|
Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve
The Jasper Ridge Biological Preserve is a nature preserve and biological field station formally established as a reserve in 1973. The biological preserve is owned by Stanford University, and is part of the Stanford School of Humanities and Sciences. It is located at south of Sand Hill Road and west of Interstate 280 in Portola Valley, San Mateo County, California. It is used by students, researchers, and docents to conduct biology research, and teach the community about the importance of that research. The preserve encompasses Jasper Ridge and Searsville Lake (actually a reservoir) and the upper reaches of San Francisquito Creek, along with the latter's Corte Madera Creek and Bear Creek tributaries. Geology Jasper Ridge is part of the foothills northeast of the Santa Cruz Mountains and is bounded by San Francisquito Creek, Corte Madera Creek and Los Trancos Creek, although the preserve occupies only the northwestern half of the ridge. The hilly mass runs about ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Fir On Jasper Ridge 2011-06-18
Douglas may refer to: People * Douglas (given name) * Douglas (surname) Animals * Douglas (parrot), macaw that starred as the parrot ''Rosalinda'' in Pippi Longstocking * Douglas the camel, a camel in the Confederate Army in the American Civil War Businesses * Douglas Aircraft Company * Douglas (cosmetics), German cosmetics retail chain in Europe * Douglas Holding, former German company * Douglas (motorcycles), British motorcycle manufacturer Peerage and Baronetage * Duke of Douglas * Earl of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Marquess of Douglas, or any holder of the title * Douglas baronets Peoples * Clan Douglas, a Scottish kindred * Dougla people, West Indians of both African and East Indian heritage Places Australia * Douglas, Queensland, a suburb of Townsville * Douglas, Queensland (Toowoomba Region), a locality * Port Douglas, North Queensland, Australia * Shire of Douglas, in northern Queensland Canada * Douglas, New Brunswick * Douglas Parish, New Brunswick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avena Barbata
''Avena barbata'' is a species of Avena, wild oat known by the common name slender wild oat. It has edible seeds. It is a diploidized autotetraploid grass (2n=4x=28). Its diploid ancestors are ''A. hirtula'' Lag. and ''A. wiestii'' Steud (2n=2x=14), which are considered Mediterranean and desert ecotypes, respectively, comprising a single species. ''A. wiestii'' and ''A. hirtula'' are widespread in the Mediterranean Basin, growing in mixed stands with ''A. barbata'', though they are difficult to tell apart. This is a winter annual grass with thin tillers (stems) growing up to 60 to 80 centimeters in maximum height, but known to sometimes grow taller. The bristly spikelets are 2 to 3 centimeters long, not counting the bent Awn (botany), awn which is up to 4 centimeters in length. ''Avena barbata'' largely reproduces by selfing in natural populations, with very low rates of outcrossing. ''A. barbata'' is native to central Asia (as far east as Pakistan) and the Mediterranean Basin. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Experiments
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management, and human ecology. The word ''ecology'' () was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Erns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Restoration
Ecological restoration, or ecosystem restoration, is the process of assisting the recovery of an ecosystem that has been degraded, damaged, destroyed or transformed. It is distinct from conservation in that it attempts to retroactively repair already damaged ecosystems rather than take preventative measures. Ecological restoration can help to reverse biodiversity loss, combat climate change, support the provision of ecosystem services and support local economies. The United Nations has named 2021–2030 the Decade on Ecosystem Restoration. Habitat restoration involves the deliberate rehabilitation of a specific area to reestablish a functional ecosystem. This may differ from historical baselines (the ecosystem's original condition at a particular point in time). To achieve successful habitat restoration, it is essential to understand the life cycles and interactions of species, as well as the essential elements such as food, water, nutrients, space, and shelter needed to supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Reserves In California
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history (Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn at the same time, especially after Charles Darwin. Within the various uses of the word t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organization Of Biological Field Stations
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is an entity—such as a company, or corporation or an institution (formal organization), or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose. Organizations may also operate secretly or illegally in the case of secret societies, criminal organizations, and resistance movements. And in some cases may have obstacles from other organizations (e.g.: MLK's organization). What makes an organization recognized by the government is either filling out incorporation or recognition in the form of either societal pressure (e.g.: Advocacy group), causing concerns (e.g.: Resistance movement) or being considered the spokesperson of a group of people subject to negotiation (e.g.: the Polisario Front being recognized as the sole representative of the Sahrawi people and forming a partially recognized state.) Compare the concept of social groups, which may include non-organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Ant
The Argentine ant (''Linepithema humile'', formerly ''Iridomyrmex humilis'') is an ant native to northern Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Bolivia and southern Brazil. This invasive species was inadvertently introduced by humans on a global scale and has become established in many Mediterranean climate areas, including South Africa, New Zealand, Japan, Easter Island, Australia, the Azores, Europe, Hawaii, and the continental United States. Argentine ants are significant pests within agricultural and urban settings, and are documented to cause substantial harm to communities of native arthropods, vertebrates, and plants within their invaded range. Description ''Linepithema humile'' is a small-bodied (2.2–2.6 mm) ant species, dull light to dark brown in color. Within the invasion zone, ant colonies are large and include many workers and multiple queens. Argentine ants are opportunistic with regard to nesting preferences. Colony nests have been found in the ground, in cracks in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Green Building
Green building (also known as green construction, sustainable building, or eco-friendly building) refers to both a structure and the application of processes that are environmentally responsible and resource-efficient throughout a building's life-cycle: from planning to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. This requires close cooperation of the contractor, the architects, the engineers, and the client at all project stages.Yan Ji and Stellios Plainiotis (2006): Design for Sustainability. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press. The Green Building practice expands and complements the classical building design concerns of economy, utility, durability, and comfort. Green building also refers to saving resources to the maximum extent, including energy saving, land saving, water saving, material saving, etc., during the whole life cycle of the building, protecting the environment and reducing pollution, providing people with healthy, comfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
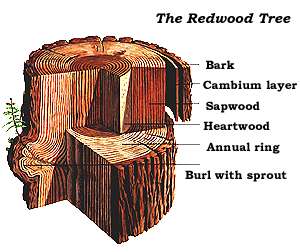
Coast Redwood
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995: 606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the longest-living trees on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. Being the tallest tree species, with a small range and an extremely long lifespan, many redwoods are preserved in various state and nation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudotsuga Menziesii
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is the tallest tree in the Pinaceae family. It is native plant, native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three varieties: coast Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''menziesii''), Rocky Mountain Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca'') and Mexican Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''lindleyana''). Despite its common names, it is not a true fir (genus ''Fir, Abies''), spruce (genus ''Spruce, Picea''), or pine (genus ''Pine, Pinus''). It is also not a Tsuga, hemlock; the genus name ''Pseudotsuga'' means "false hemlock". Description Douglas-firs are medium-sized to extremely large evergreen trees, tall (although only coast Douglas-firs reach heights near 100 m) and commonly reach in diameter, although trees with diameters of almost exist. The largest coast Douglas-firs regularl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecological Succession
Ecological succession is the process of how species compositions change in an Community (ecology), ecological community over time. The two main categories of ecological succession are primary succession and secondary succession. Primary succession occurs after the initial Colonisation (biology), colonization of a newly created habitat with no living organisms. Secondary succession occurs after a Disturbance (ecology), disturbance such as fire, habitat destruction, or a natural disaster destroys a pre-existing community. Both consistent patterns and variability are observed in ecological succession. Theories of ecological succession identify different factors that help explain why plant communities change the way they do. Succession was among the first theories advanced in ecology. Ecological succession was first documented in the Indiana Dunes of Northwest Indiana by Henry Chandler Cowles during the late 19th century and remains a main Ecology, ecological topic of study. Over ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |