|
Jiangqu
Qiangqu (; r. 179–188 AD) was the Western Wise Prince, successor to Huzheng, and ''chanyu'' of the Southern Xiongnu from 179 to 188 AD. Qiangqu's reign coincided with a troublesome time for the Han Empire, and few records address Chinese relations with the Southern Xiongnu. In 187 AD Qiangqu sent Southern Xiongnu cavalry troops under command of the Eastern Tuqi Prince (Wise Prince) to aid the governor of Yuzhou province against the former governor, Zhongshan province, Zhang Chun, who had rebelled in alliance with the Wuhuan. This caused discontent among the elders, who were alarmed by the frequency with which Qiangqu sent their men off to battle for the Han dynasty. In 188 AD, the Xiuchuge people rose in rebellion in the Hetao region of Bing province and killed the provincial inspector after invading Xihe Commandery. The Southern Xiongnu dissidents, led by the Xiluo clan of the Right Division, formed an alliance with the Xiuchuge, and together they killed Qiangqu. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chanyu
Chanyu () or Shanyu (), short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu (), was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "''Khagan''" in 402 AD. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and Han dynasty (206 BC – 220 AD). It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Tujue leaders. Etymology According to the ''Book of Han'', "the Xiongnu called the Tian, Heaven (天) ''Tengri, Chēnglí'' (撐犁) and they called a child (子) ''gūtú'' (孤塗). As for ''Chányú'' (單于), it is a "vast [and] great appearance" (廣大之貌).". L. Rogers and Edwin G. Pulleyblank argue that the title ''chanyu'' may be equivalent to the later attested title ''tarkhan'', suggesting that the Chinese pronunciation was originally ''dān-ĥwāĥ'', an approximation for ''*darxan''.Universität Bonn. Seminar für Sprach- und Kulturwissenschaft Zentrala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chuge
The Chuge ( zh, c=屠各, p=Chúgè, w=Ch'u-ko), also known as Xiuchuge ( zh, c=休屠各, p=Xiūchúgè, w=Hsiu-ch'u-ko) or Xiuchu ( zh, c=休屠, p=Xiūchú, w=Hsiu-ch'u) were a Xiongnu tribe and later ethnic group that lived in ancient China. They were described as the most influential among the Xiongnu tribes that resettled within the Great Wall, and a branch of them, the Liu clan, founded the Han-Zhao dynasty in 304 AD during the Sixteen Kingdoms period. The Chuge's influence were as such that by the 4th century, they were seen as a distinct ethnic group from the rest of the Xiongnu, and they continued to appear in history until the late Northern Wei period of the 6th century. Their name can also be transcribed as Tuge, Xiutuge, and Xiutu. Origins and theories According to the ''Book of Jin'', the Chuge were one of the nineteen recorded Xiongnu tribes that resettled in northern China. By the Jin dynasty period, they rose to be the most honored and prestigious among the Xio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xubu
The Xubu (; LHC: *''sio-pok'') was a tribe of the Xiongnu that flourished between 3rd century BCE and the 4th century CE. Chinese annals noted that the Xubu tribe replaced the Huyan tribe, which was an earlier maternal dynastic tribe of the dynastic union with the paternal dynastic tribe Luandi. The traditional system of conjugal unions is a form of the nomadic exogamic society. The male members of the maternal dynastic line were not eligible to be ''chanyu'', only the male members of the Luandi line, whose father was a Luanti Chanyu, and mother was a Xubu Khatun (Queen) were eligible to be ''chanyu''. A Xubu could only become a ''chanyu'' after a palace coup. The Huyan tribe moved from the Right (Western) Wing, where the maternal dynastic tribe is traditionally assigned, to the Left (Eastern) Wing. The ''Book of the Later Han'' (chapter 89, l. 7b) stated that of the noble tribes other than Luanti, Huyan, Xubu, Qiulin and Lan, Huyan already belonged to the dominating Left Wing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marquis Of Xubu
The Marquis of Xubu (died 189) was a ''chanyu'' of the Southern Xiongnu during the late period of the Han dynasty. He was installed by a rebellious faction of the Southern Xiongnu after they killed the previous ''chanyu'', Qiangqu and ousted his son, Yufuluo. History In 188 AD, the Xiuchuge people and a part of the Southern Xiongnu rebelled in Bing province, killing the Chinese provincial inspector and their ''chanyu'', Qiangqu. Initially, Qiangqu's son, Yufuluo was installed as the new ''chanyu'', but soon, the rebellious faction ousted him and replaced him with a marquis of the Xubu clan whose is known today as the Marquis of Xubu. Yufuluo went to the Han capital, Luoyang to complain, but at the time, the capital was thrown into chaos by the death of Emperor Ling. When Yufuluo returned to Bing, the rebels refused him entry, and he was forced to camp at Hedong Commandery east of the Fen River The Fen River drains the center of Shanxi Province, China. It originates in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xihe Commandery
Xihe Commandery ( zh, 西河郡) was a historical commandery of China, located in modern northern Shanxi and part of Inner Mongolia. The name "Xihe" referred to a southward section in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. The commandery was separated from Shang Commandery in 125 BC. In 2 AD, there were 36 counties in the commandery, including Fuchang (富昌), Zouyu (騶虞), Huze (鵠澤), Pingding (平定), Meiji (美稷), Zhongyang (中陽), Lejie (樂街), Tujing (徒經), Gaolang (臯狼), Dacheng (大成), Guangtian (廣田), Huanyin (圜陰), Yilan (益闌), Pingzhou (平周), Hongmen (鴻門), Lin (藺), Xuanwu (宣武), Qianzhang (千章), Zengshan (增山), Huanyang (圜陽), Guangyan (廣衍), Wuche (武車), Humeng (虎猛), Lishi (離石), Guluo (穀羅), Rao (饒), Fangli (方利), Xicheng (隰成), Linshui (臨水), Tujun (土軍), Xidu (西都), Pinglu (平陸), Yinshan (陰山), Nishi (觬氏), Boling (博陵) and Yanguan (鹽官). The population in 2 AD was 698,8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bingzhou
Bingzhou, or Bing Province, was a location in ancient China. According to legend, when Yu the Great (–2100 BC) tamed the flood, he divided the land of China into the Nine Provinces. Historical texts such as the ''Rites of Zhou'', and "Treatise on Geography" section (volume 28) of the ''Book of Han'', recorded that Bingzhou was one of the Nine Provinces. Bingzhou covered roughly the areas around present-day Baoding, Hebei, and Taiyuan and Datong in Shanxi. History Han dynasty and earlier Since the fifth century BC Bingzhou had been separated from the Ordos Desert repeatedly by a series of walls that would form the Great Wall of China. In 106 BC, during the Western Han dynasty (206 BC – 9 AD), Emperor Wu divided the Han Empire into thirteen administrative divisions, of which Bingzhou was one. Bingzhou covered most of present-day Shanxi and parts of Hebei and Inner Mongolia. During the Eastern Han dynasty (25–220) Bingzhou's capital was designated in Jinyang County (晉陽 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
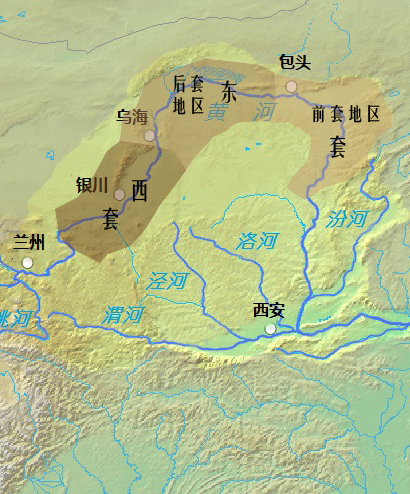
Hetao
Hetao () is a C-shaped region in northwestern China consisting of a collection of flood plains stretching from the banks of the northern half of the Ordos Loop, a large northerly rectangular bend of the Yellow River, that forms the river's entire middle section. The region makes up the northern margin of the Ordos Basin, bounded in the west by the Helan Mountains, the north by the Yin Mountains, the east by the northern portion of Lüliang Mountains, and the south by the Ordos Desert and the Loess Plateau (separated by the course of the Ming Great Wall). The Hetao region is divided into two main sections — the "West Loop" () in Ningxia, and the "East Loop" () in Inner Mongolia. The west section includes the alluvial Yinchuan Plain (, a.k.a. Ningxia Plain) around Shizuishan, Yinchuan, and Wuzhong, and the Weining Plain () around Zhongwei. The east section is further divided into two parts — the western "Back Loop" (), which includes the Bayannur Plain () around B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huzheng
Huzheng succeeded his father Tute Ruoshi Zhujiu as ''chanyu'' of the Xiongnu in 178 AD. He was killed by the Han emissary Zhang Xiu in 179 AD. The title of ''chanyu'' passed to the Western Tuqi Prince Qiangqu Qiangqu (; r. 179–188 AD) was the Western Wise Prince, successor to Huzheng, and ''chanyu'' of the Southern Xiongnu from 179 to 188 AD. Qiangqu's reign coincided with a troublesome time for the Han Empire, and few records address Chin .... Footnotes References * *Bichurin N.Ya., ''"Collection of information on peoples in Central Asia in ancient times"'', vol. 1, Sankt Petersburg, 1851, reprint Moscow-Leningrad, 1950 * * * * * *Taskin B.S., ''"Materials on Sünnu history"'', Science, Moscow, 1968, p. 31 (In Russian) * {{s-end Chanyus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuhuan
The Wuhuan (, < Eastern Han Chinese: *''ʔɑ-ɣuɑn'', < (c. 78 BCE): *''ʔâ-wân'' < *''Awar'') were a Proto-MongolicPulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Press p. 452 of pp. 411–466. or |