|
Duodecimal
The duodecimal system, also known as base twelve or dozenal, is a positional numeral system using twelve as its base. In duodecimal, the number twelve is denoted "10", meaning 1 twelve and 0 units; in the decimal system, this number is instead written as "12" meaning 1 ten and 2 units, and the string "10" means ten. In duodecimal, "100" means twelve squared (144), "1,000" means twelve cubed (1,728), and "0.1" means a twelfth (0.08333...). Various symbols have been used to stand for ten and eleven in duodecimal notation; this page uses and , as in hexadecimal, which make a duodecimal count from zero to twelve read 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, , , and finally 10. The Dozenal Societies of America and Great Britain (organisations promoting the use of duodecimal) use turned digits in their published material: (a turned 2) for ten (dek, pronounced dɛk) and (a turned 3) for eleven (el, pronounced ɛl). The number twelve, a superior highly composite number, is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwandara Language
Gwandara is a West Chadic language, and the closest relative of Hausa. Its several dialects are spoken in northern Nigeria, predominantly in the north central region of Nigeria by the Gwandara people and some settlers who are about 30,000 people. They are found in large numbers in Abuja, Niger, Kaduna, Kogi and a resettlement town of New Karshi, Karu LGA, Nasarawa State. New Karshi has a Gwandara first class emir Muhammadu Bako III (PhD). The Gwandara people are one of the indigenous tribes of FCT Abuja, the capital city of Nigeria. The Nimbia dialect has a duodecimal numeral system (they count in base 12), whereas other dialects, such as Karshi below, have decimal systems: It is thought that Nimbia, which is isolated from the rest of Gwandara, acquired its duodecimal system from neighboring East Kainji languages. It is duodecimal even to powers of base twelve: The Nimbia 12 number set number system is known for making division easier. References Language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12 (number)
12 (twelve) is the natural number following 11 (number), 11 and preceding 13 (number), 13. Twelve is the 3rd superior highly composite number, the 3rd colossally abundant number, the 5th highly composite number, and is divisible by the numbers from 1 (number), 1 to 4 (number), 4, and 6 (number), 6, a large number of divisors comparatively. It is central to many systems of timekeeping, including the Gregorian calendar, Western calendar and time, units of time of day, and frequently appears in the world's major religions. Name Twelve is the largest number with a monosyllable, single-syllable name in English language, English. Early Germanic languages, Germanic numbers have been theorized to have been non-decimal: evidence includes the unusual phrasing of 11 (number), eleven and twelve, the long hundred, former use of "hundred" to refer to groups of 120 (number), 120, and the presence of glosses such as "tentywise" or "ten-count" in medieval texts showing that writers could not pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecimal
Hexadecimal (also known as base-16 or simply hex) is a Numeral system#Positional systems in detail, positional numeral system that represents numbers using a radix (base) of sixteen. Unlike the decimal system representing numbers using ten symbols, hexadecimal uses sixteen distinct symbols, most often the symbols "0"–"9" to represent values 0 to 9 and "A"–"F" to represent values from ten to fifteen. Software developers and system designers widely use hexadecimal numbers because they provide a convenient representation of binary code, binary-coded values. Each hexadecimal digit represents four bits (binary digits), also known as a nibble (or nybble). For example, an 8-bit byte is two hexadecimal digits and its value can be written as to in hexadecimal. In mathematics, a subscript is typically used to specify the base. For example, the decimal value would be expressed in hexadecimal as . In programming, several notations denote hexadecimal numbers, usually involving a prefi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positional Notation
Positional notation, also known as place-value notation, positional numeral system, or simply place value, usually denotes the extension to any radix, base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system (or decimal, decimal system). More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred (however, the values may be modified when combined). In modern positional systems, such as the decimal, decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string. The Babylonian Numerals, Babylonian numeral system, base 60, was the first positional sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
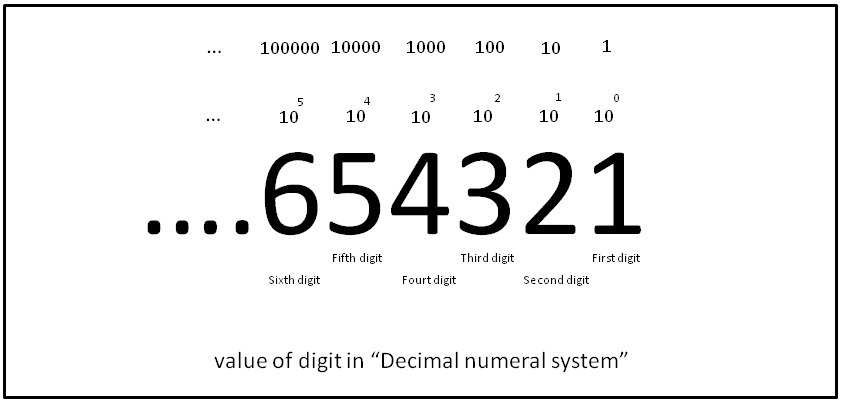
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminating Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Janji Language
Janji is a Kainji language of Nigeria. Numerals Janji has, or had, a duodecimal number system A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can .... References East Kainji languages Languages of Nigeria {{Kainji-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gbiri-Niragu Language
Gbiri-Niragu, also known as Gure-Kahugu, is a Kainji language of Nigeria. Speakers are shifting to Hausa. Tugbiri is the name of the language of the Gbiri people, and is spoken in and around the village of Gure in Lere LGA, southern Kaduna State. Niragu speakers live directly to the north of Tugbiri speakers. Numerals Gbiri-Niragu has, or had, a duodecimal number system A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The most basic examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can .... References East Kainji languages Languages of Nigeria {{Kainji-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, a population of more than 230 million, it is the List of African countries by population, most populous country in Africa, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, world's sixth-most populous country. Nigeria borders Niger in Niger–Nigeria border, the north, Chad in Chad–Nigeria border, the northeast, Cameroon in Cameroon–Nigeria border, the east, and Benin in Benin–Nigeria border, the west. Nigeria is a Federation, federal republic comprising 36 States of Nigeria, states and the Federal Capital Territory, Nigeria, Federal Capital Territory, where its capital, Abuja, is located. The List of Nigerian cities by population, largest city in Nigeria by population is Lagos, one of the largest List of largest cities, metr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piti Language
Piti (Pitti, Bishi, Bisi) is a minor Kainji language of Kaduna State, Nigeria Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, .... Bishi speakers live in at least 26 villages. Ngmgbang (Riban, Rigmgbang) was formerly listed as a dialect of Bishi, but is clearly a distinct although related language. It is spoken in a few villages in Kaduna State. References East Kainji languages Languages of Nigeria {{Kainji-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China China–Nepal border, to the north, and India India–Nepal border, to the south, east, and west, while it is narrowly separated from Bangladesh by the Siliguri Corridor, and from Bhutan by the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Sikkim. Nepal has a Geography of Nepal, diverse geography, including Terai, fertile plains, subalpine forested hills, and eight of the world's ten List of highest mountains#List, tallest mountains, including Mount Everest, the highest point on Earth. Kathmandu is the nation's capital and List of cities in Nepal, its largest city. Nepal is a multi-ethnic, multi-lingual, multi-religious, and multi-cultural state, with Nepali language, Nepali as the official language. The name "Nepal" is first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chepang Language
Chepang is a language spoken by approximately 59,000 people in South-Central Nepal. The people are known as Chepang. In 2003, Randy LaPolla proposed that the Chepang may be part of a larger " Rung" group. Another group who speaks Chepang, living across the Gandaki river, call themselves Bujheli. Phonology Consonants Phonetic Realizations The glottal stop is realized in some contexts, though usually not as a full closure and is instead presented as falling pitch, laryngealization, re-articulation, or by lengthening of the segment before. Some example of possible occurrences are listed below: * Syllable Initial ** Full closure �at the beginning of words — (ʔ / #__) ** Re-articulation at the beginning of words — ( Vowels Research suggests that Chepang may have had a three vowel system at one point in time. Those vowels being /i/ /u/ and /ə/, this is uncommon for a three vowel system as commonly they consist of /a/ /i/ and /u/ as seen in Classical Arabic, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |