|
Je–Tupi–Carib Languages
Je–Tupi–Carib (or TuKaJê) is a proposed language family composed of the Macro-Ge languages, Macro-Je (or Macro-Gê), Tupian languages, Tupian and Cariban languages of South America. Aryon Rodrigues (2000) based this proposal on shared morphological patterns. In an earlier proposal, Rodrigues (1985) had also proposed a ''Tupí-Cariban'' language family. However, in some cases, similarities among the language families are clearly due to more recent linguistic diffusion, as with Tupian and Jê languages (Timbira language, Timbira; Guajajara language, Guajajara, Tembe language, Tembe, Guaja language, Guaja, Urubu-Ka'apor language, Urubu-Ka'apor, etc.) in the lower Tocantins River, Tocantins-Mearim River, Mearim area.Cabral, Ana Suelly Arruda Câmara; Beatriz Carreta Corrêa da Silva; Maria Risolta Silva Julião; Marina Maria Silva Magalhães. 2007. Linguistic diffusion in the Tocantins-Mearim area. In: Ana Suelly Arruda Câmara Cabral; Aryon Dall’Igna Rodrigues (ed.), ''Língu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of the Americas. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean, and to the south by the Drake Passage; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. The Dutch Caribbean ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, and Curaçao) and Trinidad and Tobago are geologically located on the South-American continental shel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tembe Language
Tenetehára is a Tupi–Guarani language spoken in the state of Maranhão in Brazil. Sociolinguistically, it is two languages, each spoken by the Guajajara and the Tembé people, though these are mutually intelligible. Tembé was spoken by less than a quarter of its ethnic population of 820 in 2000; Guajajara, on the other hand, is more robust, being spoken by two-thirds of its 20,000 people. History Tenetehára speakers were first contacted in 1615 by a French expedition in the margins of the Pindaré river. They clashed against slaver raids until Jesuit missions were set up among them (1653-1755). After the Jesuits were expelled from Brazil, the various Tenetehára groups went back to a life with very limited contact with the settler society. At the end of the 19th century the members of the community started to be employed as collectors of natural resources. After some abuse by white settlers in their vicinity, in 1901 the Guajajara group revolted against a nearby Capuch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundurukuan Languages
The Mundurukú languages of Brazil form a branch of the Tupian language family. They are Munduruku and the extinct Kuruáya. Varieties Loukotka (1968) lists the following names for Mundurucú language varieties, including names of unattested varieties. *Mundurucú / Paiquizé / Pari / Weidéñe - originally spoken along the Tapajós River The Tapajós ( ) is a river in Brazil. It runs through the Amazon Rainforest and is a major tributary of the Amazon River. When combined with the Juruena River, the Tapajós is approximately long. Prior to a drastic increase in illegal gold mi ..., now on the Urariá River and Maué-assú River, Amazonas. *Kuruáya / Caravare / Curivere / Guahuara / Curuapa - spoken on the Curua River, now perhaps extinct. Proto-language Some Proto-Mundurukú reconstructions by Picanço (2005) are as follows.Picanço, Gessiane Lobato. 2005. Munduruku: Phonetics, phonology, synchrony, diachrony'. Doctoral dissertation, University of Vancouver. : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
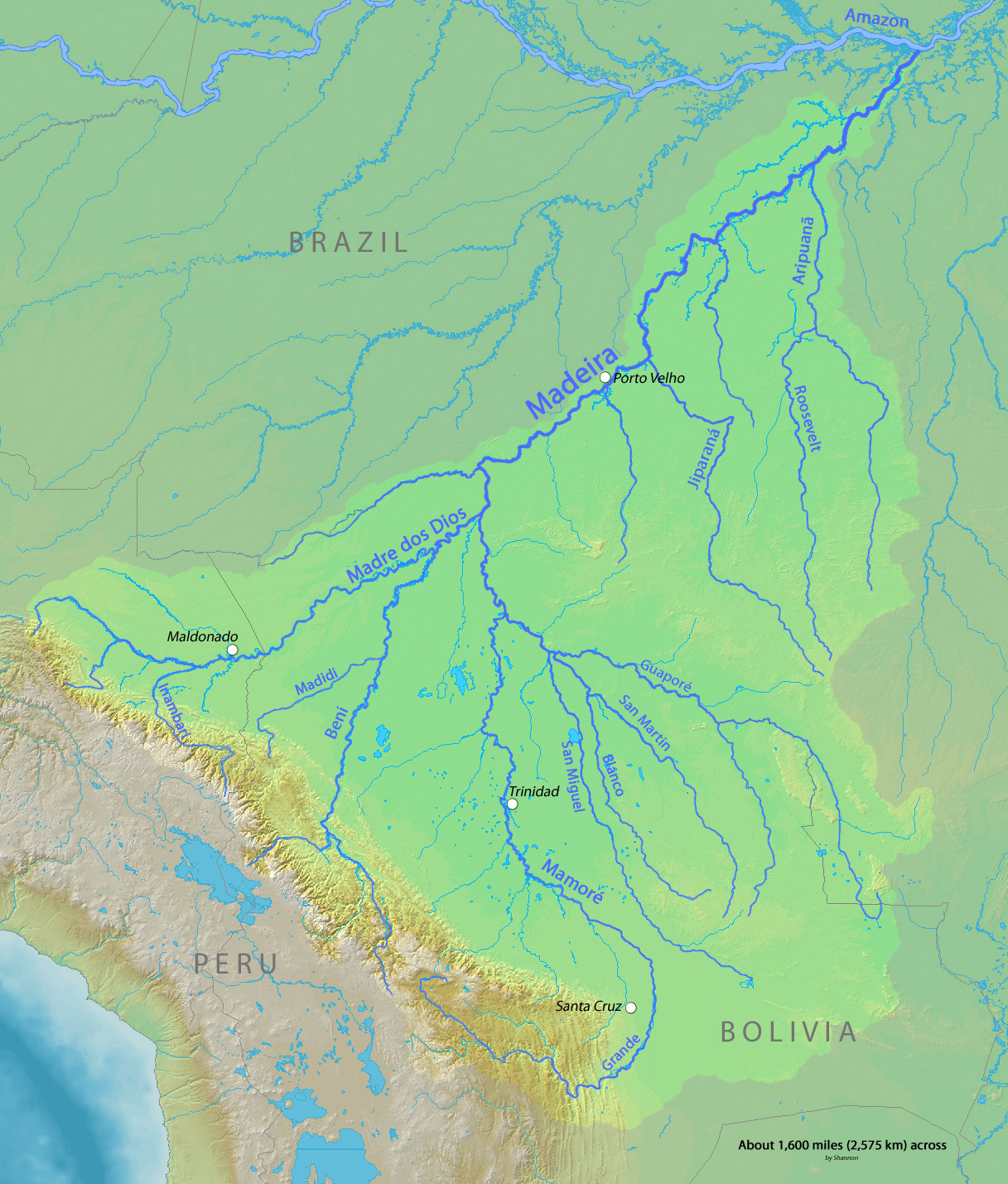
Proto-Tupian Language
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the Tupian languages. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method from data of the descendant languages. In Brazil, Tupian historical-comparative studies are being developed mainly by two scientific teams: one from the Laboratório de Línguas Indígenas (LALI) of the University of Brasília, under the coordination of Aryon Rodrigues; and the other one from the Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi, located in Belém, under the orientation of Denny Moore. These studies provide evidence about the Proto-Tupian economy and culture, suggesting, for example, that they had agriculture. The most accepted theory is that the Tupian language family originated between the Guaporé and Aripuanã rivers, in the Madeira River basin. There are currently 70 Tupian languages, including Tupi, Paraguayan Guarani, Awetï, Ayvu, etc. Linguistic homeland Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Language Relationship
The ''Journal of Language Relationship'' (abbreviated ''JLR''; Russian: Вопросы языкового родства) is a quarterly academic journal published in Russia and the United States. It focuses on historical linguistics, with many articles relating to long-range comparative linguistics. Overview In 2008, founded the journal in Moscow. The journal is currently published by the Russian State University for the Humanities (RSUH) and the Institute of Linguistics of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Moscow, and by Gorgias Press in the United States. The journal is open access. Editors (past and current) include Vladimir Dybo (editor-in-chief, 2009–2023), George Starostin (editor-in-chief, 2024–present), Anna Dybo, Ilya Yakubovich, Kirill Babaev, and others. The advisory board includes (as of 2020) Heiner Eichner (chairman), William H. Baxter, Alexander Militarev, Valentin Vydrin, Václav Blažek, Murray Gell-Mann Murray Gell-Mann (; September 15, 1929&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pará Arára Language
Arára () is a Cariban language of Pará, Brazil. It is spoken by the Arara and perhaps other related groups. Arára forms part of the '' Kampot dialect cluster'' along with Ikpeng, Apiaká do Tocantins, Parirí, and Yarumá.Carvalho, Fernando O. de (2020)Tocantins Apiaká, Parirí and Yarumá as Members of the Pekodian Branch (Cariban) ''Revista Brasileira de Línguas Indígenas - RBLI''. Macapá, v. 3, n. 1, p. 85-93, 2020. Phonology Consonants Two of the sixteen consonants, /ʙ̥, h/ occur infrequently. /ʙ̥/ only occurs in expressive words, or before the vowel /u/. /h/ only occurs after a coronal consonant, like /a/ or /u/. There is also a specially rare occurrence of two implosive consonants, and . Vowels Area The language is spoken by a people which includes groups that are still uncontacted. They live mainly in three villages: Cachoeira Seca, Laranjal and Maia. However, the natives of the latter have switched to Portuguese, while 85 speakers still remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Cariban
The Cariban languages are a family of languages Indigenous to north-eastern South America. They are widespread across northernmost South America, from the mouth of the Amazon River to the Colombian Andes, and they are also spoken in small pockets of central Brazil. The languages of the Cariban family are relatively closely related. There are about three dozen, but most are spoken only by a few hundred people. Macushi is the only language among them with numerous speakers, estimated at 30,000. The Cariban family is well known among linguists partly because one language in the family— Hixkaryana—has a default word order of object–verb–subject. Prior to their discovery of this, linguists believed that this order did not exist in any spoken natural language. In the 16th century, Cariban peoples expanded into the Lesser Antilles. There they killed or displaced, and also mixed with the Arawak peoples who already inhabited the islands. The resulting language— Kalhíphona or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Tupian
Proto-Tupian (PT) is the reconstructed common ancestor of all the Tupian languages. It consists, therefore, of a hypothetical language, reconstructed by the comparative method from data of the descendant languages. In Brazil, Tupian historical-comparative studies are being developed mainly by two scientific teams: one from the Laboratório de Línguas Indígenas (LALI) of the University of Brasília, under the coordination of Aryon Rodrigues; and the other one from the Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi, located in Belém, under the orientation of Denny Moore. These studies provide evidence about the Proto-Tupian economy and culture, suggesting, for example, that they had agriculture. The most accepted theory is that the Tupian language family originated between the Guaporé and Aripuanã rivers, in the Madeira River basin. There are currently 70 Tupian languages, including Tupi, Paraguayan Guarani, Awetï, Ayvu, etc. Linguistic homeland Rodrigues (2007) considers the Proto-T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lomonosov Moscow State University
Moscow State University (MSU), officially M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University,. is a public research university in Moscow, Russia. The university includes 15 research institutes, 43 faculties, more than 300 departments, and six branches. Alumni of the university include past leaders of the Soviet Union and other governments. As of 2019, 13 Nobel laureates, six Fields Medal winners, and one Turing Award winner were affiliated with the university. History Imperial Moscow University Ivan Shuvalov and Mikhail Lomonosov promoted the idea of a university in Moscow, and Russian Empress Elizabeth decreed its establishment on . The first lectures were given on . Saint Petersburg State University and MSU each claim to be Russia's oldest university. Though Moscow State University was founded in 1755, St. Petersburg which has had a continuous existence as a "university" since 1819 sees itself as the successor of an academy established on in 1724, by a decree of Peter the Great. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xingu Indigenous Park
The Xingu Indigenous Park (, pronounced ) is an indigenous territory of Brazil, first created in 1961 as a national park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Its official purposes are to protect the environment and the several nations of Xingu Indigenous peoples in the area. Location The Xingu Indigenous Park is on the upper Xingu River in the northeast of the state of Mato Grosso, in the south of the Amazon biome. It covers 26,420 square km (2,642,003 hectares, 6,528,530 acres), with savannah and drier semi-deciduous forests in the south transitioning to Amazon rain forest in the north. There is a rainy season from November to April. The headwaters of the Xingu River are in the south of the park. The area covered by the park was defined in 1961 and covers parts of the municipalities of Canarana, Paranatinga, São Félix do Araguaia, São José do Xingu, Gaúcha do Norte, Feliz Natal, Querência, União do Sul, Nova Ubiratã and Marcelândia in the state of Mato Gross ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mearim River
The Mearim River () is a river in Maranhão state of northern Brazil. The river originates in the southern part of Maranhão, and drains north into the Baía de São Marcos, an estuary that also receives the Pindaré and Grajaú rivers, which are sometimes considered tributaries of the Mearim. The lower Mearim is known for its pororoca, or tidal bore A tidal bore, often simply given as bore in context, is a tidal phenomenon in which the leading edge of the incoming tide forms a wave (or waves) of water that travels up a river or narrow bay, reversing the direction of the river or bay's cu .... The Mearim is approximately 800 kilometers long, flowing through the marshlands of the Atlantic Coastal Plain. It meets the Atlantic Ocean at the Sao Marcos Bay, where it forms a common estuary with another river, Pindare. The Mearim's primary source of water is rain. The river's upper and middle courses are characterized by rapids. Only the lower sections of the Mearim are suitabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |