|
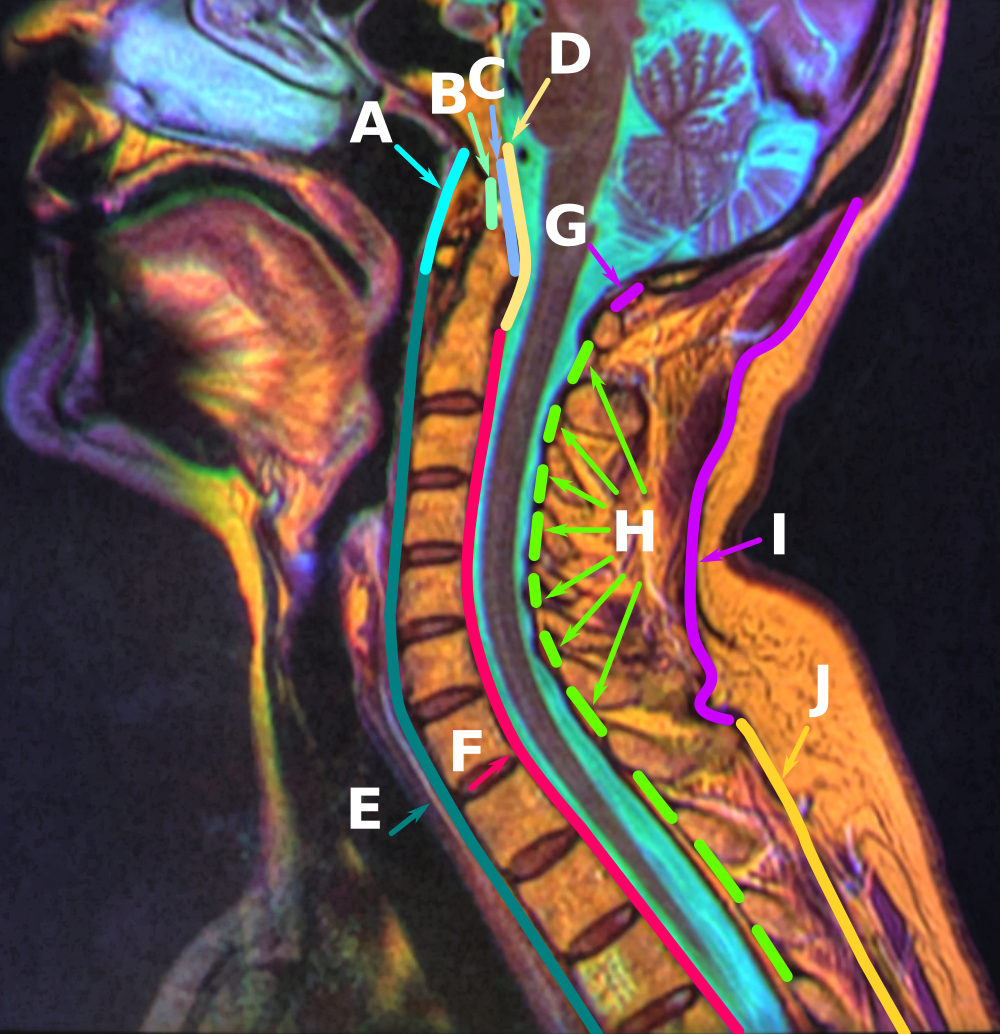
Transforaminal Ligaments
Transforaminal ligaments are inconstant ligaments that extend through an intervertebral foramen. They are thought to protect the adjacent spinal nerve A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each s ... and vessels. The ligaments are not widely known and were once considered anomalous; there are no widely accepted criteria for their identification and classification. They were once postulated to be a cause of spinal nerve entrapment (as they may occupy a significant share of the lumen of a foramen), however, at present, their role in the radicular pain has is unclear. Anatomy There are five types of transforaminal ligaments: * The superior corporotransverse ligament attaches at the posterolateral aspect of the body of the vertebra, and at the accessory process of the transverse pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligaments. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Comparative anatomy Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regeneration of periodontist ligament. The study of ligaments is known as . Humans Other ligame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intervertebral Foramen
The intervertebral foramen (also neural foramen) (often abbreviated as IV foramen or IVF) is an opening between (the intervertebral notches of) two pedicles (one above and one below) of adjacent vertebra in the articulated spine. Each intervertebral foramen gives passage to a spinal nerve and spinal blood vessels, and lodges a posterior (dorsal) root ganglion. Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae all have intervertebral foramina. Anatomy Structure In the thoracic region and lumbar region, each vertebral foramen is additionally bounded anteriorly by (the inferior portion of) the body of vertebra (particularly in the thoracic region) and adjacent intervertebral disc (particularly in the lumbar region). In the cervical region, a small part of the body of vertebra inferior to the intervertebral disc also forms the anterior boundary of the IVF (due to the fact that the junction of the pedicle with the body of vertebra is situated somewhat more inferiorly on the body). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Nerve
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries Motor neuron, motor, Sensory neuron, sensory, and Autonomic nervous system, autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical vertebrae, cervical, thoracic vertebrae, thoracic, lumbar vertebrae, lumbar, sacral vertebrae, sacral and coccygeal vertebrae, coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve root axon, fibers from its Dorsal root of spinal nerve, dorsal and Ventral root of spinal nerve, ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent nerve fiber, afferent sensory root and carries sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anulus Fibrosus Disci Intervertebralis
An intervertebral disc (British English), also spelled intervertebral disk (American English), lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold the vertebrae together, and to function as a shock absorber for the spine. Structure Intervertebral discs consist of an outer fibrous ring, the ''anulus (or annulus) fibrosus disci intervertebralis'', which surrounds an inner gel-like center, the ''nucleus pulposus''. The ''anulus fibrosus'' consists of several layers (laminae) of fibrocartilage made up of both type I and type II collagen. Type I is concentrated toward the edge of the ring, where it provides greater strength. The stiff laminae can withstand compressive forces. The fibrous intervertebral disc contains the ''nucleus pulposus'' and this helps to distribute pressure evenly across the disc. This prevents the development of stress conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligamentum Flavum
The ligamenta flava (: ligamentum flavum, Latin for ''yellow ligament'') are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. They help to preserve upright posture, preventing hyperflexion, and ensuring that the vertebral column straightens after flexion. Hypertrophy can cause spinal stenosis. They appear yellowish in colour due to their high elastic fibre content. Anatomy Each ligamentum flavum connects the laminae of two adjacent vertebrae. They attach to the anterior portion of the upper lamina above, and the posterior portion of the lower lamina below. They begin with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra, continuing down to the junction of the 5th lumbar vertebra and the sacrum. In the neck region the ligaments are thin, but broad and long; they are thicker in the thoracic region, and thickest in the lumbar region. They are thinnest between the atlas bone (C1) and the axis bone (C2), and may be absent in some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
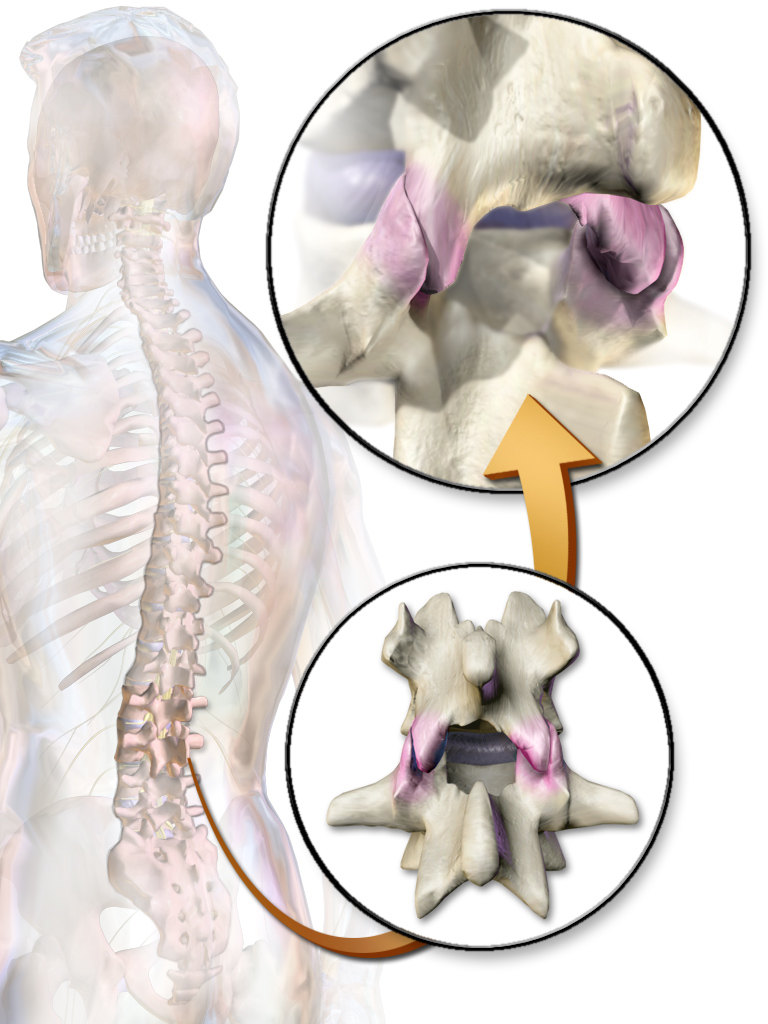
Zygapophyseal Joint
The facet joints (also zygapophysial joints, zygapophyseal, apophyseal, or Z-joints) are a set of synovial, plane joints between the articular processes of two adjacent vertebrae. There are two facet joints in each spinal motion segment and each facet joint is innervated by the recurrent meningeal nerves. Innervation Innervation to the facet joints vary between segments of the spinal, but they are generally innervated by medial branch nerves that come off the dorsal rami. It is thought that these nerves are for primary sensory input, though there is some evidence that they have some motor input local musculature. Within the cervical spine, most joints are innervated by the medial branch nerve (a branch of the dorsal rami) from the same levels. In other words, the facet joint between C4 and C5 vertebral segments is innervated by the C4 and C5 medial branch nerves. However, there are two exceptions: # The facet joint between C2 and C3 is innervated by the third occipital ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |