|
Ioxynil
Ioxynil is a Postemergence, post-emergent selective nitrile herbicide. It is used in Australia, New Zealand and Japan to control broadleaf weeds via the inhibition of photosynthesis. It is used notably on onion crops, among others, normally at 300–900 g/Ha. It was introduced in 1966. The supply of ioxynil is decreasing, as of 2019 but the herbicide remains effective. History Ioxynil and bromoxynil (along with 2,4-DB and MCPB) were patented by Louis Wain as joint-head of the chemistry department at Wye College, and coincidentally discovered independently by May & Baker in England screening spare nitriles for herbicide activity, and by Amchem Products Inc in America doing similar screening, all in 1963. Commercial prospects were promising, as cereals could tolerate large amounts, over 2 lbs/ac; even 4 lbs/ac only temporarily scorches. Wain theorised ioxynil and bromoxynil, the nitrile (-CN) group herbicides, because of the chemical similarity to a Nitro compound, nitro (NO2) grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ioxynil Octanoate
Ioxynil is a post-emergent selective nitrile herbicide. It is used in Australia, New Zealand and Japan to control broadleaf weeds via the inhibition of photosynthesis. It is used notably on onion crops, among others, normally at 300–900 g/Ha. It was introduced in 1966. The supply of ioxynil is decreasing, as of 2019 but the herbicide remains effective. History Ioxynil and bromoxynil (along with 2,4-DB and MCPB) were patented by Louis Wain as joint-head of the chemistry department at Wye College, and coincidentally discovered independently by May & Baker in England screening spare nitriles for herbicide activity, and by Amchem Products Inc in America doing similar screening, all in 1963. Commercial prospects were promising, as cereals could tolerate large amounts, over 2 lbs/ac; even 4 lbs/ac only temporarily scorches. Wain theorised ioxynil and bromoxynil, the nitrile (-CN) group herbicides, because of the chemical similarity to a nitro (NO2) group, and on their success, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoxynil Octanoate
Bromoxynil octanoate is a herbicide active ingredient, closely related to bromoxynil, ioxynil, and ioxynil octanoate. Bromoxynil controls broad leafed weeds in many crops, and is used in the USA, Europe and Australia, on crops, roadsides and turf. Bromoxynil octanoate in the environment has a half-life of about 10 days, and breaks down into harmless compounds. It breaks down much quicker than bromoxynil, ioxynil or chloroxynil, which all last about a month in aerobic soil. Bromoxynil octanoate acts by inhibiting photosynthesis at photosystem II, destroying cells, making it a Group C, (Aus), Group C3, (Global), or Group 6 (numeric) under the HRAC system. Weeds show symptoms after four to seven days of chlorotic leaves and desiccation Desiccation is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroxynil
Chloroxynil is a postemergent benzonitrile herbicide, used to control broad leaved weeds on cereal crops. It was manufactured by Rhone-Poulenc and May & Baker, and is now considered obsolete, though its usage may continue. Chloroxynil was developed as a variant of bromoxynil, which is identical except for bromines replacing chloroxynil's chlorines. A 1972 study found chloroxynil less injurious to alfalfa and red clover, but also less potent at controlling broadleaf weeds. Chloroxynil's MoA inhibits electron transfer in the photosystem II receptor. Its HRAC group is Group C, (Australia) C3 (global) or 6 (numeric). Genetic engineering Chloroxynil can greatly improve the speed and efficiency of agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plants. Compared to the control, acetosyringone was 6 times faster, and chloroxynil was 60 times faster. Chloroxynil's related herbicides were also tested: bromoxynil was 18 times faster than control but caused plant damage, and ioxynil showed no s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromoxynil
Bromoxynil is an organic compound with the formula HOBr2C6H2CN. It is classified as a nitrile herbicide, and as such sold under many trade names. It is a white solid. It works by inhibiting photosynthesis. It is moderately toxic to mammals. It is used in Australia, New Zealand, and the USA, which used 614,000 lbs of it in 1974. Production and use It is produced by bromination of 4-hydroxybenzonitrile. It is a post-emergence to control annual broadleaved weeds.Franz Müller and Arnold P. Applebyki "Weed Control, 2. Individual Herbicides" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2010 Degradation Bromoxynil decomposes with a half life of approximately two weeks in soil. Persistence increases in soils with elevated clay or organic matter content, suggesting the compound has somewhat limited bioavailability to microorganisms in these environments. Under aerobic conditions in soils or pure cultures, products of bromoxynil degradation often retain the original bromine gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transthyretin
Transthyretin (TTR or TBPA) is a transport protein in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid that transports the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4) and retinol to the liver. This is how transthyretin gained its name: ''transports thyroxine and retinol''. The liver secretes TTR into the blood, and the choroid plexus secretes TTR into the cerebrospinal fluid. TTR was originally called prealbumin (or thyroxine-binding prealbumin) because it migrated faster than albumin on electrophoresis gels. Prealbumin was felt to be a misleading name, it is not a synthetic precursor of albumin. The alternative name TTR was proposed by DeWitt Goodman in 1981. Human transthyretrin protein is encoded by the ''TTR'' gene, which is located on the long arm of chromosome 18, in cytogenetic band 18q12.1. Binding affinities It functions in concert with two other thyroid hormone-binding proteins in the serum: In cerebrospinal fluid TTR is the primary carrier of T4. TTR also acts as a carrier of retinol ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphnia
''Daphnia'' is a genus of small planktonic crustaceans, in length. ''Daphnia'' are members of the Order (biology), order Anomopoda, and are one of the several small aquatic crustaceans commonly called water fleas because their Saltation (gait), saltatory swimming style resembles the movements of fleas. ''Daphnia'' spp. live in various aquatic environments ranging from acidic swamps to Fresh water, freshwater lakes and ponds. The two most commonly found species of ''Daphnia'' are ''Daphnia pulex, D. pulex'' (small and most common) and ''Daphnia magna, D. magna'' (large). They are often associated with a related genus in the order Cladocera: ''Moina'', which is in the Moinidae group instead of the Daphniidae, and is much smaller than ''D. pulex'' (roughly half the maximum length). Appearance and characteristics The body of a ''Daphnia'' species is usually long, and is divided into Segmentation (biology), segments, although this division is not visible. The hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide Resistance Classification
The Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) classifies herbicides by their mode of action (MoA) to provide a uniform way for farmers and growers to identify the agents they use and better manage pesticide resistance around the world. It is run by CropLife International in conjunction with the Weed Science Society of America (WSSA). Resistance overview A weed that develops resistance to one herbicide typically has resistance to other herbicides with the same mode of action (MoA), so herbicides with different MoAs, or different resistance groups, are needed. Preventative weed resistance management rotates herbicide types to prevent selective breeding of resistance to the same mode of action. By rotating MoAs, successive generations gain no advantage from any resistant mutations of the last generation. ''Cross-resistant'' and ''multiply resistant'' weeds resist multiple MoAs, and are particularly difficult to control. There is limited evidence of resistance undoing other resis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Group 6 Herbicides
Group 6 is a category of the HRAC classification system by herbicidal mode of action In pharmacology and biochemistry, mode of action (MoA) describes a functional or anatomical change, resulting from the exposure of a living organism to a substance. In comparison, a mechanism of action (MOA) describes such changes at the molecul .... It is equivalent to Group C3 (Global), and a part of Group C (Australia). Herbicides by numeric HRAC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
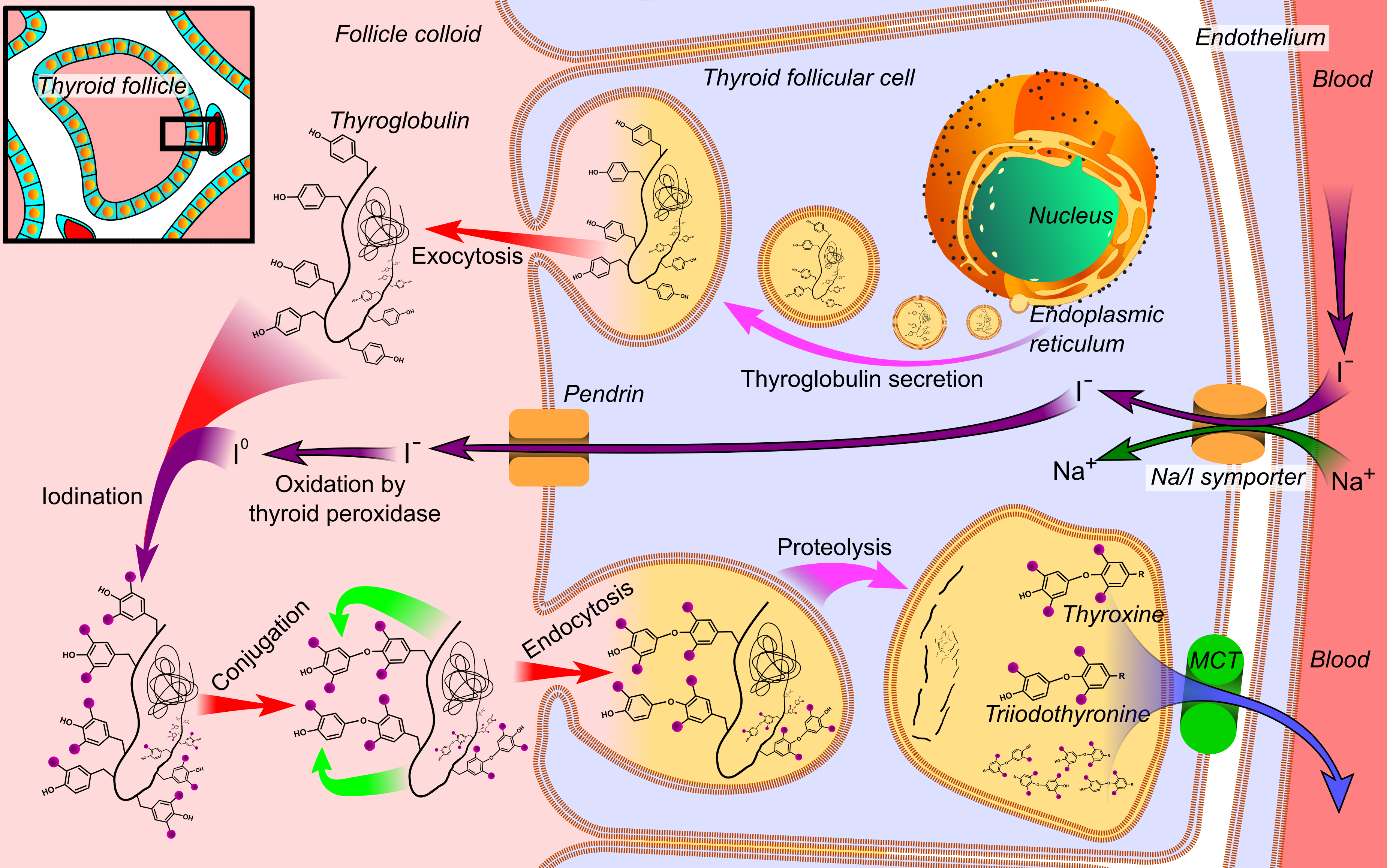
Thyroid Hormone
File:Thyroid_system.svg, upright=1.5, The thyroid system of the thyroid hormones triiodothyronine, T3 and T4 rect 376 268 820 433 Thyroid-stimulating hormone rect 411 200 849 266 Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rect 297 168 502 200 Hypothalamus rect 66 216 386 256 Anterior pituitary, Anterior pituitary gland rect 66 332 342 374 Negative feedback rect 308 436 510 475 Thyroid, Thyroid gland rect 256 539 563 635 Thyroid hormones rect 357 827 569 856 Catecholamine rect 399 716 591 750 Metabolism desc bottom-left Thyroid hormones are two hormones produced and released by the thyroid gland, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). They are tyrosine-based hormones that are primarily responsible for regulation of metabolism. T3 and T4 are partially composed of iodine, derived from food. A deficiency of iodine leads to decreased production of T3 and T4, enlarges the thyroid, thyroid tissue and will cause the disease known as simple goitre. The major form of thyroid hormone in the blood ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotic
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. The term "necrosis" came about in the mid-19th century and is commonly attributed to German pathologist Rudolf Virchow, who is often regarded as one of the founders of modern pathology. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated digestion of cell components. In contrast, ''apoptosis'' is a naturally occurring programmed and targeted cause of cellular death. While apoptosis often provides beneficial effects to the organism, necrosis is almost always detrimental and can be fatal. Cellular death due to necrosis does not follow the apoptotic signal transduction pathway, but rather various receptors are activated and result in the loss of cell membrane integrity and an uncontrolled release of products of cell death into the extracellular space. This initiates an inflammatory response in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
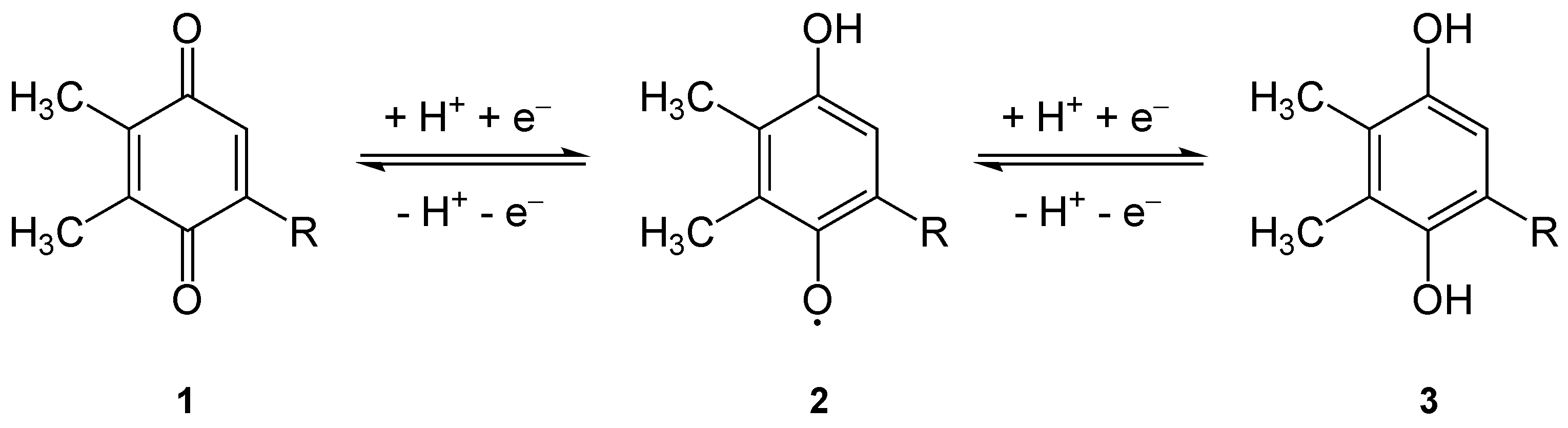
Plastoquinone
Plastoquinone (PQ) is a terpenoid-quinone ( meroterpenoid) molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. The most common form of plastoquinone, known as PQ-A or PQ-9, is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4- benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units. There are other forms of plastoquinone, such as ones with shorter side chains like PQ-3 (which has 3 isoprenyl side units instead of 9) as well as analogs such as PQ-B, PQ-C, and PQ-D, which differ in their side chains. The benzoquinone and isoprenyl units are both nonpolar, anchoring the molecule within the inner section of a lipid bilayer, where the hydrophobic tails are usually found. Plastoquinones are very structurally similar to ubiquinone, or coenzyme Q10, differing by the length of the isoprenyl side chain, replacement of the methoxy groups with methyl groups, and removal of the methyl group in the 2 position on the quinone. Like ubiquinone, it can come in severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |