|
Invitational Rhetoric
Invitational rhetoric is a theory of rhetoric developed by Sonja K. Foss and Cindy L. Griffin in 1995. Invitational rhetoric is defined as “an invitation to understanding as a means to create a relationship rooted in equality, immanent value, and self-determination.” The theory challenges the traditional definition of rhetoric as persuasion—the effort to change others—because the objective of invitational rhetoric is not to persuade but to gain an understanding of the perspectives of others. Invitational rhetoric is part of an effort to formulate alternative conceptions of rhetoric that are not “exploitative and oppressive but that contribute to a more respectful way of being a rhetor in the world.” A major assumption behind invitational rhetoric is that “the communication discipline, through its traditional constructs and theories, participates in this culture of domination,” and invitational rhetoric constitutes an effort to “contribute to the creation of mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetoric
Rhetoric is the art of persuasion. It is one of the three ancient arts of discourse ( trivium) along with grammar and logic/ dialectic. As an academic discipline within the humanities, rhetoric aims to study the techniques that speakers or writers use to inform, persuade, and motivate their audiences. Rhetoric also provides heuristics for understanding, discovering, and developing arguments for particular situations. Aristotle defined rhetoric as "the faculty of observing in any given case the available means of persuasion", and since mastery of the art was necessary for victory in a case at law, for passage of proposals in the assembly, or for fame as a speaker in civic ceremonies, he called it "a combination of the science of logic and of the ethical branch of politics". Aristotle also identified three persuasive audience appeals: logos, pathos, and ethos. The five canons of rhetoric, or phases of developing a persuasive speech, were first codified in classical Rome: i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intellect
Intellect is a faculty of the human mind that enables reasoning, abstraction, conceptualization, and judgment. It enables the discernment of truth and falsehood, as well as higher-order thinking beyond immediate perception. Intellect is distinct from ''intelligence'', which refers to the general ability to learn, adapt, and solve problems, whereas ''intellect'' concerns the application of reason to abstract or philosophical thought. In philosophy, intellect () has often been contrasted with , a term referring to the faculty of direct intuitive knowledge. While intellect engages in discursive reasoning, breaking down concepts into logical sequences, ''nous'' is considered a higher cognitive faculty that allows for direct perception of truth, especially in Platonism and Neoplatonism. Aristotle distinguished between the active intellect (), which abstracts universal concepts, and the passive intellect, which receives sensory input. During late antiquity and the Middle Ages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biologism
Biological determinism, also known as genetic determinism, is the belief that human behaviour is directly controlled by an individual's Genetics, genes or some component of their physiology, generally at the expense of the role of the environment, whether in embryonic development or in learning. Genetic reductionism is a similar concept, but it is distinct from genetic determinism in that the former refers to the level of understanding, while the latter refers to the supposed causal role of genes. Biological determinism has been associated with movements in science and society including eugenics, scientific racism, and the debates around the heritability of IQ, the basis of Biology and sexual orientation, sexual orientation, and evolutionary foundations of cooperation in sociobiology. In 1892, the German evolutionary biologist August Weismann proposed in his germ plasm theory that heritable information is transmitted only via germ cells, which he thought contained determinants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theory
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, and research. Theories can be scientific, falling within the realm of empirical and testable knowledge, or they may belong to non-scientific disciplines, such as philosophy, art, or sociology. In some cases, theories may exist independently of any formal discipline. In modern science, the term "theory" refers to Scientific theory, scientific theories, a well-confirmed type of explanation of nature, made in a way Consistency, consistent with the scientific method, and fulfilling the Scientific theory#Characteristics of theories, criteria required by modern science. Such theories are described in such a way that scientific tests should be able to provide Empirical evidence, empirical support for it, or Empirical evidence, empirical contradi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialogic
Dialogic refers to the use of conversation or shared dialogue to explore the meaning of something. (This is as opposed to monologic which refers to one entity with all the information simply giving it to others without exploration and clarification of meaning through discussion.) The word "dialogic" relates to or is characterized by dialogue and its use. A dialogic is communication presented in the form of dialogue. Dialogic processes refer to implied meaning in words uttered by a speaker and interpreted by a listener. Dialogic works carry on a continual dialogue that includes interaction with previous information presented. The term is used to describe concepts in literary theory and analysis as well as in philosophy. Along with ''dialogism'', the term can refer to concepts used in the work of Russian philosopher Mikhail Bakhtin, especially the texts ''Problems of Dostoevsky's Poetics'' and '' The Dialogic Imagination: Four Essays by M.M. Bakhtin''. Overview Bakhtin contrasts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gender
Gender is the range of social, psychological, cultural, and behavioral aspects of being a man (or boy), woman (or girl), or third gender. Although gender often corresponds to sex, a transgender person may identify with a gender other than their sex assigned at birth. Most cultures use a gender binary, in which gender is divided into two categories, and people are considered part of one or the other;Kevin L. Nadal, ''The Sage Encyclopedia of Psychology and Gender'' (2017, ), p. 401: "Most cultures currently construct their societies based on the understanding of gender binary—the two gender categorizations (male and female). Such societies divide their population based on biological sex assigned to individuals at birth to begin the process of gender socialization." those who are outside these groups may fall under the umbrella term '' non-binary''. Some societies have ''third genders'' (and ''fourth genders'', etc.) such as the hijras of South Asia and two-spirit per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coercion
Coercion involves compelling a party to act in an involuntary manner through the use of threats, including threats to use force against that party. It involves a set of forceful actions which violate the free will of an individual in order to induce a desired response. These actions may include extortion, blackmail, or even torture and sexual assault. Common-law systems codify the act of violating a law while under coercion as a duress crime. Coercion used as leverage may force victims to act in a way contrary to their own interests. Coercion can involve not only the infliction of bodily harm, but also psychological abuse (the latter intended to enhance the perceived credibility of the threat). The threat of further harm may also lead to the acquiescence of the person being coerced. The concepts of coercion and persuasion are similar, but various factors distinguish the two. These include the intent, the willingness to cause harm, the result of the interaction, and the opti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarchy
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of authority are primarily held by men. The term ''patriarchy'' is used both in anthropology to describe a family or clan controlled by the father or eldest male or group of males, and in feminist theory to describe a broader social structure in which men as a group dominance hierarchy, dominate society. Sociobiologists compare human gender roles to sexed behavior in other primates and argue that gender inequality originates from genetic and reproductive differences between men and women. Patriarchal ideology explains and rationalizes patriarchy by attributing gender inequality to inherent Gender essentialism, natural differences between men and women, divine commandment, or other fixed structures. Social constructionists sociologists tend to disagree with biological explanations of patriarchy and contend that socialization processes are primarily responsible for establishing gender roles, they further argue that gender roles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Elimination
Reductive elimination is an elementary step in organometallic chemistry in which the oxidation state of the metal center decreases while forming a new covalent bond between two ligands. It is the microscopic reverse of oxidative addition, and is often the product-forming step in many catalytic processes. Since oxidative addition and reductive elimination are reverse reactions, the same mechanisms apply for both processes, and the product equilibrium depends on the thermodynamics of both directions. General information Reductive elimination is often seen in higher oxidation states, and can involve a two-electron change at a single metal center (mononuclear) or a one-electron change at each of two metal centers (binuclear, dinuclear, or bimetallic). For mononuclear reductive elimination, the oxidation state of the metal decreases by two, while the d-electron count of the metal increases by two. This pathway is common for d8 metals Ni(II), Pd(II), and Au(III) and d6 metals Pt(I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agency (sociology)
In social science, agency is the capacity of individuals to have the power and resources to fulfill their potential. Social structure consists of those factors of influence (such as social class, religion, gender, ethnicity, ability, customs, etc.) that determine or limit agents and their decisions. The influences from structure and agency are debated—it is unclear to what extent a person's actions are constrained by social systems. One's agency is one's independent capability or ability to act on one's will. This ability is affected by the cognitive belief structure which one has formed through one's experiences, and the perceptions held by the society and the individual, of the structures and circumstances of the environment one is in and the position one is born into. Disagreement on the extent of one's agency often causes conflict between parties, e.g. parents and children. History The overall concept of agency has existed since the Enlightenment where there was debat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democracy
Democracy (from , ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which political power is vested in the people or the population of a state. Under a minimalist definition of democracy, rulers are elected through competitive Election, elections while more expansive or maximalist definitions link democracy to guarantees of civil liberties and human rights in addition to competitive elections. In a direct democracy, the people have the direct authority to Deliberation, deliberate and decide legislation. In a representative democracy, the people choose governing officials through elections to do so. The definition of "the people" and the ways authority is shared among them or delegated by them have changed over time and at varying rates in different countries. Features of democracy oftentimes include freedom of assembly, freedom of association, association, personal property, freedom of religion and freedom of speech, speech, citizenship, consent of the governe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
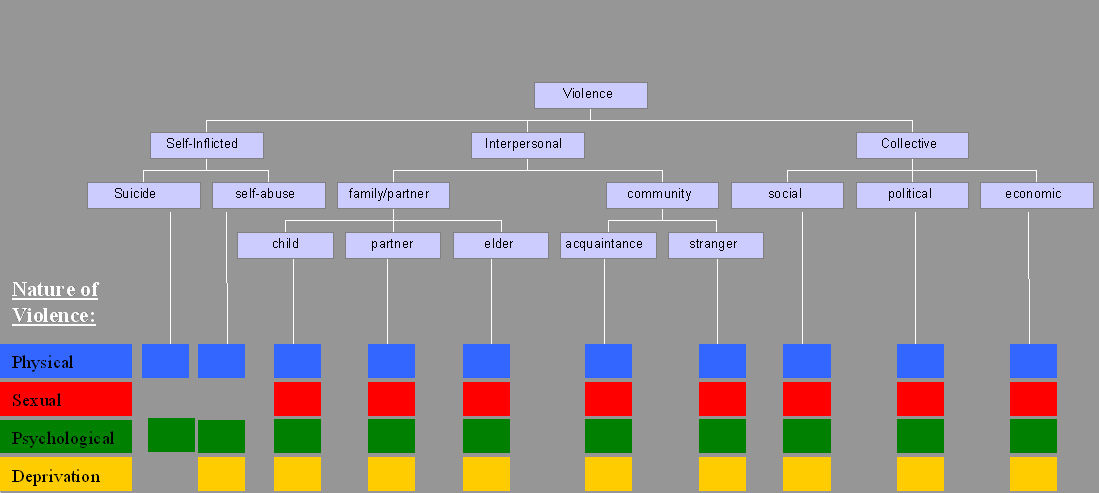
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |