 1933, Machado was forced to step down in favor of a provisional government headed by Carlos Manuel de Céspedes y Quesada and brokered by US ambassador Sumner Welles. Machado went into exile in Miami Beach, Florida. Family and education Machad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
López Serrano Building
The López Serrano Building was the tallest residential building in Cuba until the construction of the FOCSA in 1956. Designed by the architect Ricardo Mira in 1929, who in 1941 who also designed La Moderna Poesia bookstore on Obispo Street for the same owner, it is often compared to the Bacardi Building in Old Havana built two years before the López Serrano Building because of their similarity in massing and central tower. The congressman, senator, and presidential candidate Eduardo Chibás was living on the fourteenth-floor penthouse when he committed suicide in August 1951 on the air at CMQ Radio Station. History The construction of the building was promoted by José Antonio López Serrano, a publisher who ran La Moderna Poesía. He was the son of Ana Luísa Serrano and José López Rodríguez, "Pote", a banker with ties to publishing.} Pote arrived in Cuba as a poor and illiterate teenager who became an influential banker with ties to the government. In 1890 Pote marrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon Cemetery, Havana
El Cementerio de Cristóbal Colón (English: the Christopher Columbus Cemetery), also called La Necrópolis de Cristóbal Colón, was founded in 1876 in the Vedado neighbourhood of Havana, Cuba, to replace the Espada Cemetery in the Barrio de San Lázaro, Havana, Barrio de San Lázaro. Named for Christopher Columbus, the cemetery is noted for its many elaborately sculpted memorials. It is estimated the cemetery has more than 500 major mausoleums. Before the Espada Cemetery and the Colon Cemetery were built, interments took place in crypts at the various churches throughout Havana, for example, at the Havana Cathedral or Iglesia del Espíritu Santo, Havana#History, Church Crypts in Havana Vieja. Overview The Colon Cemetery is one of the most important cemeteries in the world and is generally held to be one of the most important in Latin America in historical and architectural terms, second only to La Recoleta Cemetery, La Recoleta in Buenos Aires. Prior to the opening of the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Evans Hughes
Charles Evans Hughes (April 11, 1862 – August 27, 1948) was an American politician, academic, and jurist who served as the 11th chief justice of the United States from 1930 to 1941. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he previously was the 36th governor of New York (1907–1910), an associate justice of the Supreme Court (1910–1916), and 44th U.S. secretary of state (1921–1925). As the Republican nominee in the 1916 United States presidential election, 1916 presidential election, he narrowly lost to Woodrow Wilson. Born to a Welsh people, Welsh immigrant preacher and his wife in Glens Falls, New York, Hughes graduated from Brown University and Columbia Law School and practiced law in New York City. After working in private practice for several years, in 1905 he led successful state investigations into public utilities and the life insurance industry. He won election as the governor of New York in 1906, and implemented several Progressivism in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1920 Cuban General Election
General elections were held in Cuba on 1 November 1920.Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p203 Alfredo Zayas y Alfonso won the presidential election, whilst the National League (an alliance of the National Conservative Party and the Cuban Popular Party) emerged as the largest faction in the House of Representatives, winning 31 of the 59 seats. The Liberal Party accused Zayas and the Conservative Party of election fraud. The U.S. Ambassador to Cuba, Enoch Crowder, substantiated that fraud had occurred. As a consequence, new elections were held in four provinces. Zayas was inaugurated on May 20, 1921. Results President The figures do not include the results for Havana Province due to fraud and subsequent re-runs.Nohlen, p215 Senate House of Representatives References {{Cuban elections Cuba General Presidential elections in Cuba Parliamentary elections in Cuba Cuba Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1916 Cuban General Election
General elections were held in Cuba on 1 November 1916.Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p203 Mario García Menocal was re-elected in the presidential election, whilst the National Conservative Party and the Liberal Party both won 27 seats in the House of Representatives. Results Of the population of 2.6 million, only 796,636 – less than a third – were registered to vote. Of these 353,002 voted in the elections, a voter turnout of 44.31%. Office of the Historian Senate House of Representatives References {{Cuban elections |
1905 Cuban General Election
General elections were held in Cuba on 1 December 1905.Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p203 Tomás Estrada Palma won the presidential election, whilst his Moderate Party won all twelve seats in the Senate and 31 of the 32 seats in the House of Representatives, winning 27 of the 63 seats. Voter turnout was 74%. Results President Senate House of Representatives Aftermath The election results were highly contested and accusations of fraud were made. Registration of voters by local electoral boards resulted in an electoral roll of 423,313, a figure American Secretary of War William Howard Taft and Assistant Secretary of State Robert Bacon declared to be 150,000 names too high. According to American professor Russell H. Fitzgibbon, ''La Discussion'', a leading moderate newspaper, protested about electoral fraud. According to a Taft Bacon report of 1906, Freyre de Andrade, a Cuban minister, told American commissioners that it was "im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Cuban General Election
General elections were held in Cuba on 1 November 1912.Dieter Nohlen (2005) ''Elections in the Americas: A data handbook, Volume I'', p203 Mario García Menocal won the presidential election running under the Conjunción Patriótica banner (an alliance of the National Conservative Party and the National Liberal Party), whilst the alliance also emerged as the largest faction in the House of Representatives, winning 26 of the 50 seats. Results President Senate House of Representatives References {{Cuban elections Cuba General Presidential elections in Cuba Parliamentary elections in Cuba Cuba Cuba, officially the Republic of Cuba, is an island country, comprising the island of Cuba (largest island), Isla de la Juventud, and List of islands of Cuba, 4,195 islands, islets and cays surrounding the main island. It is located where the ... Election and referendum articles with incomplete results ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |