|
Joint Expert Speciation System
Joint Expert Speciation System (JESS) is a package of computer software and data developed collaboratively at Murdoch University and elsewhere by researchers interested in the chemical thermodynamics of water solutions with important applications in industry, biochemistry, medicine and the environment. Using information from the chemical literature, stored in databases for numerous chemical properties, JESS achieves coherence between frequently conflicting sources by automatic methods. JESS places a strong emphasis on the concept of chemical speciation (''i.e''. the identity and relative abundance of different chemical entities which may be present), which can be predicted from known stability constants of metal-ligand complexes. Characteristic quantities for water solutions such as solubilities, equilibrium constants, activity coefficients, heat capacities and densities can be calculated from changes in the chemical speciation. Recent examples of practical problems that can be i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murdoch University
Murdoch University is a public university in Perth, Western Australia, with campuses also in Singapore and Dubai. It began operations as the state's second university on 25 July 1973, and accepted its first undergraduate students in 1975. Its name is taken from Sir Walter Murdoch (1874–1970), the Founding Professor of English and former Chancellor of the University of Western Australia. Murdoch is a verdant university and a member of the Innovative Research Universities. In 2018, Murdoch University was recognised as producing the most employable graduates of all Australian universities after 3 years of graduating from their courses. In 2019, the university ranked third in overall student satisfaction amongst all public universities in Western Australia. History In 1962, the Government of Western Australia earmarked an area of land in Bull Creek to be the site of a future, second, state university. Integral to the planning of the creation of Western Australia's second un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Thermodynamics
Chemical thermodynamics is the study of the interrelation of heat and work with chemical reactions or with physical changes of state within the confines of the laws of thermodynamics. Chemical thermodynamics involves not only laboratory measurements of various thermodynamic properties, but also the application of mathematical methods to the study of chemical questions and the ''spontaneity'' of processes. The structure of chemical thermodynamics is based on the first two laws of thermodynamics. Starting from the first and second laws of thermodynamics, four equations called the "fundamental equations of Gibbs" can be derived. From these four, a multitude of equations, relating the thermodynamic properties of the thermodynamic system can be derived using relatively simple mathematics. This outlines the mathematical framework of chemical thermodynamics. History In 1865, the German physicist Rudolf Clausius, in his ''Mechanical Theory of Heat'', suggested that the principles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Speciation
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances (substances consisting of a single chemical element), chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical substances are often called 'pure' to set them apart from mixtures. A common example of a chemical substance is pure water; it has the same properties and the same ratio of hydrogen to oxygen whether it is isolated from a river or made in a laboratory. Other chemical substances commonly encountered in pure form are diamond (carbon), gold, table salt (sodium chloride) and refined sugar (sucrose). However, in practice, no substance is entirely pure, and chemical purity is specified according to the intended use of the chemical. Chemical substances exist as solid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stability Constants Of Complexes
In coordination chemistry, a stability constant (also called formation constant or binding constant) is an equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex in solution. It is a measure of the strength of the interaction between the reagents that come together to form the complex. There are two main kinds of complex: compounds formed by the interaction of a metal ion with a ligand and supramolecular complexes, such as host–guest complexes and complexes of anions. The stability constant(s) provide(s) the information required to calculate the concentration(s) of the complex(es) in solution. There are many areas of application in chemistry, biology and medicine. History Jannik Bjerrum (son of Niels Bjerrum) developed the first general method for the determination of stability constants of metal-ammine complexes in 1941. The reasons why this occurred at such a late date, nearly 50 years after Alfred Werner had proposed the correct structures for coordination complexes, have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solubility Equilibrium
Solubility equilibrium is a type of dynamic equilibrium that exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution of that compound. The solid may dissolve unchanged, with dissociation, or with chemical reaction with another constituent of the solution, such as acid or alkali. Each solubility equilibrium is characterized by a temperature-dependent ''solubility product'' which functions like an equilibrium constant. Solubility equilibria are important in pharmaceutical, environmental and many other scenarios. Definitions A solubility equilibrium exists when a chemical compound in the solid state is in chemical equilibrium with a solution containing the compound. This type of equilibrium is an example of dynamic equilibrium in that some individual molecules migrate between the solid and solution phases such that the rates of dissolution and precipitation are equal to one another. When equilibrium is established and the solid has not all diss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
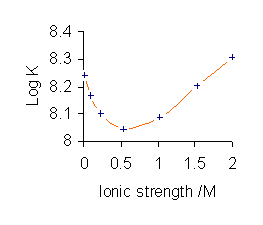
Equilibrium Constant
The equilibrium constant of a chemical reaction is the value of its reaction quotient at chemical equilibrium, a state approached by a dynamic chemical system after sufficient time has elapsed at which its composition has no measurable tendency towards further change. For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium constant is independent of the initial analytical concentrations of the reactant and product species in the mixture. Thus, given the initial composition of a system, known equilibrium constant values can be used to determine the composition of the system at equilibrium. However, reaction parameters like temperature, solvent, and ionic strength may all influence the value of the equilibrium constant. A knowledge of equilibrium constants is essential for the understanding of many chemical systems, as well as biochemical processes such as oxygen transport by hemoglobin in blood and acid–base homeostasis in the human body. Stability constants, formation con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
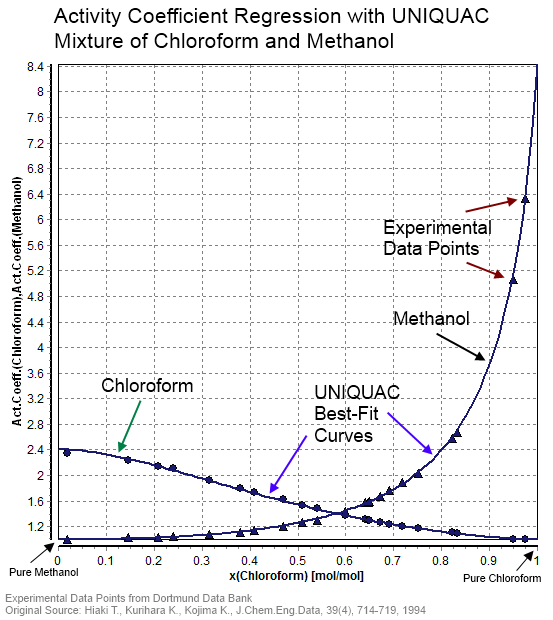
Activity Coefficient
In thermodynamics, an activity coefficient is a factor used to account for deviation of a mixture of chemical substances from ideal behaviour. In an ideal mixture, the microscopic interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same (or macroscopically equivalent, the enthalpy change of solution and volume variation in mixing is zero) and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed directly in terms of simple concentrations or partial pressures of the substances present e.g. Raoult's law. Deviations from ideality are accommodated by modifying the concentration by an ''activity coefficient''. Analogously, expressions involving gases can be adjusted for non-ideality by scaling partial pressures by a fugacity coefficient. The concept of activity coefficient is closely linked to that of activity in chemistry. Thermodynamic definition The chemical potential, \mu_\mathrm, of a substance B in an ideal mixture of liquids or an ideal solution is given by :\mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
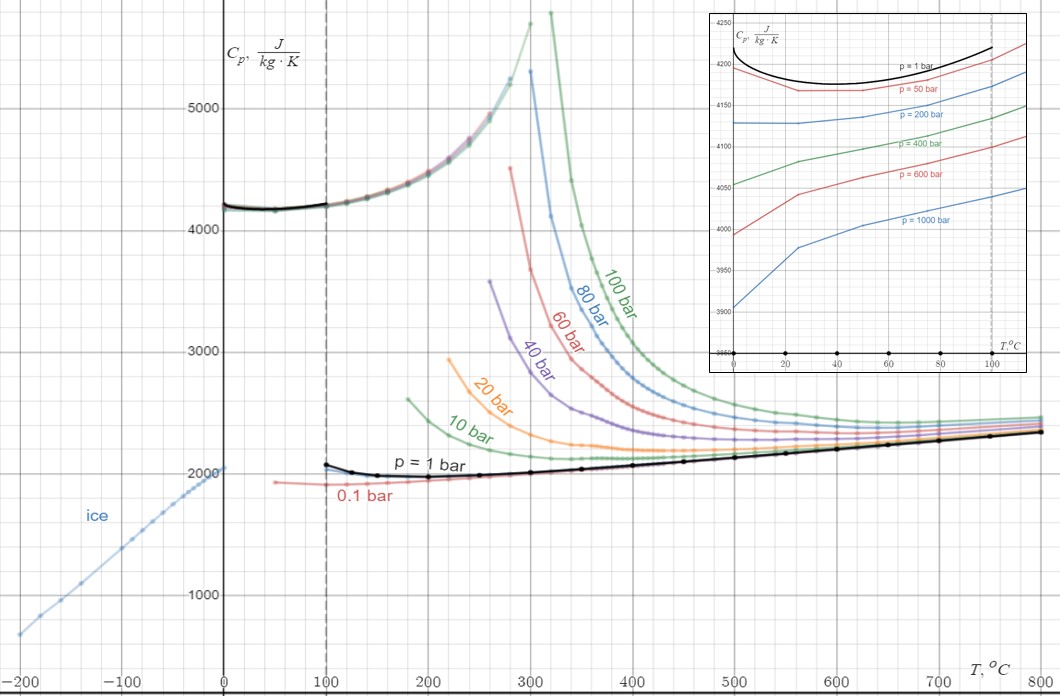
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its thermal mass. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit : C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Stone
Kidney stone disease, also known as nephrolithiasis or urolithiasis, is a crystallopathy where a solid piece of material (kidney stone) develops in the urinary tract. Kidney stones typically form in the kidney and leave the body in the urine stream. A small stone may pass without causing symptoms. If a stone grows to more than , it can cause blockage of the ureter, resulting in sharp and severe pain in the lower back or abdomen. A stone may also result in blood in the urine, vomiting, or painful urination. About half of people who have had a kidney stone will have another within ten years. Most stones form by a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Risk factors include high urine calcium levels, obesity, certain foods, some medications, calcium supplements, hyperparathyroidism, gout and not drinking enough fluids. Stones form in the kidney when minerals in urine are at high concentration. The diagnosis is usually based on symptoms, urine testing, and me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilson’s Disease
Wilson's disease is a genetic disorder in which excess copper builds up in the body. Symptoms are typically related to the brain and liver. Liver-related symptoms include vomiting, weakness, fluid build up in the abdomen, swelling of the legs, yellowish skin and itchiness. Brain-related symptoms include tremors, muscle stiffness, trouble in speaking, personality changes, anxiety, and psychosis. Wilson's disease is caused by a mutation in the Wilson disease protein (''ATP7B'') gene. This protein transports excess copper into bile, where it is excreted in waste products. The condition is autosomal recessive; for a person to be affected, they must inherit a mutated copy of the gene from both parents. Diagnosis may be difficult and often involves a combination of blood tests, urine tests and a liver biopsy. Genetic testing may be used to screen family members of those affected. Wilson's disease is typically treated with dietary changes and medication. Dietary changes involve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |