|
Intervertebral Foramina
The intervertebral foramen (also neural foramen) (often abbreviated as IV foramen or IVF) is an opening between (the intervertebral notches of) two pedicles (one above and one below) of adjacent vertebra in the articulated spine. Each intervertebral foramen gives passage to a spinal nerve and spinal blood vessels, and lodges a posterior (dorsal) root ganglion. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina. Anatomy Structure In the thoracic region and lumbar region, each vertebral foramen is additionally bounded anteriorly by (the inferior portion of) the body of vertebra (particularly in the thoracic region) and adjacent intervertebral disc (particularly in the lumbar region). In the cervical region, a small part of the body of vertebra inferior to the intervertebral disc also forms the anterior boundary of the IVF (due to the fact that the junction of the pedicle with the body of vertebra is situated somewhat more inferiorly on the body). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacrum
The sacrum (: sacra or sacrums), in human anatomy, is a triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of the sacral vertebrae (S1S5) between ages 18 and 30. The sacrum situates at the upper, back part of the pelvic cavity, between the two wings of the pelvis. It forms joints with four other bones. The two projections at the sides of the sacrum are called the alae (wings), and articulate with the ilium at the L-shaped sacroiliac joints. The upper part of the sacrum connects with the last lumbar vertebra (L5), and its lower part with the coccyx (tailbone) via the sacral and coccygeal cornua. The sacrum has three different surfaces which are shaped to accommodate surrounding pelvic structures. Overall, it is concave (curved upon itself). The base of the sacrum, the broadest and uppermost part, is tilted forward as the sacral promontory internally. The central part is curved outward toward the posterior, allowing greater room for the pelvic cavity. In a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
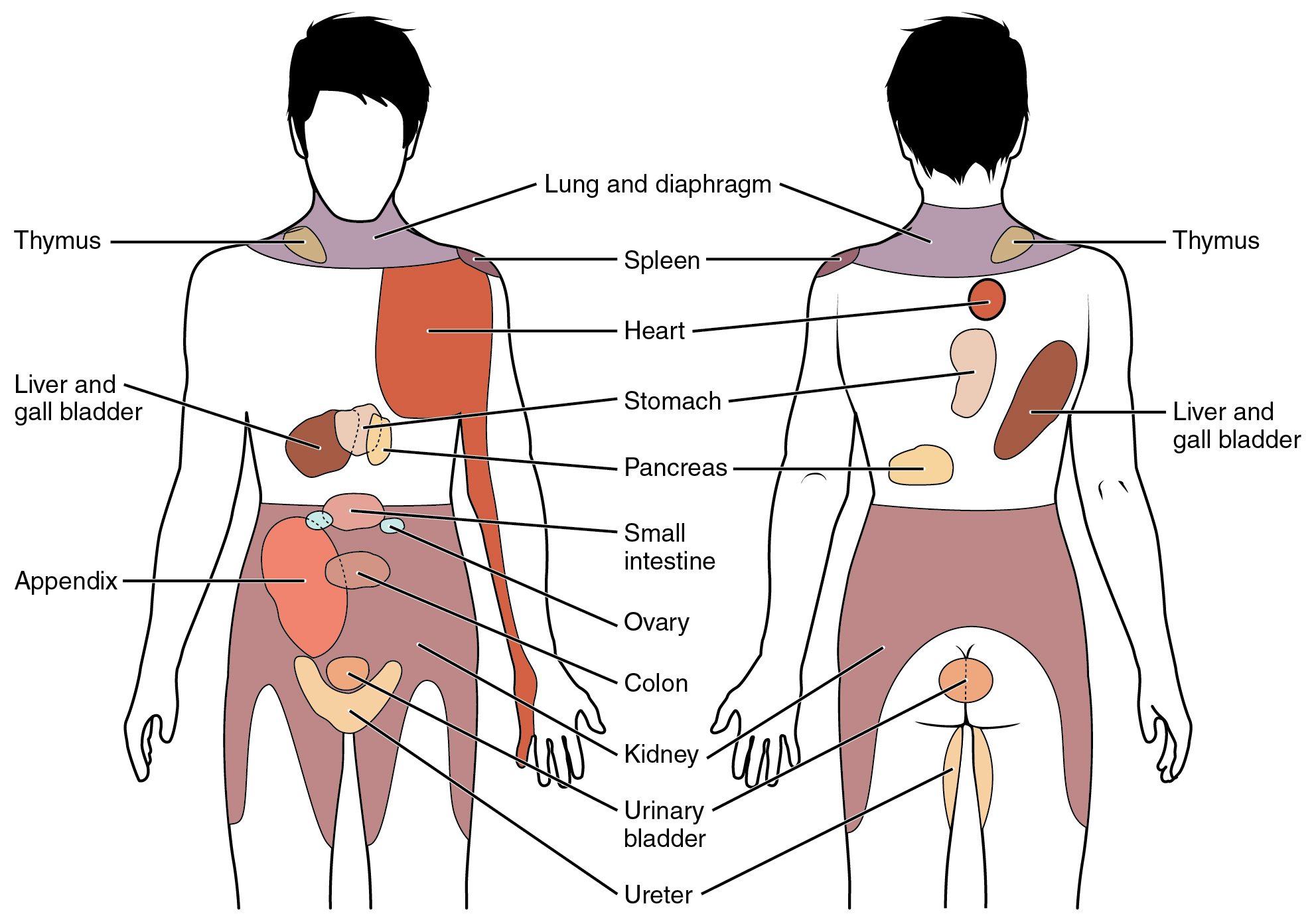
Lymphatic Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelium, endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillary, capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermatome (anatomy)
A dermatome is an area of skin that is mainly supplied by afferent nerve fibres from the dorsal root of any given spinal nerve. There are 8 cervical nerves (C1 being an exception with no dermatome), 12 thoracic nerves, 5 lumbar nerves and 5 sacral nerves. Each of these nerves relays sensation (including pain) from a particular region of skin to the brain. The term is also used to refer to a part of an embryonic somite. Along the thorax and abdomen, the dermatomes are like a stack of discs forming a human, each supplied by a different spinal nerve. Along the arms and the legs, the pattern is different: the dermatomes run longitudinally along the limbs. Although the general pattern is similar in all people, the precise areas of innervation are as unique to an individual as fingerprints. An area of skin innervated by a single nerve is called a peripheral nerve field. The word ''dermatome'' is formed from Ancient Greek 'skin, hide' and 'cut'. Clinical significance A derma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Spinal Nerve 4
Cervical spinal nerve 4, also called C4, is a spinal nerve of the cervical segment. It originates from the spinal cord above the 4th cervical vertebra (C4). It contributes nerve fibers to the phrenic nerve, the motor nerve to the thoracoabdominal diaphragm. It also provides motor nerves for the longus capitis, longus colli, anterior scalene, middle scalene, and levator scapulae muscles. C4 contributes some sensory fibers to the supraclavicular nerves, responsible for sensation from the skin above the clavicle. C4 and C5 are the areas that see the highest amount of cervical spine trauma. , Table 64, page 66 Gallery [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nape
The nape is the back of the neck. In technical anatomical/medical terminology, the nape is also called the nucha (from the Medieval Latin rendering of the Arabic , ). The corresponding adjective is ''nuchal'', as in the term ''nuchal rigidity'' for neck stiffness. In many mammals, the nape bears a loose, non-sensitive area of skin, known as the scruff, by which a mother carries her young by her teeth, temporarily immobilizing it during transport. In the mating of cats, the male will grip the female's scruff with his teeth to help immobilize her during the act, a form of pinch-induced behavioral inhibition. Cultural connotations In traditional Japanese culture, the was one of the few areas of the body (other than face and hands) left uncovered by women's attire. The nape of a woman's neck held a strong attraction for many Japanese men (see ). In Egyptian and Lebanese culture, slapping the nape is considered a gesture of utter humiliation. References External links * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projectional Radiograph
Projectional radiography, also known as conventional radiography, is a form of radiography and medical imaging that produces two-dimensional images by X-ray radiation. The image acquisition is generally performed by radiographers, and the images are often examined by radiologists. Both the procedure and any resultant images are often simply called 'X-ray'. Plain radiography or roentgenography generally refers to projectional radiography (without the use of more advanced techniques such as CT scan, computed tomography that can generate 3D-images). ''Plain radiography'' can also refer to radiography without a radiocontrast agent or radiography that generates single static images, as contrasted to fluoroscopy, which are technically also projectional. Equipment X-ray generator Projectional radiographs generally use X-rays created by X-ray generators, which generate X-rays from X-ray tubes. Grid An anti-scatter grid may be placed between the patient and the detector to reduce the q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Disc Herniation
A disc herniation or spinal disc herniation is an injury to the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae, usually caused by excessive strain or trauma to the spine. It may result in back pain, pain or sensation in different parts of the body, and physical disability. The most conclusive diagnostic tool for disc herniation is MRI, and treatments may range from painkillers to surgery. Protection from disc herniation is best provided by core strength and an awareness of body mechanics including good posture. When a tear in the outer, fibrous ring of an intervertebral disc allows the soft, central portion to bulge out beyond the damaged outer rings, the disc is said to be herniated. Disc herniation is frequently associated with age-related degeneration of the outer ring, known as the '' annulus fibrosus'', but is normally triggered by trauma or straining by lifting or twisting. Tears are almost always posterolateral (on the back sides) owing to relative narrowness of the post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, which may be called a tumour or tumor.'' ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, such as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word neoplasm is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthritic
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, swelling, and decreased range of motion of the affected joints. In certain types of arthritis, other organs such as the skin are also affected. Onset can be gradual or sudden. There are several types of arthritis. The most common forms are osteoarthritis (most commonly seen in weightbearing joints) and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis usually occurs as an individual ages and often affects the hips, knees, shoulders, and fingers. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that often affects the hands and feet. Other types of arthritis include gout, lupus, and septic arthritis. These are inflammatory based types of rheumatic disease. Early treatment for arthritis commonly includes resting the affected joint and conservative measures such as heating or icing. Weight loss and exercise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transforaminal Ligaments
Transforaminal ligaments are inconstant ligaments that extend through an intervertebral foramen. They are thought to protect the adjacent spinal nerve A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ... and vessels. The ligaments are not widely known and were once considered anomalous; there are no widely accepted criteria for their identification and classification. They were once postulated to be a cause of spinal nerve entrapment (as they may occupy a significant share of the lumen of a foramen), however, at present, their role in the radicular pain has is unclear. Anatomy There are five types of transforaminal ligaments: * The superior corporotransverse ligament attaches at the posterolateral aspect of the body of the vertebra, and at the accessory process of the transverse pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural Space
In anatomy, the epidural space is the potential space between the dura mater and vertebrae ( spine). The anatomy term "epidural space" has its origin in the Ancient Greek language; , "on, upon" + dura mater also known as "epidural cavity", "extradural space" or "peridural space". In humans the epidural space contains lymphatics, spinal nerve roots, loose connective tissue, adipose tissue, small arteries, dural venous sinuses and a network of internal vertebral venous plexuses. Cranial epidural space In the skull, the periosteal layer of the dura mater adheres to the inner surface of the skull bones while the meningeal layer lays over the arachnoid mater. Between them is the epidural space. The two layers of the dura mater separate at several places, with the meningeal layer projecting deeper into the brain parenchyma forming fibrous septa that compartmentalize the brain tissue. At these sites, the epidural space is wide enough to house the epidural venous sinuses. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |