|
Invertin
β-Fructofuranosidase is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis (breakdown) of the table sugar sucrose into fructose and glucose. Sucrose is a fructoside. Alternative names for β-fructofuranosidase include invertase, saccharase, glucosucrase, β-fructosidase, invertin, fructosylinvertase, alkaline invertase, and acid invertase. The resulting mixture of fructose and glucose is called inverted sugar syrup. Related to invertases are sucrases. Invertases and sucrases hydrolyze sucrose to give the same mixture of glucose and fructose. Invertase is a glycoprotein that hydrolyses (cleaves) the non-reducing terminal β-fructofuranoside residues. Invertases cleave the O-C(fructose) bond, whereas the sucrases cleave the O-C(glucose) bond. Invertase cleaves the α-1,2-glycosidic bond of sucrose. For industrial use, invertase is usually derived from yeast. It is also synthesized by bees, which use it to make honey from nectar. The temperature optimum is 60 °C and a pH optimum is 4. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penicillium Chrysogenum
''Penicillium chrysogenum'' (formerly known as ''Penicillium notatum'') is a species of fungus in the genus ''Penicillium''. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes ''P. notatum'', ''P. meleagrinum,'' and ''P. cyaneofulvum.'' Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, '' P. rubens'', and not of ''P. notatum.'' It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of ''P. chrysogenum'' include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin. Like the many other species of the genus ''Pen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC 3
EC3 can refer to: People * Ethan Carter III (EC3) (born 1983), American professional wrestler Places * EC3, a district in the London EC postcode area Groups, organizations, companies * European Cybercrime Centre * EarthCheck, formerly EC3 Global; international tourism advisory group Transportation * BJEV ''EC3'', a Chinese electric vehicle * KUR ''EC3 class'', a class of steam locomotive * EC-3 radar, Italian WWII radar Other uses * Dolby Digital Plus, also known as EC-3 * Hydrolase enzymes (EC 3); see List of EC numbers (EC 3) See also * ECCC (other) {{Letter-NumberCombDisambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
β-propeller
In structural biology, a beta-propeller (β-propeller) is a type of all-β protein fold, all-β protein architecture characterized by 4 to 8 highly symmetrical blade-shaped beta sheets arranged toroidally around a central axis. Together the beta-sheets form a funnel-like active site. Structure Each beta-sheet typically has four Antiparallel (biochemistry), anti-parallel beta sheet, β-strands arranged in the beta-zigzag motif. The strands are twisted so that the first and fourth strands are almost perpendicular to each other. There are five classes of beta-propellers, each arrangement being a highly symmetrical structure with 4–8 beta sheets, all of which generally form a central tunnel that yields pseudo-symmetric axes. While, the protein's official active site for ligand-binding is formed at one end of the central tunnel by loops between individual beta-strands, protein-protein interactions can occur at multiple areas around the domain. Depending on the packing and tilt of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Tertiary Structure
Protein tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of a protein. The tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain "backbone" with one or more protein secondary structures, the protein domains. Amino acid side chains and the backbone may interact and bond in a number of ways. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. The protein tertiary structure is defined by its atomic coordinates. These coordinates may refer either to a protein domain or to the entire tertiary structure. A number of these structures may bind to each other, forming a quaternary structure. History The science of the tertiary structure of proteins has progressed from one of hypothesis to one of detailed definition. Although Emil Fischer had suggested proteins were made of polypeptide chains and amino acid side chains, it was Dorothy Maud Wrinch who incorporated geometry into the prediction of protein structures. Wrinch demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (H-bond) is a specific type of molecular interaction that exhibits partial covalent character and cannot be described as a purely electrostatic force. It occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom, Covalent bond, covalently bonded to a more Electronegativity, electronegative donor atom or group (Dn), interacts with another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Unlike simple Dipole–dipole attraction, dipole–dipole interactions, hydrogen bonding arises from charge transfer (nB → σ*AH), Atomic orbital, orbital interactions, and quantum mechanical Delocalized electron, delocalization, making it a resonance-assisted interaction rather than a mere electrostatic attraction. The general notation for hydrogen bonding is Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line represents a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are nitrogen (N), oxyg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-competitive Inhibition
Non-competitive inhibition is a type of enzyme inhibition where the inhibitor reduces the activity of the enzyme and binds equally well to the enzyme regardless of whether it has already bound the substrate. This is unlike competitive inhibition, where binding affinity for the substrate in the enzyme is decreased in the presence of an inhibitor. The inhibitor may bind to the enzyme regardless of whether the substrate has already been bound, but if it has a higher affinity for binding the enzyme in one state or the other, it is called a mixed inhibitor. History During his years working as a physician Leonor Michaelis and a friend Peter Rona built a compact lab, in the hospital, and over the course of five years – Michaelis successfully became published over 100 times. During his research in the hospital, he was the first to view the different types of inhibition; specifically using fructose and glucose as inhibitors of maltase activity. Maltase breaks maltose into two units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea
Urea, also called carbamide (because it is a diamide of carbonic acid), is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two Amine, amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the cellular metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. ''Urea'' is Neo-Latin, , , itself from Proto-Indo-European ''*h₂worsom''. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor base (chemistry), alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably metabolic waste#Nitrogen wastes, nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylose Isomerase
In enzymology, a xylose isomerase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the interconversion of D-xylose and D-xylulose. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically those intramolecular oxidoreductases interconverting aldoses and ketoses. The isomerase has now been observed in nearly a hundred species of bacteria. Xylose-isomerases are also commonly called glucose isomerase or fructose isomerases due to their ability to interconvert glucose and fructose. The systematic name of this enzyme class is α-D-xylopyranose aldose-ketose-isomerase. Other names in common use include D-xylose isomerase, D-xylose ketoisomerase, and D-xylose ketol-isomerase. History The activity of D-xylose isomerase was first observed by Mitsuhashi and Lampen in 1953 in the bacterium ''Lactobacillus pentosus''. It has also been successfully produced in transformed ''E.coli''. In 1957, the D-xylose isomerase activity on D-glucose conversion to D-fructose was noted by Kooi and Marshall. It is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudomonas
''Pseudomonas'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria belonging to the family Pseudomonadaceae in the class Gammaproteobacteria. The 348 members of the genus demonstrate a great deal of metabolic diversity and consequently are able to colonize a wide range of niches and hosts. Their ease of culture ''in vitro'' and availability of an increasing number of ''Pseudomonas'' strain genome sequences has made the genus an excellent focus for scientific research; the best studied species include '' P. aeruginosa'' in its role as an opportunistic human pathogen, the plant pathogen '' P. syringae'', the soil bacterium '' P. putida'', and the plant growth-promoting '' P. fluorescens, P. lini, P. migulae'', and '' P. graminis''. Because of their widespread occurrence in water and plant seeds such as dicots, the pseudomonads were observed early in the history of microbiology. The generic name ''Pseudomonas'' created for these organisms was defined in rather vague terms by Walter Migula i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
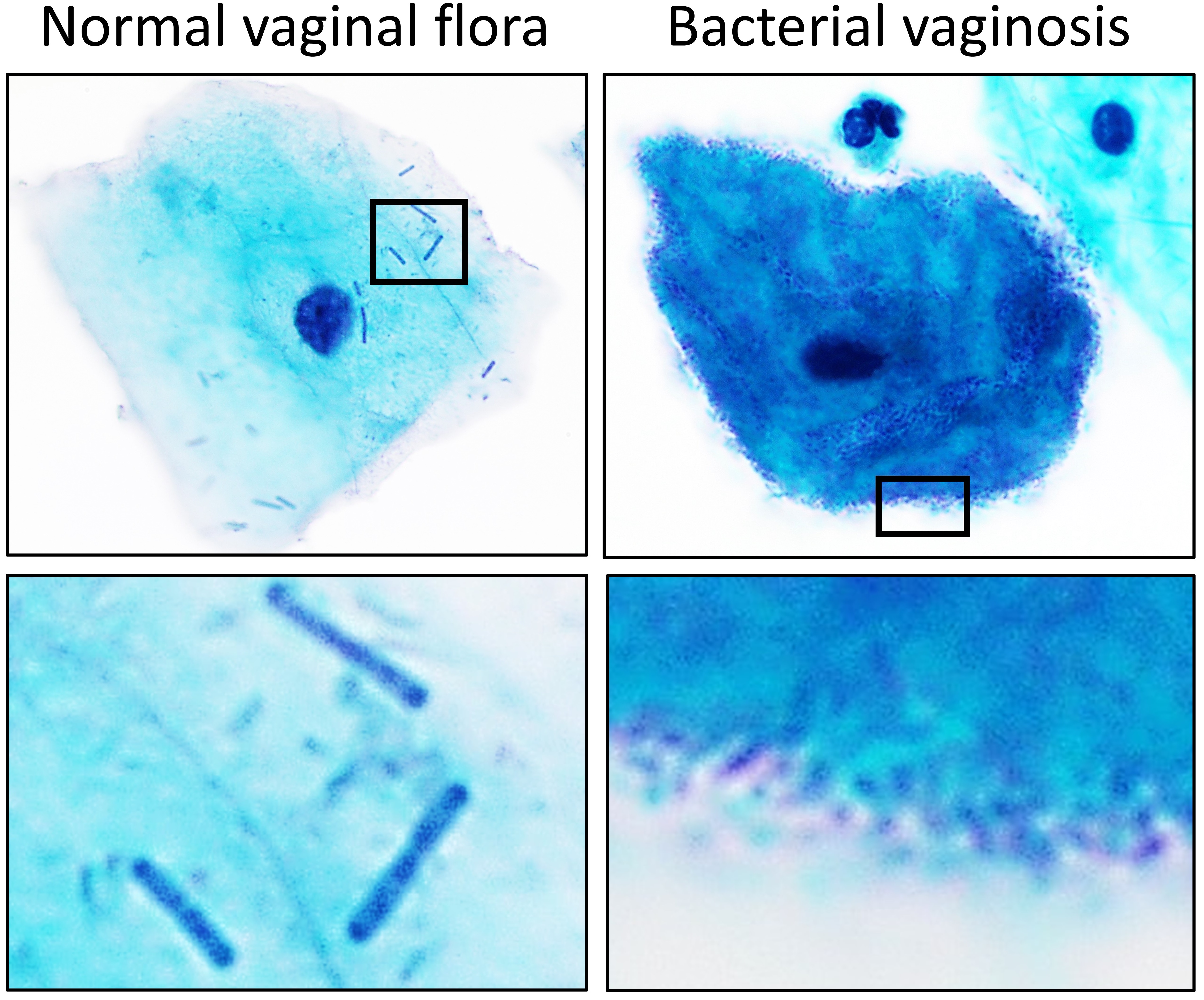
Lactobacillus
''Lactobacillus'' is a genus of gram-positive, aerotolerant anaerobes or microaerophilic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming bacteria. Until 2020, the genus ''Lactobacillus'' comprised over 260 phylogenetically, ecologically, and metabolically diverse species; a taxonomic revision of the genus assigned lactobacilli to 25 genera (see below). ''Lactobacillus'' species constitute a significant component of the human and animal microbiota at a number of body sites, such as the digestive system and the female genital system. In women of European ancestry, ''Lactobacillus'' species are normally a major part of the vaginal microbiota. ''Lactobacillus'' forms biofilms in the vaginal and gut microbiota, allowing them to persist in harsh environmental conditions and maintain ample populations. ''Lactobacillus'' exhibits a mutualistic relationship with the human body, as it protects the host against potential invasions by pathogens, and in turn, the host provides a source of nutrients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |