|
Itakura–Saito Distance
The Itakura–Saito distance (or Itakura–Saito divergence) is a measure of the difference between an original spectrum P(\omega) and an approximation \hat(\omega) of that spectrum. Although it is not a perceptual measure, it is intended to reflect perceptual (dis)similarity. It was proposed by Fumitada Itakura and Shuzo Saito in the 1960s while they were with NTT. The distance is defined as: : D_(P(\omega),\hat(\omega))=\frac\int_^ \left \frac-\log \frac - 1 \right\, d\omega The Itakura–Saito distance is a Bregman divergence generated by minus the logarithmic function, but is not a true metric since it is not symmetric and it does not fulfil triangle inequality. In Non-negative matrix factorization, the Itakura-Saito divergence can be used as a measure of the quality of the factorization: this implies a meaningful statistical model of the components and can be solved through an iterative method. The Itakura-Saito distance is the Bregman divergence associated with the Gamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. As scientific understanding of light advanced, it came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum. It thereby became a mapping of a range of magnitudes (wavelengths) to a range of qualities, which are the perceived "colors of the rainbow" and other properties which correspond to wavelengths that lie outside of the visible light spectrum. Spectrum has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a broad range of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Similarity Function
In statistics and related fields, a similarity measure or similarity function or similarity metric is a real-valued function that quantifies the similarity between two objects. Although no single definition of a similarity exists, usually such measures are in some sense the inverse of distance metrics: they take on large values for similar objects and either zero or a negative value for very dissimilar objects. Though, in more broad terms, a similarity function may also satisfy metric axioms. Cosine similarity is a commonly used similarity measure for real-valued vectors, used in (among other fields) information retrieval to score the similarity of documents in the vector space model. In machine learning, common kernel functions such as the RBF kernel can be viewed as similarity functions. Use in clustering In spectral clustering, a similarity, or affinity, measure is used to transform data to overcome difficulties related to lack of convexity in the shape of the data distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumitada Itakura
is a Japanese scientist. He did pioneering work in statistical signal processing, and its application to speech analysis, synthesis and coding, including the development of the linear predictive coding (LPC) and line spectral pairs (LSP) methods. Biography Itakura was born in Toyokawa, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. He received undergraduate and graduate degrees from Nagoya University in 1963 and 1965, respectively. In 1966, while studying his PhD at Nagoya, he developed the earliest concepts for what would later become known as linear predictive coding (LPC), along with Shuzo Saito from Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT). They described an approach to automatic phoneme discrimination that involved the first maximum likelihood approach to speech coding. In 1968, he joined the NTT Musashino Electrical Communication Laboratory in Tokyo. The same year, Itakura and Saito presented the Itakura–Saito distance algorithm. The following year, Itakura and Saito introduced partial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nippon Telegraph And Telephone
, commonly known as NTT, is a Japanese telecommunications company headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. Ranked 55th in ''Fortune'' Global 500, NTT is the fourth largest telecommunications company in the world in terms of revenue, as well as the third largest publicly traded company in Japan after Toyota and Sony, as of June 2022. The company is incorporated pursuant to the NTT Law (). The purpose of the company defined by the law is to own all the shares issued by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone East Corporation (NTT East) and Nippon Telegraph and Telephone West Corporation (NTT West) and to ensure proper and stable provision of telecommunications services all over Japan including remote rural areas by these companies as well as to conduct research relating to the telecommunications technologies that will form the foundation for telecommunications. On 1 July 2019, NTT Corporation launched NTT Ltd., an $11 billion de facto holding company business consisting of 28 brands from across NTT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
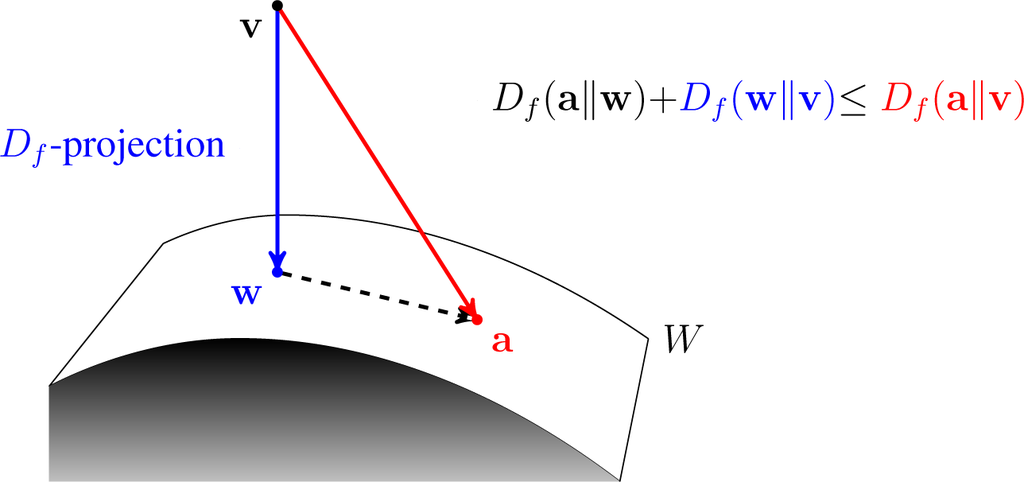
Bregman Divergence
In mathematics, specifically statistics and information geometry, a Bregman divergence or Bregman distance is a measure of difference between two points, defined in terms of a strictly convex function; they form an important class of divergences. When the points are interpreted as probability distributions – notably as either values of the parameter of a parametric model or as a data set of observed values – the resulting distance is a statistical distance. The most basic Bregman divergence is the squared Euclidean distance. Bregman divergences are similar to metrics, but satisfy neither the triangle inequality (ever) nor symmetry (in general). However, they satisfy a generalization of the Pythagorean theorem, and in information geometry the corresponding statistical manifold is interpreted as a (dually) flat manifold. This allows many techniques of optimization theory to be generalized to Bregman divergences, geometrically as generalizations of least squares. Bregman diverg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metric (mathematics)
In mathematics, a metric space is a set together with a notion of '' distance'' between its elements, usually called points. The distance is measured by a function called a metric or distance function. Metric spaces are the most general setting for studying many of the concepts of mathematical analysis and geometry. The most familiar example of a metric space is 3-dimensional Euclidean space with its usual notion of distance. Other well-known examples are a sphere equipped with the angular distance and the hyperbolic plane. A metric may correspond to a metaphorical, rather than physical, notion of distance: for example, the set of 100-character Unicode strings can be equipped with the Hamming distance, which measures the number of characters that need to be changed to get from one string to another. Since they are very general, metric spaces are a tool used in many different branches of mathematics. Many types of mathematical objects have a natural notion of distance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-negative Matrix Factorization
Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF or NNMF), also non-negative matrix approximation is a group of algorithms in multivariate analysis and linear algebra where a matrix is factorized into (usually) two matrices and , with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements. This non-negativity makes the resulting matrices easier to inspect. Also, in applications such as processing of audio spectrograms or muscular activity, non-negativity is inherent to the data being considered. Since the problem is not exactly solvable in general, it is commonly approximated numerically. NMF finds applications in such fields as astronomy, computer vision, document clustering, missing data imputation, chemometrics, audio signal processing, recommender systems, and bioinformatics. History In chemometrics non-negative matrix factorization has a long history under the name "self modeling curve resolution". In this framework the vectors in the right matrix are continuous cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iterative Method
In computational mathematics, an iterative method is a mathematical procedure that uses an initial value to generate a sequence of improving approximate solutions for a class of problems, in which the ''n''-th approximation is derived from the previous ones. A specific implementation of an iterative method, including the termination criteria, is an algorithm of the iterative method. An iterative method is called convergent if the corresponding sequence converges for given initial approximations. A mathematically rigorous convergence analysis of an iterative method is usually performed; however, heuristic-based iterative methods are also common. In contrast, direct methods attempt to solve the problem by a finite sequence of operations. In the absence of rounding errors, direct methods would deliver an exact solution (for example, solving a linear system of equations A\mathbf=\mathbf by Gaussian elimination). Iterative methods are often the only choice for nonlinear equations. Howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Computation (journal)
''Neural Computation'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of neural computation, including modeling the brain and the design and construction of neurally-inspired information processing systems. It was established in 1989 and is published by MIT Press. The editor-in-chief is Terrence J. Sejnowski (Salk Institute for Biological Studies). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 2.207. References External links * Neuroscience journals MIT Press academic journals Monthly journals English-language journals Publications established in 1989 Cognitive science journals {{neuroscience-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log-spectral Distance
The log-spectral distance (LSD), also referred to as log-spectral distortion or root mean square log-spectral distance, is a distance measure between two spectra. The log-spectral distance between spectra P\left(\omega\right) and \hat\left(\omega\right) is defined as p-norm: : D_=^, where P\left(\omega\right) and \hat\left(\omega\right) are power spectra. Unlike the Itakura–Saito distance, the log-spectral distance is symmetric. In speech coding, log spectral distortion for a given frame is defined as the root mean square difference between the original LPC log power spectrum and the quantized or interpolated LPC log power spectrum. Usually the average of spectral distortion over a large number of frames is calculated and that is used as the measure of performance of quantization or interpolation. Meaning When measuring the distortion between signals, the scale or temporality/spatiality of the signals can have different levels of significance to the distortion measures. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |