|
Isopropylmagnesium Chloride
Isopropylmagnesium chloride is an organometallic compound with the general formula (CH3)2HCMgCl. This highly flammable, colorless, and moisture sensitive material is the Grignard reagent derived from isopropyl chloride. It is commercially available, usually as a solution in tetrahydrofuran. Synthesis and reactivity Solutions of isopropylmagnesium chloride by treating isopropyl chloride with magnesium metal in refluxing ether: : This reagent is used to prepare other Grignard reagents by transmetalation. An illustrative reaction involves the generation of the Grignard reagent derived from bromo-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)benzene: :(CH3)2HCMgCl + (CF3)2C6H3Br → (CH3)2HCCl + (CF3)2C6H3MgBr Addition of one equivalent of Lithium chloride, LiCl to isopropylmagnesium chloride gives "Turbo Grignard" solutions, named so due to the increased rate and efficiency for transmetalation reactions. Isopropylmagnesium chloride is also used to prepare isopropyl compounds, such as chlorodiisopropyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (Metal carbonyl, metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganics, metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagent
Grignard reagents or Grignard compounds are chemical compounds with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon–carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. Grignard reagents are rarely isolated as solids. Instead, they are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran using air-free techniques. Grignard reagents are complex with the magnesium atom bonded to two ether ligands as well as the halide and organyl ligands. The discovery of the Grignard reaction in 1900 was recogn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isopropyl Chloride
Isopropyl chloride is an organic compound with the chemical formula (CH3)2CHCl. It is a colourless to slightly yellow, volatile, flammable liquid with a sweet, ether-like (almost like petroleum) odour. It is used as an industrial solvent. It is produced industrially by the addition of HCl to propylene: :CH3CH=CH2 + HCl → (CH3)2CHCl Isopropyl chloride can be easily produced in the lab by reacting concentrated hydrochloric acid with isopropyl alcohol in the presence of a calcium chloride or zinc chloride catalyst. The common ratio of alcohol to acid to catalyst is 1:2:1 using 30% HCl and near pure isopropyl alcohol. The reaction mixture is refluxed for several hours, or distilled over several hours. The isopropyl chloride is then separated from the remaining isopropyl alcohol by washing with water (the isopropyl chloride will form in insoluble layer above the water, while the alcohol will dissolve into solution along with any HCl present). In the presence of a catalyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water- miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. It is an isomer of another solvent, butanone. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-Butanediol, 1,4-butanediol. Ashland Inc., Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from Condensation reaction, condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing Butane#Isomers, ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic table), it occurs naturally only in combination with other elements and almost always has an oxidation state of +2. It reacts readily with air to form a thin Passivation (chemistry), passivation coating of magnesium oxide that inhibits further corrosion of the metal. The free metal burns with a brilliant-white light. The metal is obtained mainly by electrolysis of magnesium Salt (chemistry), salts obtained from brine. It is less dense than aluminium and is used primarily as a component in strong and lightweight magnesium alloy, alloys that contain aluminium. In the cosmos, magnesium is produced in large, aging stars by the sequential addition of three Helium nucleus, helium nuclei to a carbon nucleus. When such stars explo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmetalation
Transmetalation (alt. spelling: transmetallation) is a type of organometallic reaction that involves the transfer of ligands from one metal to another. It has the general form: :M1–R + M2–R′ → M1–R′ + M2–R where R and R′ can be, but are not limited to, an alkyl, aryl, alkynyl, allyl, halogen, or pseudohalogen group. The reaction is usually an irreversible process due to thermodynamic and kinetic reasons. Thermodynamics will favor the reaction based on the electronegativities of the metals and kinetics will favor the reaction if there are empty orbitals on both metals. There are different types of transmetalation including redox-transmetalation and redox-transmetalation/ligand exchange. During transmetalation the metal-carbon bond is activated, leading to the formation of new metal-carbon bonds. Transmetalation is commonly used in catalysis, synthesis of main group complexes, and synthesis of transition metal complexes. Types of transmetalation There are two mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents (83.05 g/100 mL of water at 20 °C) and its hygroscopic properties. Chemical properties The salt forms crystalline hydrates, unlike the other alkali metal chlorides. Mono-, tri-, and pentahydrates are known. The anhydrous salt can be regenerated by heating the hydrates. LiCl also absorbs up to four equivalents of ammonia/mol. As with any other ionic chloride, solutions of lithium chloride can serve as a source of chloride ion, e.g., forming a precipitate upon treatment with silver nitrate: : LiCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + LiNO3 Preparation Lithium chloride is produced by treatment of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Anhydrous LiCl is prepared from the hydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorodiisopropylphosphine
Chlorodiisopropylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH3)2CHsub>2PCl. It is a colorless liquid that reacts with water and oxygen. The compound is used to prepare tertiary phosphines and phosphinite ligands. Synthesis and reactions The compound is prepared by treating phosphorus trichloride with the Grignard reagent isopropylmagnesium chloride: :PCl3 + 2 (CH3)2CHMgCl → CH3)2CHsub>2PCl + 2 MgCl2 Relative to the reaction of less hindered Grignard reagents with PCl3, this reaction affords a superior yield of the monochloro derivative. Chlorodiisopropylphosphine reacts with Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds to give phosphines: : CH3)2CHsub>2PCl + RM → CH3)2CHsub>2PR + MCl Chlorodiisopropylphosphine reacts with alcohols and phenols to give phosphinites, this reaction typically is conducted in the presence of a base: : CH3)2CHsub>2PCl + ROH → CH3)2CHsub>2POR + HCl Phosphinites are versatile ligand In coordination chemistry, a ligand i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Chloride
Lithium chloride is a chemical compound with the formula Li Cl. The salt is a typical ionic compound (with certain covalent characteristics), although the small size of the Li+ ion gives rise to properties not seen for other alkali metal chlorides, such as extraordinary solubility in polar solvents (83.05 g/100 mL of water at 20 °C) and its hygroscopic properties. Chemical properties The salt forms crystalline hydrates, unlike the other alkali metal chlorides. Mono-, tri-, and pentahydrates are known. The anhydrous salt can be regenerated by heating the hydrates. LiCl also absorbs up to four equivalents of ammonia/mol. As with any other ionic chloride, solutions of lithium chloride can serve as a source of chloride ion, e.g., forming a precipitate upon treatment with silver nitrate: : LiCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + LiNO3 Preparation Lithium chloride is produced by treatment of lithium carbonate with hydrochloric acid. Anhydrous LiCl is prepared from the hydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
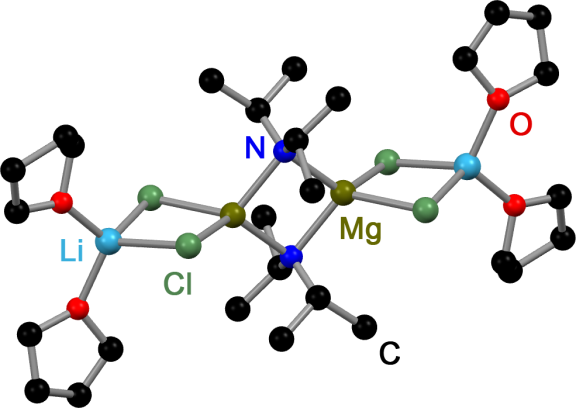
Turbo-Hauser Base
''Turbo''-Hauser bases are Hauser base, amido magnesium halides that contain stoichiometric amounts of Lithium chloride, LiCl. These mixed Mg/Li amides of the type R2NMgCl⋅LiCl are used in organic chemistry as non-nucleophilic bases for metalation, metalation reactions of aromatic and heteroaromatic substrates. Compared to their LiCl free ancestors ''Turbo''-Hauser bases show an enhanced kinetic basicity, excellent regioselectivity, high functional group tolerance and a better solubility. Preparation Typically ''Turbo''-Hauser bases are prepared by treating an amine with a Grignard reaction, Grignard reagent and lithium chloride. In some cases they are prepared by treating a lithium amide with MgCl2: : : Common ''Turbo''-Hauser bases: R'2NH = ''i''Pr2NMgCl·LiCl (''i''Pr-''Turbo''-Hauser base), TMPMgCl·LiCl, TMP (''Turbo''-Hauser base or ''Knochel''-Hauser Base) Structure In solution, ''Turbo''-Hauser bases participate in temperature- and concentration-dependent equilibria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Group Compatibility
Functional may refer to: * Movements in architecture: ** Functionalism (architecture) ** Form follows function * Functional group, combination of atoms within molecules * Medical conditions without currently visible organic basis: ** Functional symptom ** Functional disorder * Functional classification for roads * Functional organization * Functional training In mathematics * Functional (mathematics), a term applied to certain scalar-valued functions in mathematics and computer science ** Minnesota functionals ** Functional analysis, a branch of mathematical analysis ** Linear functional, a type of functional often simply called a functional in the context of functional analysis * Higher-order function, also called a functional, a function that takes other functions as arguments In computer science, software engineering * "Functional" (noun) may be used as a synonym for Higher-order function * (C++), a header file in the C++ Standard Library * Functional design, a paradig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |