|
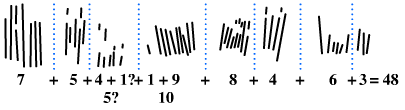
Ishango Bone
The Ishango bone, discovered at the "Fisherman Settlement" of Ishango in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, is a bone tool and possible mathematical device that dates to the Upper Paleolithic era. The curved bone is dark brown in color, about 10 centimeters in length, and features a sharp piece of quartz affixed to one end, perhaps for engraving. Because the bone has been narrowed, scraped, polished, and engraved to a certain extent, it is no longer possible to determine what animal the bone belonged to, although it is assumed to have been a mammal.Association pour la diffusion de l'information archéologique/Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, Brussels (n.d.). "Have You Heard of Ishango?" (PDF). ''Natural Sciences''. The ordered engravings have led many to speculate the meaning behind these marks, including interpretations like mathematical significance or astrological relevance. It is thought by some to be a tally stick, as it features a series of what has been in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nile River
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer.Amazon Longer Than Nile River, Scientists Say Of the world's major rivers, the Nile has one of the lowest average annual flow rates. About long, its covers eleven countries: the |
Slide Rule
A slide rule is a hand-operated mechanical calculator consisting of slidable rulers for conducting mathematical operations such as multiplication, division, exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is one of the simplest analog computers. Slide rules exist in a diverse range of styles and generally appear in a linear, circular or cylindrical form. Slide rules manufactured for specialized fields such as aviation or finance typically feature additional scales that aid in specialized calculations particular to those fields. The slide rule is closely related to nomograms used for application-specific computations. Though similar in name and appearance to a standard ruler, the slide rule is not meant to be used for measuring length or drawing straight lines. Maximum accuracy for standard linear slide rules is about three decimal significant digits, while scientific notation is used to keep track of the order of magnitude of results. English mathematician and clergy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodecimal
The duodecimal system, also known as base twelve or dozenal, is a positional numeral system using twelve as its base. In duodecimal, the number twelve is denoted "10", meaning 1 twelve and 0 units; in the decimal system, this number is instead written as "12" meaning 1 ten and 2 units, and the string "10" means ten. In duodecimal, "100" means twelve squared (144), "1,000" means twelve cubed (1,728), and "0.1" means a twelfth (0.08333...). Various symbols have been used to stand for ten and eleven in duodecimal notation; this page uses and , as in hexadecimal, which make a duodecimal count from zero to twelve read 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, , , and finally 10. The Dozenal Societies of America and Great Britain (organisations promoting the use of duodecimal) use turned digits in their published material: (a turned 2) for ten (dek, pronounced dɛk) and (a turned 3) for eleven (el, pronounced ɛl). The number twelve, a superior highly composite number, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Pletser
Vladimir Pletser (born 28 February 1956) is Director of Space Training Operations at Blue Abyss since 2018, where he is in charge of developing astronaut training programs. From 2016 to early 2018, he was a Visiting Professor and Scientific Adviser at the Technology and Engineering Centre for Space Utilization (CSU) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, China. He supported the preparation of scientific experiments in microgravity for the Chinese Tiangong space station and for aircraft parabolic flights. He worked previously from 1985 till early 2016 as a senior Physicist Engineer at the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) of ESA. He is an expert in microgravity during aircraft parabolic flights for which he holds a world record. He is known as ‘Mister Parabolic Flights’, ‘Mister Parabolas’, ‘Homo Parabolicus’ or ‘Mister Microgravity’. An astronaut candidate for Belgium since 1991, he spent two months in training in 1995 at NASA's Johnson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numeral System
A numeral system is a writing system for expressing numbers; that is, a mathematical notation for representing numbers of a given set, using digits or other symbols in a consistent manner. The same sequence of symbols may represent different numbers in different numeral systems. For example, "11" represents the number ''eleven'' in the decimal or base-10 numeral system (today, the most common system globally), the number ''three'' in the binary or base-2 numeral system (used in modern computers), and the number ''two'' in the unary numeral system (used in tallying scores). The number the numeral represents is called its ''value''. Additionally, not all number systems can represent the same set of numbers; for example, Roman, Greek, and Egyptian numerals don't have a representation of the number zero. Ideally, a numeral system will: *Represent a useful set of numbers (e.g. all integers, or rational numbers) *Give every number represented a unique representation (or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a Product (mathematics), product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, or , involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorization, factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order. The property of being prime is called primality. A simple but slow primality test, method of checking the primality of a given number , called trial division, tests whether is a multiple of any integer between 2 and . Faster algorithms include the Miller–Rabin primality test, which is fast but has a small chance of error ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopes Of Carbon
Carbon (6C) has 14 known isotopes, from to as well as , of which only and are stable. The longest-lived radioisotope is , with a half-life of years. This is also the only carbon radioisotope found in nature, as trace quantities are formed cosmogenically by the reaction + → + . The most stable artificial radioisotope is , which has a half-life of . All other radioisotopes have half-lives under 20 seconds, most less than 200 milliseconds. The least stable isotope is , with a half-life of . Light isotopes tend to decay into isotopes of boron and heavy ones tend to decay into isotopes of nitrogen. List of isotopes , -id=Carbon-8 , , style="text-align:right" , 6 , style="text-align:right" , 2 , , [] , proton emission, 2p , Also immediately emits two protons for the net reaction of → + 4 , 0+ , , , -id=Carbon-9 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 6 , rowspan=3 style="text-align:right" , 3 , rowspan=3, , rowspan=3, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Belgian Institute Of Natural Sciences
The Museum of Natural Sciences (, ; , ) is a Brussels museum dedicated to natural history. It is a part of the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences (; ), itself part of the institutions of the Belgian Federal Science Policy Office (BELSPO). The Dinosaur Hall of the museum is the world's largest museum hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs. Its most important pieces are 30 fossilised ''Iguanodon'' skeletons, which were discovered in 1878 in Bernissart, Belgium. Another famous piece is the Ishango bone, which was discovered in 1960 by Jean de Heinzelin de Braucourt in the Belgian Congo. The museum also houses a research department and a public exhibit department. The museum is located at 29, /, in Leopold Park, close to the Brussels and the European Union#European Quarter, European institutions and the House of European History (HEH). This area is served by Brussels-Luxembourg railway station, as well as by the Brussels Metro, metro stations Maalbeek/Maelbeek metro statio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |