|
Jean-Pierre Aulneau
Jean-Pierre Aulneau de la Touche (21 April 1705 Moutiers-sur-le-Lay, La Vendée, Kingdom of France – 8 June 1736 Massacre Island, Lake of the Woods, New France, now Ontario, Canada) was a Jesuit missionary priest from La Vendée and a pioneering linguist of the Assiniboine and Cree languages. Shortly after his arrival in New France following an 80-day voyage from La Rochelle and his subsequent ordination to the Roman Catholic priesthood, Fr. Aulneau was assigned as a military chaplain to the legendary Voyageur explorer Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye at Fort St. Charles, on the Northwest Angle of what is now Minnesota. Only two years after his arrival in North America, Fr. Aulneau insisted on traveling to Fort Michilimackinac, located at what is now Mackinaw City in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan, with a pre-winter resupply mission led by the commander's son, Jean Baptiste de La Vérendrye. Fr. Aulneau had hopes of a last visit to the Sacrament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moutiers-sur-le-Lay
Moutiers-sur-le-Lay (, literally ''Moutiers on the Lay'') is a commune in the Vendée department in the Pays de la Loire region in western France. Geography The village lies on the left bank of the river Lay, which flows southwestward through the southern part of the commune. Local people * Fr. Jean-Pierre Aulneau (1705-1736) a Roman Catholic priest of the Society of Jesus who died while serving as a missionary to the First Nations peoples of New France. Fr. Aulneau, who was born in Moutiers and from the local French nobility, was dubbed Minnesota's Forgotten Martyr A martyr (, ''mártys'', 'witness' Word stem, stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external party. In ..." in 1961. Edited by Rev. Vincent A. Yzermans (1961), ''Catholic Origins of Minnesota'', Published by the Minnesota Fourth Degree Knights of Columbus. Pages 28 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaultier De Varennes, Sieur De La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and established trading posts there. They were part of a process that added Western Canada to the original New France territory that was centred along the Saint Lawrence basin. He was the first known European to reach present-day North Dakota and the upper Missouri River in the United States. In the 1740s, two of his sons crossed the prairie as far as present-day Wyoming, United States, and were the first Europeans to see the Rocky Mountains north of New Mexico. Early life Born in Trois-Rivières, New France, Pierre was the eldest son of René Gaultier de Varennes, who came to Canada as a soldier in 1665, and Marie, the daughter of Pierre Boucher, the first Governor of Trois-Rivières. The Gaultier family were minor nobility or landowners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
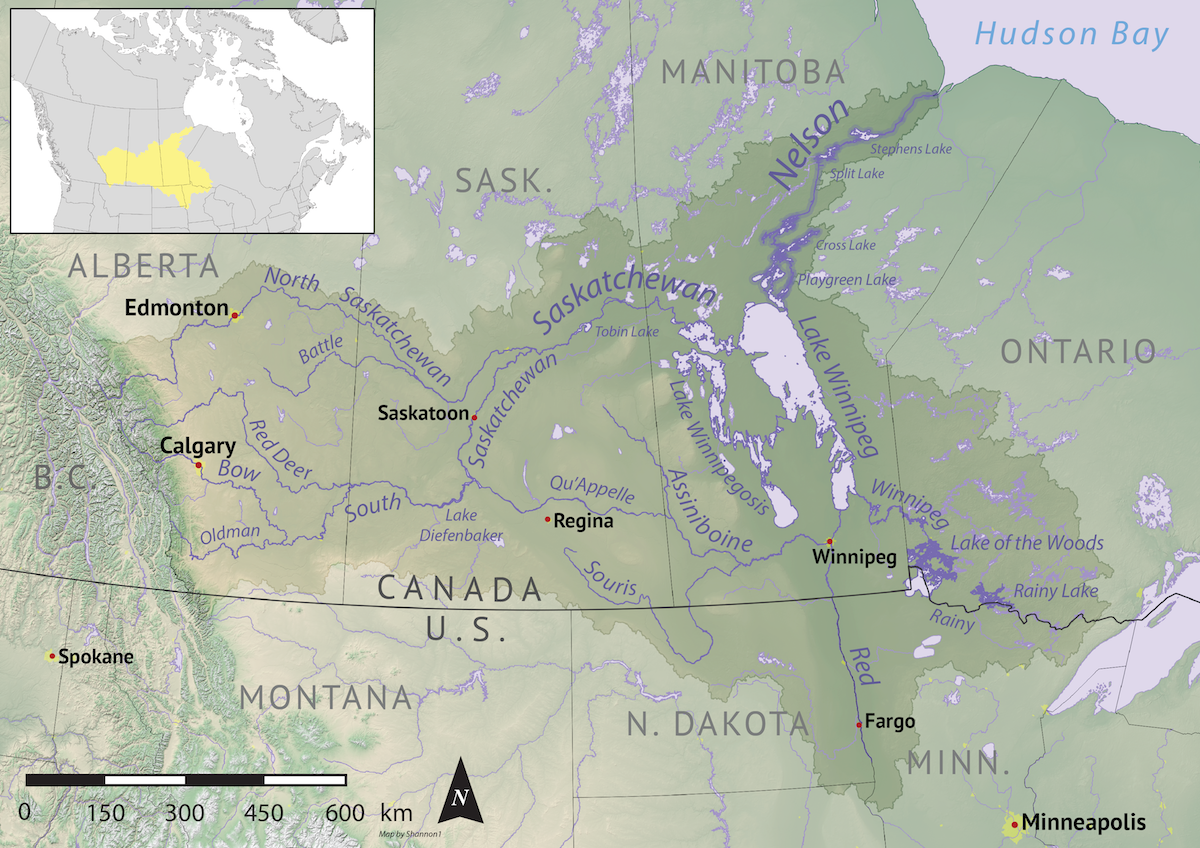
Lake Of The Woods Massacre
On June 6, 1736, a party of twenty one French explorers led by Jean Baptiste de La Vérendrye were massacred by Lakota and Dakota warriors on an island in Lake of the Woods. The massacre came about as a result of a recent French alliance with the Cree, who, under French protection, had been attacking Lakotas. The explorers had been en route to Fort Kaminstiquia on the northern shore of Lake Superior when the group of about one hundred warriors descended on and killed them in revenge for the French-sponsored Cree raids and French slave trading. Background French trade with the Sioux The fur-trade in North America with New France led to much competition and conflict among indigenous nations. In the early and mid-eighteenth century, French trade had come to favor the Sioux, who received guns in return for pelts from their beaver-rich homeland, which had been relatively untouched by trade in comparison with other nations. Hoping to coax the Sioux out of an alliance with the Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Australia in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), the Pacific Ocean is the largest division of the World Ocean and the hydrosphere and covers approximately 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of the planet's total surface area, larger than its entire land area ().Pacific Ocean . ''Encyclopædia Britannica, Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the Land and water hemispheres, water hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere, as well as the Pole of inaccessi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea lane between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, near the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters. For centuries, European explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus in 1492, sought a navigable passage as a possible trade route to Asia, but were blocked by North, Central, and South America; by ice, or by rough waters (e.g. Tierra del Fuego). An ice-bound northern route was discovered in 1850 by the Irish explorer Robert McClure, whose expedition completed the passage by hauling sledges. Scotsman John Rae (explorer), John Rae explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandan People
The Mandan () are a Native American tribe of the Great Plains who have lived for centuries primarily in what is now North Dakota. They are enrolled in the Three Affiliated Tribes of the Fort Berthold Reservation. About half of the Mandan still reside in the area of the reservation; the rest reside around the United States and in Canada. The Mandan historically lived along both banks of the Upper Missouri River and two of its tributaries—the Heart and Knife rivers—in present-day North and South Dakota. Speakers of Mandan, a Siouan language, they developed a settled, agrarian culture. They established permanent villages featuring large, round, earth lodges, some in diameter, surrounding a central plaza. Matrilineal families lived in the lodges. The Mandan were a great trading nation, trading especially their large corn surpluses with other tribes in exchange for bison meat and fat. Food was the primary item, but they also traded for horses, guns, and other trade goods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrament Of Confession
The Sacrament of Penance (also commonly called the Sacrament of Reconciliation or Confession) is one of the seven sacraments of the Catholic Church (known in Eastern Christianity as sacred mysteries), in which the faithful are absolved from sins committed after baptism and reconciled with the Christian community. During reconciliation, mortal sins must be confessed and venial sins may be confessed for devotional reasons. According to the dogma and unchanging practice of the church, only those ordained as priests may grant absolution. Nature The church teaches, based on the Parable of the Prodigal Son, that confession is not a tribunal or criminal court, where one is condemned by God like a criminal, but a "wedding banquet hall, where the community celebrates Easter, Christ's victory over sin and death, in the joyful experience of his forgiving mercy." In confession, the church believes, God judges a person in the sense of bringing to light his or her sins, by granting the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Baptiste De La Vérendrye
Jean-Baptiste Gaultier de la Vérendrye (September 3, 1713 – June 6, 1736) was the eldest son of Pierre Gaultier de Varennes et de La Vérendrye and Marie-Anne Dandonneau Du Sablé. He was born on Île Dupas near Sorel, New France Jean Baptiste, with three brothers, Pierre Gaultier de La Vérendrye, François de La Vérendrye, and Louis-Joseph Gaultier de La Vérendrye, served in the expedition his father led west in 1731. When they arrived at Fort Kaministiquia some of the '' engagés'' (indentured employees), exhausted by the long journey by canoe from Montreal and discouraged by the difficult portages facing them, refused to go on. His father's second in command, Christopher Dufrost de La Jemeraye and Jean Baptiste led a smaller advance party west to Rainy Lake and established a fort they named Fort St. Pierre (after the parish church where Jean Baptiste was baptised). The following year Jean Baptiste was instrumental in founding Fort St. Charles on Lake of the Wood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Peninsula Of Michigan
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the Geography of Michigan, two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula of Michigan, Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the Straits of Mackinac. It is surrounded by water on all sides except its southern border, which it shares with Indiana and Ohio. Although the Upper Peninsula is commonly referred to as "the U.P.", it is uncommon for the Lower Peninsula to be called "the L.P.". Because of its recognizable shape, the Lower Peninsula is nicknamed The Mitten, with the eastern region identified as "The Thumb". This has led to several folklore, folkloric creation myths for the area, one being that it is a handprint of Paul Bunyan, a giant lumberjack and popular European-American folk character in Michigan. When asked where they live, Lower Peninsula residents may hold up their right palm and point to a spot on it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mackinaw City, Michigan
Mackinaw City ( ) is a village at the northernmost point of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan, United States. Divided between Cheboygan and Emmet counties, Mackinaw City is located at the southern end of the Mackinac Bridge, which carries Interstate 75 over the Straits of Mackinac to St. Ignace, in the Upper Peninsula. Mackinaw City and St. Ignace also serve as access points for ferries to and from Mackinac Island. For these reasons, Mackinaw City is considered one of Michigan's most popular tourist attractions. The Mackinaw City area is home to a number of historic sites, including Fort Michilimackinac, Historic Mill Creek State Park, Old Mackinac Point Light, McGulpin Point Light, and the retired US Coast Guard Icebreaker ''Mackinaw''. History Etymology and early settlement The name of Mackinaw is a respelling of "Mackinac", a strait between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan, an island in the strait, and an important trading-post on the island; ultimately from Ojibw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac (/fóːt ˌmɪʃələˈmækənɔː/ FAWT MISH-ə-lə-MAK-ə-naw) was an 18th-century French, and later British, fort and trading post at the Straits of Mackinac; it was built on the northern tip of the lower peninsula of the present-day state of Michigan in the United States. Built around 1715, and abandoned in 1783, it was located along the straits that connect Lake Huron and Lake Michigan of the Great Lakes of North America. A reconstruction of the fort is preserved as the main feature of Colonial Michilimackinac Historic State Park. The present-day village of Mackinaw City developed around the site of the fort, which has been designated as a National Historic Landmark. It is preserved as an open-air historical museum, with several reconstructed wooden buildings and palisades, and is now part of the state park. History The primary purpose of the fort was as part of the French-Canadian trading post system, which stretched from the Atlantic Coast a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |