|
James Till
James Edgar Till (August 25, 1931 – May 18, 2025) was a University of Toronto biophysicist, best known for demonstrating – in a partnership with Ernest McCulloch – the existence of stem cells. Early work Till was born in Lloydminster, which is located on the border between Saskatchewan and Alberta. The family farm was located north of Lloydminster, in Alberta; the eastern margin of the farm was the Alberta–Saskatchewan boundary. He attended the University of Saskatchewan with scholarships awarded by the Standard Oil Company and the National Research Council, graduating with a B.Sc. in 1952 and a M.Sc. in physics in 1954. Some of his early work was conducted with Harold E. Johns, a pioneer in cobalt-60 radiotherapy. Till proceeded to Yale University, where he received a Ph.D. in biophysics in 1957. He then became a post-doctoral fellow at the University of Toronto. Stem cells Harold E. Johns recruited Till to the Ontario Cancer Institute at Princess Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloydminster, Alberta
Lloydminster is a city in Canada which has the unusual geographic distinction of straddling the Provinces and territories of Canada, provincial border between Alberta and Saskatchewan. The city is incorporated by both provinces as a single city with a single municipal administration. Located in the heart of Treaty 6, Lloydminster is the traditional homeland of the Plains Cree people, Plains Cree, Wood Cree, Dene, Saulteaux and homeland of the Métis. History Intended to be an exclusively British utopian settlement centred on the idea of sobriety, Lloydminster was founded in 1903 by the Barr Colonists, who came directly from the United Kingdom. At a time when the area was still part of the Northwest Territories, North-West Territories, the town was located astride the Fourth Meridian of the Dominion Land Survey. This meridian was intended to coincide with the 110th meridian west, 110° west longitude, although the imperfect surveying methods of the time led to the surveyed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Oil
Standard Oil Company was a Trust (business), corporate trust in the petroleum industry that existed from 1882 to 1911. The origins of the trust lay in the operations of the Standard Oil of Ohio, Standard Oil Company (Ohio), which had been founded in 1870 by John D. Rockefeller. The trust was born on January 2, 1882, when a group of 41 investors signed the Standard Oil Trust Agreement, which pooled their securities of 40 companies into a single holding agency managed by nine trustees. The original trust was valued at $70 million. On March 21, 1892, the Standard Oil Trust was dissolved and its holdings were reorganized into 20 independent companies that formed an unofficial union referred to as "Standard Oil Interests." In 1899, the ExxonMobil, Standard Oil Company (New Jersey) acquired the shares of the other 19 companies and became the holding company for the trust. Jersey Standard operated a near monopoly in the American oil industry from 1899 until 1911 and was the largest corp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Access (publishing)
Open access (OA) is a set of principles and a range of practices through which nominally copyrightable publications are delivered to readers free of access charges or other barriers. With open access strictly defined (according to the 2001 definition), or libre open access, barriers to copying or reuse are also reduced or removed by applying an open license for copyright, which regulates post-publication uses of the work. The main focus of the open access movement has been on "peer reviewed research literature", and more specifically on academic journals. This is because: * such publications have been a subject of serials crisis, unlike newspapers, magazines and fiction writing. The main difference between these two groups is in demand elasticity: whereas an English literature curriculum can substitute '' Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'' with a free-domain alternative, such as '' A Voyage to Lilliput,'' an emergency room physician treating a patient for a lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Mining
{{debate, date=September 2015 List mining can be defined as the use, for purposes of scientific research, of messages sent to Internet-based electronic mailing lists. List mining raises novel issues in Internet research ethics. These ethical issues are especially important for health related lists. Some questions that need to be considered by a Research Ethics Committee (or an Institutional Review Board) when reviewing research proposals that involve list mining include these: Are participants in mailing lists "research subjects"? Should those participants in a health related electronic mailing list who were the original sources of messages sent to such lists be regarded as "research subjects"? If so, then several ethical issues need to be considered. These include those pertaining to privacy, informed consent, whether the research is intrusive and has potential for harm, and whether the list should be perceived as "private" or "public" space. Are participants in mailing lists "pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Research Ethics
Internet research ethics involves the research ethics of social science, humanities, and scientific research carried out via the Internet. Of particular interest is the example of English Wikipedia and research ethics. The usual view is that private and public spaces become blurred on the Internet. There are a number of objections to this stance, which are all relevant to English Wikipedia research. In particular, it can be difficult for researchers to ensure participant anonymity. One study of 112 published educational technology research papers was able to identify participant identities in 10 of those papers; the majority of these studies had gathered this data under conditions of anonymity. An assessment of ethics in Internet-based research, together with some recommendations, has been prepared by a Working Committee of the Interagency AdvisorPanel on Research Ethics(PRE)in Canada. PRE is a body of external experts established in November 2001 by three Canadian Research Agencies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internet Research
In its widest sense, Internet research comprises any kind of research done on the Internet or the World Wide Web. Unlike simple fact-checking or web scraping, it often involves synthesizing from diverse sources and verifying the credibility of each. In a stricter sense, "Internet research" refers to conducting scientific research using Online and offline , online tools and techniques; the discipline that studies Internet research thus understood is known as online research methods or Internet-mediated research. As with other kinds of scientific research, it involves an Internet research ethics , ethical dimension. Internet research can also be interpreted as the part of Internet studies that investigates the social, ethical, economic, managerial and political implications of the Internet. Characterization Internet research has had a profound impact on the way ideas are formed and knowledge is created. Through web search, Web page, pages with some relation to a given search entry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Canada
The Royal Society of Canada (RSC; , SRC), also known as the Academies of Arts, Humanities, and Sciences of Canada (French: ''Académies des arts, des lettres et des sciences du Canada''), is the senior national, bilingual council of distinguished Canadian scholars, humanists, scientists, and artists. The primary objective of the RSC is to promote learning and research in the arts, the humanities, and the sciences. The RSC is Canada's national academy. It promotes Canadian research and scholarly accomplishment in both official languages, recognizes academic and artistic excellence, and advises governments, non-governmental organizations, and Canadians on matters of public interest. History In the late 1870s, the Governor General of Canada, John Campbell, 9th Duke of Argyll, John Campbell, Marquis of Lorne, determined that Canada required a cultural institution to promote national scientific research and development. Since that time, succeeding governors general have remained invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Siminovitch
Louis Siminovitch (May 1, 1920 – April 6, 2021) was a Canadian molecular biologist. He was a pioneer in human genetics, researcher into the genetic basis of muscular dystrophy and cystic fibrosis, and helped establish Ontario programs exploring genetic roots of cancer. Life and career Siminovitch was born in Montreal, Quebec, the son of Goldie and Nathan Siminovitch, who were Jewish emigrants from Eastern Europe. He won a scholarship in chemistry to McGill University, earning a doctorate in 1944. He then studied at the Pasteur Institute in Paris. In 1953 he joined Toronto's Connaught Medical Research Laboratories. Later he joined the University of Toronto and worked there from 1956 to 1985. One of his doctoral students was Joyce Taylor-Papadimitriou. He helped establish the Department of Genetics at the Hospital for Sick Children as geneticist in chief, where he worked from 1970 to 1985. From 1983 to 1994 he was the founding director of research at the Samuel Lunenfeld Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features Peer review, peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2022 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 50.5), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in the autumn of 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander MacMillan (publisher), Alexander MacMillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
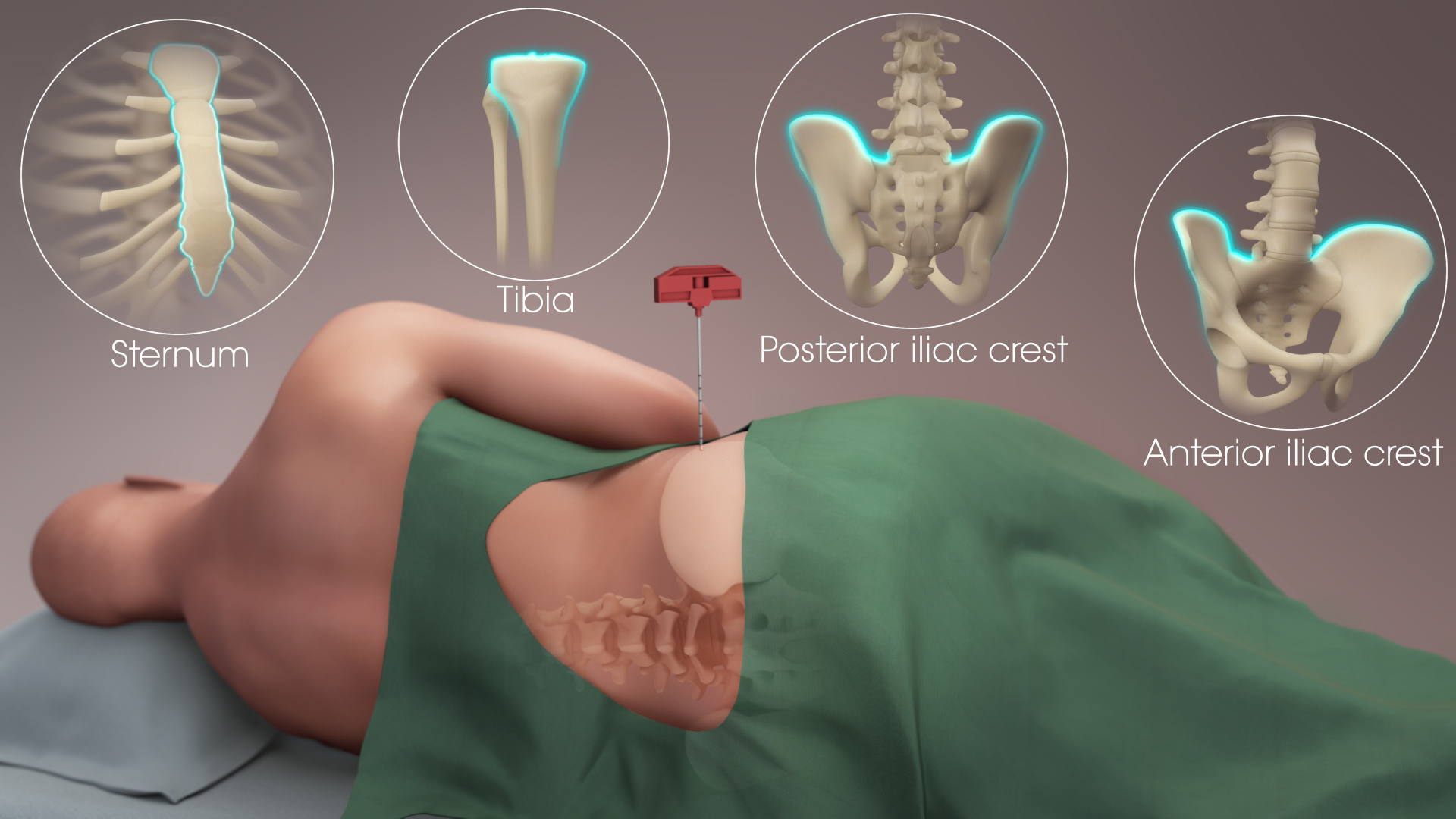
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid biological tissue, tissue found within the Spongy bone, spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of Blood cell, hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the Rib cage, ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and Pelvis, bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a person weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the Circulatory system, systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of Hematopoietic cell, hematopoietic cells, including both Myeloid tissue, myeloid and Lymphocyte, lymphoid lineages, are create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Princess Margaret Hospital (Toronto)
The Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (previously, ''Princess Margaret Hospital'') is a scientific research centre and a teaching hospital in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, affiliated with the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine as part of the University Health Network. The hospital now stands as the largest cancer centre in Canada and one of the five largest cancer centres in the world. Along with the Odette Cancer Centre, which is also associated with University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine and is independently the sixth largest cancer centre in North America, it forms one of the largest cluster of cancer hospitals in the world. The hospital is situated near the intersection of University Avenue and College Street within the Discovery District of downtown Toronto, an area with high concentration of biomedical research institutions. Named for Princess Margaret, Countess of Snowdon, the hospital is under the royal patronage of Anne, Princess Royal. The hospital specializes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |