|
Jens Beckmann
Jens Beckmann (born 1970) is a German-Australian scientist working as professor in the area of synthetic inorganic and organometallic chemistry at the University of Bremen since 2010. Previously he worked as assistant professor at the Free University of Berlin (2004–2010) and as lecturer at Deakin University in Geelong (2002–2004). He is best known for the preparation of reactive and functional molecules including the first stable nitrene. Early life and education Beckmann was born in December 1970 in Arnsberg, Westphalia, Germany, and grew up in the near village of Oeventrop. He graduated from the Gymnasium Laurentianum Arnsberg obtaining his Abitur in 1990. He studied Chemistry at the University of Dortmund, where he obtained his Diploma in 1995 and his Ph.D. ("Dr. rer nat.") in 1999 under the supervision of Prof Klaus Jurkschat. Starting in early 2000, he worked for two years as Feodor Lynen fellow of the Alexander von Humboldt foundation at Deakin University Geelong und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnsberg
Arnsberg (; ) is a town in the Hochsauerland county, in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It is the location of the Regierungsbezirk Arnsberg (region), Arnsberg administration and one of the three local administration offices of the Hochsauerlandkreis, Hochsauerlandkreis district. Geography Location Arnsberg is located in the north-east of the Sauerland in the Ruhr (river), Ruhr river valley. The river Ruhr sinuosity, meanders around the south of the old town of Arnsberg. The town is nearly completely encircled by forest, and the nature park ''Arnsberg Forest Nature Park, Arnsberger Wald'' lies to the north". Arnsberg is connected by Bundesautobahn 46, Federal Motorway 46 (Autobahn 46) Brilon in the east and (using the Bundesautobahn 445, Federal Motorway 445) Werl in the west. It is also connected by several railroad stations, which provide a connection to the major city Dortmund and the Ruhrgebiet. There is also a Flugplatz Arnsberg-Menden, regional airport, located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acid
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid. The first category of acids are the proton donors, or Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acids. In the special case of aqueous solutions, proton donors form the hydronium ion H3O+ and are known as Acid–base reaction#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius acids. Johannes Nicolaus Brønsted, Brønsted and Martin Lowry, Lowry generalized the Arrhenius theory to include non-aqueous solvents. A Brønsted–Lowry or Arrhenius acid usually contains a hydrogen atom bonded to a chemical structure that is still energetically favorable after loss of H+. Aqueous Arrhenius acids have characteristic properties that provide a practical description of an acid. Acids form aqueous solutions with a sour taste, can turn blue litmus red, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Bremen
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1970 Births
Events January * January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC. * January 5 – The 7.1 1970 Tonghai earthquake, Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity scale, Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and 14,621 are killed and 30,000 injured. * January 15 – After a 32-month fight for independence from Nigeria, Biafran forces under Philip Effiong formally surrender to General Yakubu Gowon, ending the Nigerian Civil War. February * February 1 – The Benavídez rail disaster near Buenos Aires, Argentina (a rear-end collision) kills 236. * February 10 – An avalanche at Val-d'Isère, France, kills 41 tourists. * February 11 – ''Ohsumi (satellite), Ohsumi'', Japan's first satellite, is launched on a Lambda-4 rocket. * February 22 – Guyana becomes a Republic within the Commonwealth of Nations. * February – Multi-business Conglomerate (company), conglomerate Virgin Group is founded as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Academy Of Sciences
The Russian Academy of Sciences (RAS; ''Rossíyskaya akadémiya naúk'') consists of the national academy of Russia; a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation; and additional scientific and social units such as libraries, publishing units, and hospitals. Peter the Great established the academy (then the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences) in 1724 with guidance from Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz, Gottfried Leibniz. From its establishment, the academy benefitted from a slate of foreign scholars as professors; the academy then gained its first clear set of goals from the 1747 Charter. The academy functioned as a university and research center throughout the mid-18th century until the university was dissolved, leaving research as the main pillar of the institution. The rest of the 18th century continuing on through the 19th century consisted of many published academic works from Academy scholars and a few Academy name changes, ending as The Imperial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that is used to relieve pain, fever, and inflammation. This includes dysmenorrhea, painful menstrual periods, migraines, and rheumatoid arthritis. It can be taken oral administration, orally (by mouth) or Intravenous therapy, intravenously. It typically begins working within an hour. Common side effects include heartburn, nausea, indigestion, and abdominal pain. Potential side effects include gastrointestinal bleeding. Long-term use has been associated with kidney failure, and rarely liver failure, and it can exacerbate the condition of people with heart failure. At low doses, it does not appear to increase the risk of myocardial infarction (heart attack); however, at higher doses it may. Ibuprofen can also worsen asthma. While its safety in early pregnancy is unclear, it appears to be harmful in later pregnancy, so it is not recommended during that period. It works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins by dec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
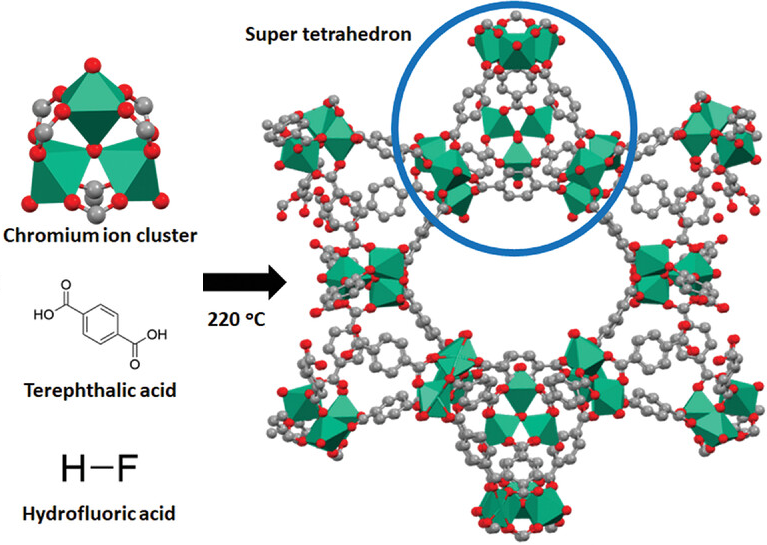
Metal–organic Framework
Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) are a class of porous polymers consisting of metal cluster compound, clusters (also known as Secondary Building Units - SBUs) coordinated to organic compound, organic ligands to form one-, two- or three-dimensional structures. The organic ligands included are sometimes referred to as "struts" or "linkers", one example being terephthalic acid, 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid (BDC). MOFs are classified as reticular materials. More formally, a metal–organic framework is a potentially porous extended structure made from metal ions and organic linkers. An extended structure is a structure whose sub-units occur in a constant ratio and are arranged in a repeating pattern. MOFs are a subclass of coordination networks, which is a coordination compound extending, through repeating coordination entities, in one dimension, but with cross-links between two or more individual chains, loops, or spiro-links, or a coordination compound extending through repeating c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoluminescence
Photoluminescence (abbreviated as PL) is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons (electromagnetic radiation). It is one of many forms of luminescence (light emission) and is initiated by photoexcitation (i.e. photons that excite electrons to a higher energy level in an atom), hence the prefix ''photo-''. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductorsHayes, G.R.; Deveaud, B. (2002). "Is Luminescence from Quantum Wells Due to Excitons?". ''Physica Status Solidi A'' 190 (3): 637–640doi:10.1002/1521-396X(200204)190:33.0.CO;2-7/ref> up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours. Observation of photoluminescence at a certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbene
In organic chemistry, a carbene is a molecule containing a neutral carbon atom with a Valence (chemistry), valence of two and two unshared valence electrons. The general formula is or where the R represents substituents or hydrogen atoms. The term "carbene" may also refer to the specific compound , also called methylene radical, methylene, the parent hydride from which all other carbene compounds are formally derived. There are two types of carbenes: singlet state, singlets or triplet state, triplets, depending upon their electronic structure. The different classes undergo different reactions. Most carbenes are extremely reactive and short-lived. A small number (the diHalogen, halocarbenes, carbon monoxide, and carbon monosulfide) can be isolated, and can stabilize as Coordination complex, metal ligands, but otherwise cannot be stored in bulk. A rare exception are the persistent carbenes, which have extensive application in modern organometallic chemistry. Generatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |