|
Interlaken Bailiwick
Interlaken (; lit.: ''between lakes'') is a Swiss town and municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Bern. It is an important and well-known tourist destination in the Bernese Oberland region of the Swiss Alps, and the main transport gateway to the mountains and lakes of that region. The town is located on flat alluvial land called Bödeli between two lakes, Brienz to the east and Thun to the west, and alongside the river Aare, which flows between them. Transport routes to the east and west alongside the lakes are complemented by a route southwards into the near mountain resorts and high mountains, e.g. the famous high Alpine peaks of Eiger, Mönch and Jungfrau, following upwards the Lütschine. Interlaken is the central town of a small agglomeration with the same name of 23,300 inhabitants. The official language of Interlaken is German,The official language in any municipality in German-speaking Switzerland is always German. In this co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlaken-Oberhasli (administrative District)
Interlaken-Oberhasli District in the Canton of Bern was created on 1 January 2010, uniting the former Interlaken District, Interlaken and Oberhasli districts. It is part of the Bernese Oberland, Oberland administrative region. It contains 28 municipalities with an area of and a population () of 48,763. Mergers * On 1 January 2014 the former municipality of Gadmen merged into the municipality of Innertkirchen.Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz accessed 13 December 2014 References {{coord, 46, 04, N, 7, 03, E, source:kolossus-eowiki, display=title Districts of the canton of Bern ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bödeli
Bödeli (lit.: the Swiss German diminutive term for ground) is the tongue of land between Lake Thun and Lake Brienz in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland. Lake Thun and Lake Brienz were not yet separate after the last ice age. The rivers Lütschine from the south and the Lombach from the north brought enough debris to cause a partitioning over the millennia. Now Lake Brienz has a water level about higher than Lake Thun and the river Aare flows from one lake to the other through the Bödeli. On the Bödeli are situated the villages and towns of Unterseen, Interlaken and Matten, which form a closed settlement area, and at the southern border are the villages of Wilderswil and Bönigen. From the south a hill range, the Ruuge, rises up. Bödelibahn Between 1870 and 1874 the Bödeli Railway (Bödelibahn) was constructed to link the steamer quay at Därligen Därligen () is a municipality in the Interlaken-Oberhasli administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernese German
Bernese German (Standard German: ''Berndeutsch'', ) is the dialect of High Alemannic German spoken in the Swiss plateau (Mittelland) part of the canton of Bern and in some neighbouring regions. A form of Bernese German is spoken by the Swiss Amish affiliation of the Old Order Amish in Adams County, Indiana, United States, as well as and other settlements in the US, primarily in Indiana. Varieties There is a lot of regional variation within Bernese German dialects. However, with the increasing importance of the big agglomeration of Bern, the variety of Bern is spreading out, levelling the old village dialects. Until the second half of the 20th century, there was a considerable range of sociolects in the city of Bern where four different groups could be distinguished: *The patrician Bernese German of the high society. It has neither l-vocalisation nor nd-velarisation, it does not employ the alveolar trill but the French uvular trill, and it has more French loanwords than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , ,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no #Conventions, defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others; ) is any of the Alemannic German, Alemannic dialects spoken in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland, and in some Alps, Alpine communities in Northern Italy bordering Switzerland. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg, which are closely associated to Switzerland's. Linguistically, Alemannic is divided into Low Alemannic German, Low, High Alemannic German, High and Highest Alemannic German, Highest Alemannic, varieties all of which are spoken both inside and outside Switzerland. The only exception within German-speaking Switzerland is the municipality of Samnaun, where a Bavarian language, Bavarian dialect is spoken. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alemanni ("all men"). Distribution Alemannic dialects are spoken by approximately ten million people in several countries: * In Europe: ** Switzerland: all German-speaking parts of the country except Samnaun ** Germany: centre and south of Baden-Württemberg, Swabia, and certain districts of Bavaria ** Austria: Vorarlberg, Reutte District of Tyrol ** Liechtenstein ** France: Alsace region ( Alsatian dialect) and in some villages of the Phalsbourg county, in Lorraine ** Italy: Gressoney-La-Trinité, Gressoney-Saint-Jean, Issime, Alagna Valsesia, Rimella and Formazza, in some other villages almost extinct *Outside Europe: ** United States: Allen and Adams County, Indiana, by the Amish there and also in their daughter settlements in Indiana and other U.S. states. ** Venezuela: Colonia Tovar ( Colonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the umbrella term for the standard language, standardized varieties of the German language, which are used in formal contexts and for communication between different dialect areas. German is a Pluricentric language, pluricentric Abstand and ausbau languages#Roofing, Dachsprache with currently three codified (or standardised) specific national varieties: German Standard German, Austrian German#Standard Austrian German, Austrian Standard German and Swiss Standard German. Regarding the spelling and punctuation, a recommended standard is published by the Council for German Orthography which represents the governments of all majority and minority German-speaking countries and dependencies. Adherence is obligatory for government institutions, including schools. Although there is no official standards body regulating pronunciation, there is a long-standing ''de facto'' standard pronu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Standard German
Swiss Standard German (SSG; ), or Swiss High German ( or ; ), referred to by the Swiss as , or , is the written form of one (German language, German) of four languages of Switzerland, national languages in Switzerland, besides French language, French, Italian language, Italian, and Romansh language, Romansh. It is a variety of Standard German, used in the German-speaking Switzerland, German-speaking part of Switzerland and in Liechtenstein. It is mainly written and rather less often spoken. Swiss Standard German differs from Swiss German, an umbrella term for the various Alemannic German dialects (in the sense of "traditional regional varieties") that are the default everyday languages in German-speaking Switzerland. Standard German is a pluricentric language. In contrast with other local Variety (linguistics), varieties of Standard German, Swiss Standard German has distinctive features in all linguistic domains: not only in phonology, but also in vocabulary, syntax, morphology ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Language
German (, ) is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western Europe, Western and Central Europe. It is the majority and Official language, official (or co-official) language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, and Liechtenstein. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, German-speaking Community of Belgium, Belgium and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in other parts of Europe, including: Poland (Upper Silesia), the Czech Republic (North Bohemia), Denmark (South Jutland County, North Schleswig), Slovakia (Krahule), Germans of Romania, Romania, Hungary (Sopron), and France (European Collectivity of Alsace, Alsace). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in the Americas. German is one of the global language system, major languages of the world, with nearly 80 million native speakers and over 130 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lütschine
The Lütschine () is a Rivers of Switzerland, river in the Bernese Oberland region of Switzerland. The Lütschine proper runs from Zweilütschinen, where its two tribututaries join, to Lake Brienz at Bönigen. The Schwarze Lütschine, or Black Lütschine, flows from Grindelwald to Zweilütschinen. The Weisse Lütschine, or White Lütschine, flows from the Lauterbrunnen Valley to Zweilütschinen. The common stretch of the river has a length of , whilst the Schwarze Lütschine is long and the Weisse Lütschine is long. Both branches of the Lütschine include a large number of mountain streams as tributaries. A notable tributary of the Schwarze Lütschine, emerging from the gorge of the Lower Grindelwald Glacier, is confusingly referred to as "Weisse Lütschine". The highest point of the drainage basin is the Jungfrau.1:25'000 Swisstopo topographic map A story passed on by word of mouth showing friendly banter between villagers that lived on the two rivers is that the people on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
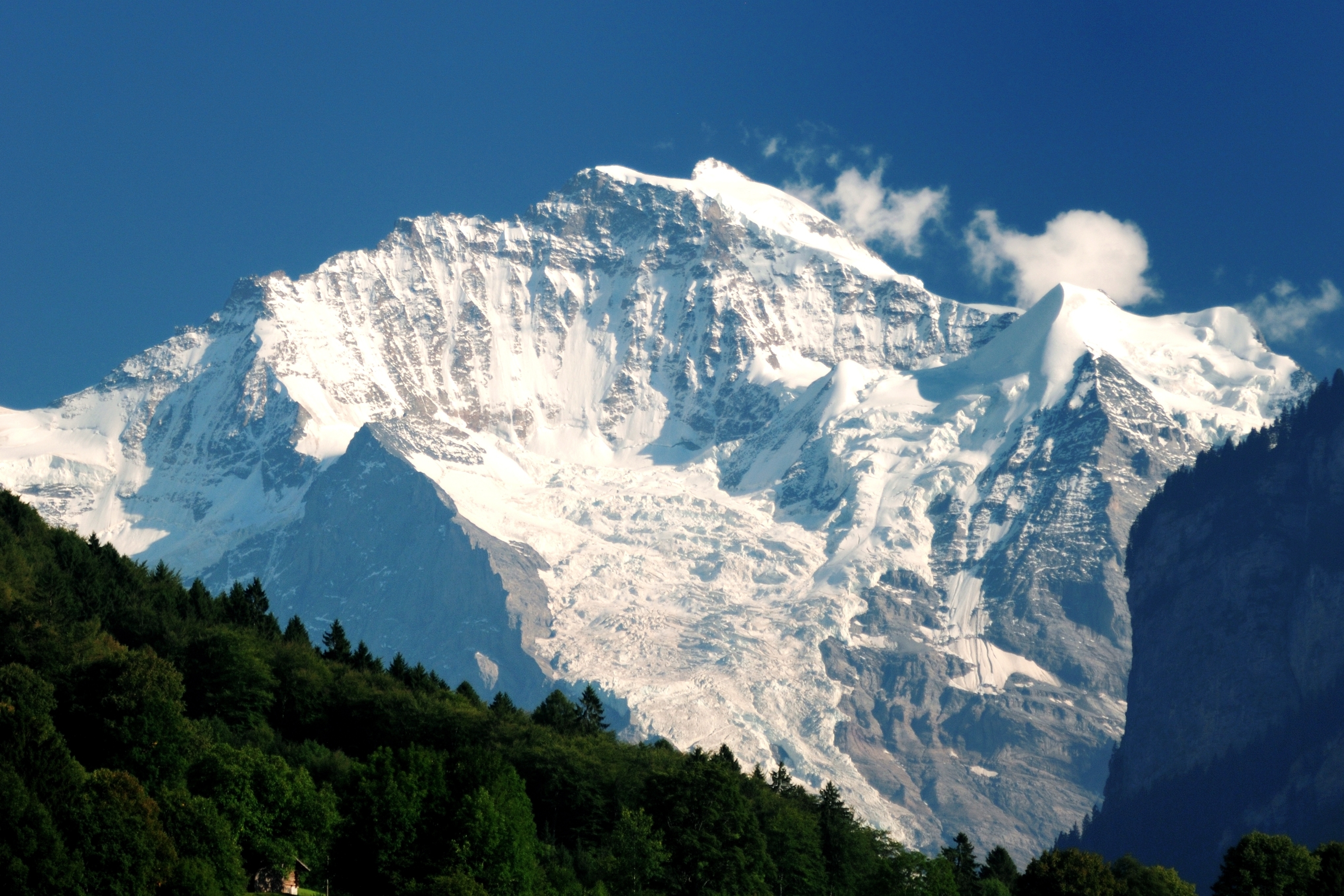
Jungfrau
The Jungfrau (, , , "maiden, virgin"), at is one of the main summits of the Bernese Alps, located between the northern canton of Bern and the southern canton of Valais, halfway between Interlaken and Fiesch. Together with the Eiger and Mönch, the Jungfrau forms a massive wall of mountains overlooking the Bernese Oberland and the Swiss Plateau, one of the most distinctive sights of the Swiss Alps. The summit was first reached on August 3, 1811, by the Meyer brothers of Aarau and two chamois hunters from Valais. The ascent followed a long expedition over the glaciers and high passes of the Bernese Alps. It was not until 1865 that a more direct route on the northern side was opened. The construction of the Jungfrau Railway in the early 20th century, which connects Kleine Scheidegg to the Jungfraujoch, the saddle between the Mönch and the Jungfrau, made the area one of the most-visited places in the Alps. Along with the Aletsch Glacier to the south, the Jungfrau is part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mönch
The Mönch (, German: "monk") at is a mountain in the Bernese Alps, in Switzerland. Together with the Eiger and the Jungfrau, it forms a highly recognisable group of mountains, visible from far away. The Mönch lies on the border between the cantons of Valais and Bern, and forms part of a mountain ridge between the Jungfrau and Jungfraujoch to the west, and the Eiger to the east. It is west of Mönchsjoch, a pass at , Mönchsjoch Hut, and north of the Jungfraufirn and Ewigschneefäld, two affluents of the Great Aletsch Glacier. The north side of the Mönch forms a step wall above the Lauterbrunnen valley. The Jungfrau railway tunnel runs right under the summit, at an elevation of approximately . The summit was first climbed on record on 15 August 1857 by Christian Almer, Christian Kaufmann (1831-1861), Ulrich Kaufmann and Sigismund Porges. Gallery Image:Moench 2348.jpg, A view of the Mönch taken from the Jungfraujoch Image:Männlichen01.jpg, Panorama from Männ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eiger
The Eiger () is a mountain of the Bernese Alps, overlooking Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen in the Bernese Oberland of Switzerland, just north of the main watershed and border with Valais. It is the easternmost peak of a ridge crest that extends across the Mönch to the Jungfrau at , constituting one of the most emblematic sights of the Swiss Alps. While the northern side of the mountain rises more than 3,000 m (10,000 ft) above the two valleys of Grindelwald and Lauterbrunnen, the southern side faces the large glaciers of the Jungfrau-Aletsch area, the most glaciated region in the Alps. The most notable feature of the Eiger is its nearly north face of rock and ice, named ''Eiger-Nordwand'', ''Eigerwand'' or just ''Nordwand'', which is the biggest north face in the Alps. This substantial face towers over the resort of Kleine Scheidegg at its base, on the eponymous pass connecting the two valleys. The first ascent of the Eiger was made by Swiss guides Christian Alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |